




Where Are Taste Buds Located on the Human Tongue?
Have you ever thought about how you can speak? There is something which helps us in talking. Can you guess? Yes, it is the tongue. The tongue is a strong organ in the mouth. The tongue is covered with pink tissue called the mucosa. Now, let us learn about the human tongue's taste buds. The papilla is a tiny elevation on the tongue.
A huge number of taste buds cover the surfaces of the tongue. The human tongue’s taste buds help us in feeling the different types of tastes like sweet, sour, salty, and bitter. The tie holding down the front of the tongue is known as the frenum. The tongue is essential for biting and gulping food. The hyoid bone is present near the tongue, which provides support to it.
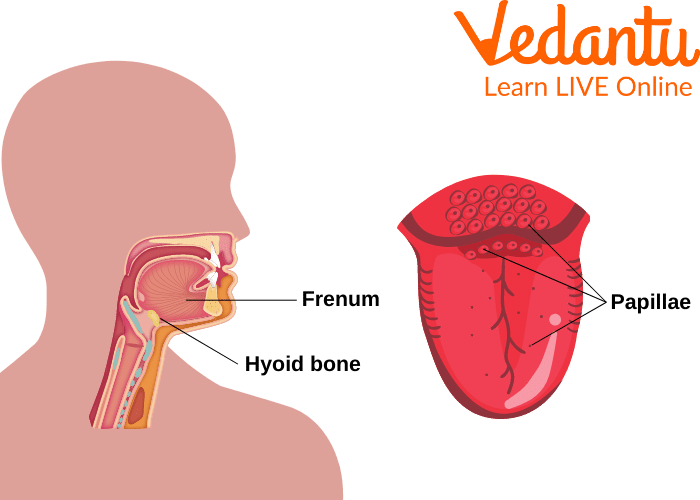
Location of the Tongue
Human Tongue and Senses
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for feeling some changes in the body like pain, fear, etc., and for gathering information about the things happening and responding to them. The senses of the tongue help in identifying the taste and help in speaking. The four normal tastes are sweet, sour, bitter, and salty. The tongue has many nerves that help identify and send taste signs to the mind.
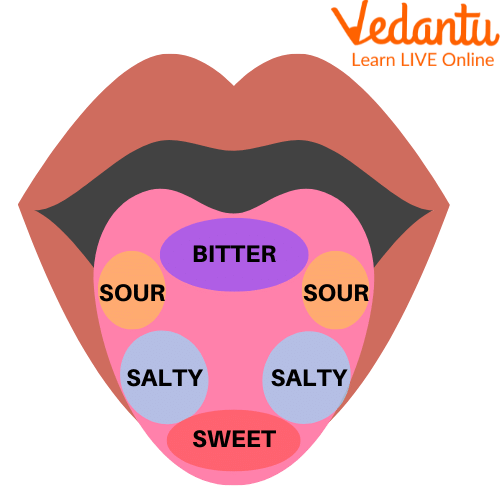
Senses of the Taste Bud on the Tongue
Taste Glands on the Tongue
Taste buds contain the taste receiving cells, which are otherwise called gustatory cells. The taste-receiving cells are situated around the little designs known as papillae tracked down on the upper surface of the tongue, delicate sense of taste, upper throat, cheek, and epiglottis.
These designs are engaged with identifying the five components of taste: pungency, acridity, sharpness, pleasantness, and umami. Little openings in the tongue lining are called taste pores, portions of the food break down in spit and come into contact with the taste receptors. So, taste glands on the tongue are very important.
Location of Taste Buds on the Tongue
Taste Buds are a group of cells — basal cells, columnar (primary) cells, and somewhere in the range of 10 and 50 taste receptor cells, which are recharged each 9-10 days. So the location of taste buds on the tongue is around the small structures called papillae.
A portion of these receptor cells contains proteins on their surfaces that tight spot to a portion of the synthetic substances from our food, while others have particle channels that are filled by various synthetics. When the receptor has distinguished a specific compound, this information is passed along a progression of brain processes onto the cerebrum, where taste is seen.
Number of Taste Buds on the Human Tongue
The quantity of taste buds individuals have can shift incredibly. A typical grown-up has somewhere in the range of 2000 and 8000 tastebuds — certain individuals have fewer, bigger taste buds while others have a lot more modest taste buds.
So, the tongue is a special organ that is present in the mouth. Now we already know the number of taste buds present on the human tongue. This number can be different for different people.
Summary
Like other organs in the human body, the tongue is another unique organ that works on its own and has specific functions attached to it like tasting with the help of taste buds, gulping, and providing enzymes for digestion. It has taste buds on the surface of the tongue which are nearly around 2000 to 8000 varying from person to person. The tongue is a super delicate organ and is known for its specialisation in one of the senses which is to taste and choose the food for the body correctly. Now that you have read this article, we hope you got hold of some important information about the human tongue and can share it with your friends.
FAQs on Human Tongue: Structure, Functions & Importance
1. What is the human tongue and where is it located?
The human tongue is a strong, flexible muscle located inside our mouth. It is anchored to the floor of the mouth and extends from the hyoid bone in the neck. Its surface is typically pink and covered in tiny bumps.
2. What are the main jobs of the tongue?
The tongue has several important jobs that help us every day. Its main functions are:
- Tasting: It helps us identify different tastes in our food, like sweet, salty, sour, and bitter.
- Eating: It helps move food around in the mouth for chewing and pushes it back for swallowing.
- Speaking: It moves to touch the teeth and roof of the mouth to help form sounds and words clearly.
- Cleaning: It can help sweep food particles from our teeth after eating.
3. What are taste buds and how do they help us taste food?
Taste buds are tiny sensory organs found on the tongue's surface, inside small bumps called papillae. When you eat, chemicals from the food dissolve in your saliva and enter the taste buds. These buds then send signals to your brain, which interprets them as different flavours.
4. Are there different sections on the tongue for tasting sweet, sour, salty, and bitter foods?
This is a common myth. While you may have seen a 'tongue map' showing specific taste zones, it is not accurate. In reality, all parts of your tongue that have taste buds can detect all the basic tastes: sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and a savory taste called umami. Some areas might be slightly more sensitive to certain tastes, but there are no strict sections.
5. Why does the tongue have a rough or bumpy texture?
The rough texture of the tongue is due to small bumps called papillae. These papillae serve two main purposes: they contain our taste buds, which allow us to taste, and they create friction to help grip food and move it around our mouth while we chew.
6. How does the tongue help us speak and form words?
The tongue is essential for speaking because of its incredible flexibility. It can move quickly and precisely to touch different parts of the mouth, like the back of the teeth or the hard palate (roof of the mouth). By changing its shape and position, it controls the flow of air from our lungs to create the different sounds that make up words.
7. How can I keep my tongue healthy?
Keeping your tongue healthy is simple. You can gently brush your tongue with your toothbrush every time you brush your teeth to remove bacteria. Drinking plenty of water also helps keep your mouth, including your tongue, clean and healthy.









