




What Makes Living Things Unique? Explore Key Features and Examples
Have you ever thought about how we respire and grow and how do these various processes occur in our body? Will it be right to say that we are living organisms? To answer these questions, we have to understand the detailed topic of living things and non-living things. Living means being alive. Living things can change their place on their own, they can breathe and show other features which we are going to discuss below. Non-living things do not have life. They cannot feel any emotions or pain.
In this article, we will learn living things' names, living things for kids and characteristics of living things for kids. So to understand all these things, let's first see what different living organisms are there in the world then we will go through the living things and nonliving things examples.

Living Things
What Are Living Things?
A living thing refers to any organism that possesses the characteristics of life or being alive. In simple words, a living thing is anything that has life. There are a variety of living things around us. Living things carry out metabolic activities inside our bodies to generate energy. Living things have a definite life span, they don’t live forever.
Characteristics of Living Things
Living things have various types of characteristics. The fundamental characteristics are as follows:
Ability to Interact: Living things can interact with other organisms. Different organisms interact with other organisms through various modes. For example, humans interact through their actions and words.

Human Interaction
Made Up of Cells: Living things are made up of cells. The cell is the basic unit of life. For example, amoeba is an organism of a single cell known as a unicellular organism, e.g. bacteria and yeast. Some organisms are made of many cells called multicellular organisms, e.g. humans.
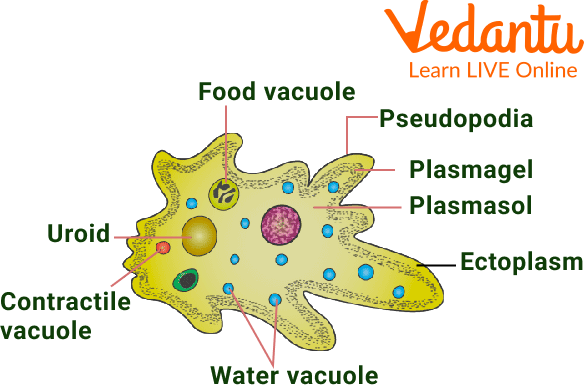
Amoeba
Living Things Need Food: Living things get energy from food and it is necessary for their growth. Many animals are dependent on other animals for their food and many animals eat plants for their survival.

Food and Water for Living Things
Respire: As we all know, we breathe in oxygen and carbon dioxide. This process is called respiration. Plants also respire.
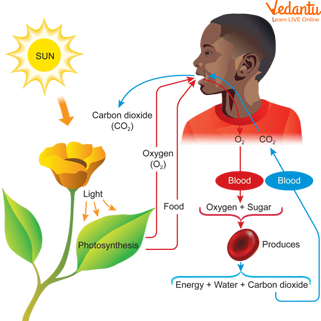
Respiration
Response to Stimuli: All living organisms respond to stimuli such as touch, light, heat, and sound. This is also called sensitivity. Living things are capable of rapid changes in the environment.
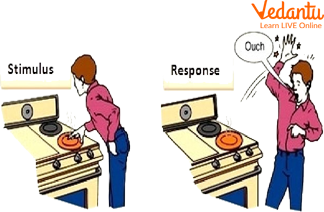
Stimulus and Response
Living Things Grow: We often see in our surroundings small plants growing into trees, newborn babies turning into a child and then into an adult. Hence, living things have the ability to grow.
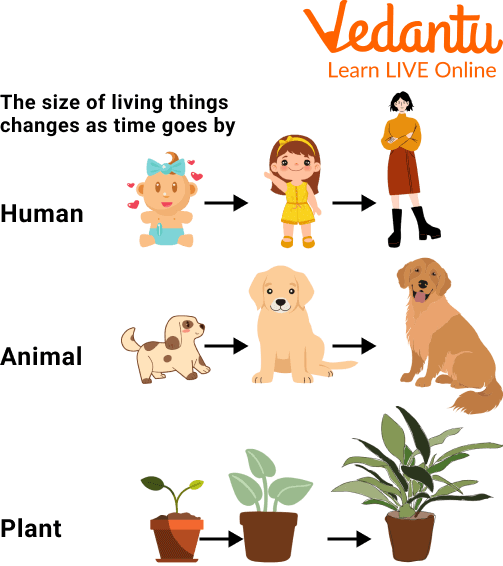
Growth in Living Things
Ability to Reproduce: Reproduction is an important characteristic of all living organisms. It is the process of producing offspring from parents; example, humans reproduce to give birth to children and plants reproduce through seeds.
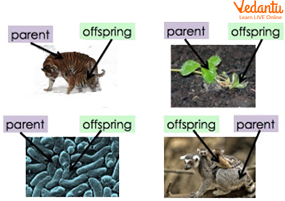
Reproduction in Various Living Organisms
Difference Between Living Things and Non-living Things
All these differences make living things different from non-living things.
Are Plants Living Things?
Yes, plants are living things as they have all the characteristics of living things, they reproduce, grow, need nutrients, excrete waste products, etc.
Examples of Living and Non-living Things
Interesting Facts About Living Things
Living things contain DNA.
They excrete to remove waste material from the body.
Living things respond to their environment.
Living things show movement.
They grow, develop and die.
Summary
All living things undergo growth and reproduction. There is a relationship between animals and plants and how every living thing depends on other living things as well as non-living things, and the environment to live in each day; eg: for respiration and for food and shelter. Animals release carbon dioxide that is used by plants for the process of photosynthesis (the process by which plants prepare their own food). Living beings are different from non living things in various aspects like growth, reproduction, digestion, metabolism, and homeostasis. Some living things examples are animals, plants, humans, birds, etc. Some examples of non-living things are chairs, beds, pens, etc. In this article, we have discussed the characteristics of living things for kids and what makes living things different from nonliving things.
FAQs on Essential Facts About Living Things
1. What are living things?
A living thing is anything that is alive, which means it needs food, water, and air to survive. All living things can grow, move, breathe, and create more of their own kind. For example, people, animals like cats and dogs, and plants like trees and flowers are all living things.
2. What is the main difference between living and non-living things?
The biggest difference is that living things have life, while non-living things do not. Living things grow, breathe, and need food. A non-living thing, like a rock, a toy car, or a pencil, cannot do any of these things on its own. It doesn't need food and doesn't grow.
3. Can you give some common examples of living things?
Yes, of course! The world is full of living things. Some common examples include:
- Animals: Dogs, birds, fish, lions, and butterflies.
- Plants: Big banyan trees, small rose bushes, grass, and vegetables.
- Humans: You, your friends, and your family are all living things.
4. What are the main things that all living things do?
All living things share a few key characteristics. They all:
- Need food and water: To get energy and stay healthy.
- Breathe: They take in air to live.
- Grow: They start small and get bigger over time.
- Move: Animals walk or fly, while plants move their leaves towards the sun.
- Reproduce: They can have babies or produce seeds to make more of themselves.
5. Why do living things need to move?
Living things move for very important reasons. Animals move to find food and water, to build a home or shelter, and to escape from danger. Plants also move, but much more slowly. Their roots grow towards water, and their stems and leaves bend towards sunlight.
6. How do we know if something is a living thing?
To figure out if something is living, you can ask a few simple questions. Does it need food? Does it breathe? Does it grow or change? Can it move by itself? If the answers are yes, it's a living thing. If the answers are no, like for a chair or a book, it's a non-living thing.
7. Why do plants seem to grow their whole life, while animals like dogs or people stop growing?
This is a great question! Plants have special parts at their tips and roots that can keep making new cells throughout their life, allowing them to grow taller or wider continuously. Animals, on the other hand, have an internal body plan that signals them to stop growing once they reach adulthood.
8. Why is it important for us to learn about living things?
Learning about living things is important because it helps us understand our world. It teaches us how to care for animals and plants, why nature is so valuable, and how all living beings depend on each other. It helps us become more responsible and curious about the life all around us.









