




What Is Hydropower and Why Is It Important for Students?
Having been established for over a generation, hydropower is today the main domestic source of clean, renewable electricity in the country. What might it be expected to do in 2050?
Hydropower supports more than 143,000 employees in engineering, manufacturing, construction, and utility operations and maintenance, all while enhancing the environment and boosting our economy. It generates around 7% of the country's electricity. Isn’t it fascinating to know? So let’s get started on learning all about Hydroelectric Power.
What is Hydropower?
All around the world, hydroelectric dams trap vast volumes of water behind a reservoir.
Most hydroelectric projects build a reservoir by constructing a sizable dam to flood a region. Through pipes in the dam, this trapped water can escape. A turbine connected to an electricity-generating generator is turned by the water flowing through the pipes.

Hydroelectric Power
Advantages of Hydropower
Water is abundant, cost-free, and regenerative.
Hydroelectric power uses water to generate electricity without emitting any carbon dioxide.
As long as there is adequate water, electricity can be produced continuously. But since the reservoir occasionally has to refuel, this cannot happen daily.
It is possible to control when electricity is generated by opening and closing the dam gates.
Altering the amount of water that may flow can affect how much electricity is generated.
Although that does depend on plenty of rain, especially for "run of the river" systems, it is significantly more dependable than solar and wind power.
Important and Fun Facts about Hydropower
In addition to generating power, dams are constructed for various purposes, including irrigation, trade and navigation, flood control, or the construction of reservoirs for recreational purposes. As per the recent data, 45.8 GW out of 375.32 GW installed power capacity belongs to hydroelectric power.
Fish and other species can freely migrate around dams and parts of rivers thanks to dam equipment. Among the methods used to assist fish migrations are fish elevators and fish ladders.
Pumped storage is a different kind of hydropower that functions similarly to a battery by storing the electricity produced by the other power sources including solar, wind, and nuclear for later use. Pumping water from a separate reservoir at a lower elevation up to a reservoir at a higher elevation is how it stores energy.
Some hydropower plants have a short ramp-up time from zero to maximum output, which makes them perfect for supplying electricity to unexpected spikes in demand.
With 63 sites identified and acknowledged for their essential grid services in national energy plans, India has a potential for approximately 90 GW of pumped storage.
The hydropower potential of India is around 1,45,000 MW and at 60% load factor, it can meet the demand of around 85, 000 MW.
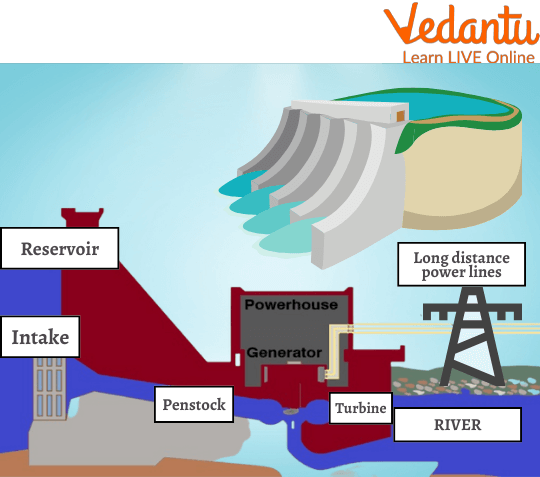
Power Generation Through Dam
Summary
A dam or other construction that alters the natural movement of a river or even other body of water is used to generate hydropower, often known as hydroelectric power. Hydropower uses the perpetual, never-ending water cycle to generate energy, which uses water as a fuel and leaves no waste products behind. Although there are many different kinds of hydropower plants, they are always propelled by the kinetic energy of water moving downstream. We hope you enjoyed reading this article, in case of any other doubts, feel free to ask in the comments.
FAQs on Facts About Hydropower
1. What is hydropower, and how does it work?
Hydropower, also known as hydroelectric power, is a form of renewable energy that uses the force of moving water to generate electricity. The process typically involves a dam that holds back a river to create a large reservoir. When electricity is needed, water is released from the reservoir and flows through a pipe called a penstock, which pushes against the blades of a turbine, causing it to spin. The spinning turbine is connected to a generator, which converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy.
2. How efficient is hydropower compared to other energy sources?
Hydropower is one of the most efficient energy sources available today. Modern hydropower plants can convert as much as 90% of the available energy from the moving water into electricity. This is significantly higher than other sources, such as fossil fuel power plants, which typically have an efficiency of only about 50-60%.
3. Is hydropower a completely clean and non-polluting source of energy?
Hydropower is considered clean because it does not burn fossil fuels, meaning it doesn't release harmful greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide into the atmosphere during operation. However, it is not entirely free of environmental impact. The creation of reservoirs can lead to the decomposition of submerged vegetation, which can release methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Despite this, its overall emissions are far lower than fossil fuels.
4. What are the main disadvantages of building a large hydropower dam?
While beneficial, large hydropower dams have several significant disadvantages. The primary concerns include:
- Environmental Impact: The dam and reservoir can drastically alter the river's ecosystem, blocking fish migration routes and changing water temperature and flow.
- High Initial Cost: Constructing a large-scale dam, powerhouse, and transmission lines requires a massive upfront financial investment.
- Displacement of Communities: The land flooded to create a reservoir often displaces thousands of people from their homes and farmlands.
- Dependence on Rainfall: Power generation can be severely reduced during droughts when water levels in the reservoir are low.
- Risk of Failure: Although rare, the failure of a large dam can cause catastrophic downstream flooding.
5. How long can a hydropower plant operate?
Hydropower plants are known for their exceptionally long lifespans. A well-maintained plant can operate for 50 to 100 years, and sometimes even longer with periodic upgrades and modernisation. This makes them a reliable long-term investment for energy infrastructure, outlasting many other types of power plants, such as solar farms or wind turbines.
6. If hydropower is renewable, why is its impact on the environment often a major concern?
The term 'renewable' refers to the energy source itself—the water cycle, which is continuous and naturally replenished. The environmental concerns are not about the source, but about the method of extraction. Building a large dam creates an artificial lake that floods vast areas of land, destroying natural habitats. It also disrupts the natural flow of a river, which can harm aquatic life and prevent species like salmon from reaching their spawning grounds. So, while the water is renewable, the infrastructure can cause significant and lasting ecological changes.
7. What is the importance of hydropower in managing a country's overall power grid?
Hydropower plays a crucial role in ensuring grid stability and reliability. Its key advantage is flexibility; hydropower plants can be started and stopped very quickly. This allows them to respond to sudden changes in electricity demand within minutes. They provide essential backup power during major outages (a function known as 'black-start capability') and help balance the variable output from other renewable sources like wind and solar.
8. What is the difference between a large hydropower dam and a run-of-river system?
The main difference lies in how they use water. A large hydropower dam involves building a massive barrier to stop a river and create a large reservoir. This stored water can be released as needed, allowing for consistent, high-capacity power generation. A run-of-river system does not require a large dam or reservoir. Instead, it diverts a portion of the river's natural flow through a channel or pipe to spin turbines. While this has a much lower environmental footprint, its electricity generation is more dependent on the river's seasonal flow.
9. What does the future of the hydropower industry look like?
The future of hydropower focuses less on building new mega-dams and more on innovation and modernisation. Key trends include upgrading older plants to increase their efficiency and lifespan, developing smaller, more environmentally friendly projects like run-of-river systems, and expanding pumped-storage hydropower. Pumped storage acts like a giant battery, using excess electricity to pump water to a higher reservoir and releasing it to generate power when demand is high.









