




Key Steps of Nerve Signal Transmission You Must Know
The nervous system in our body is made up of the brain, the spinal cord, and a vast network of nerves distributed throughout the entire body.
A neuron is a base or fundamental unit of the nervous system. It is a cell that transmits nerve signals. A neuron is also known as a ‘nerve cell’.
A nerve, on the other hand, is a bundle of fibres that carry the nerve signal from the central nervous system to the targeted part of the body.
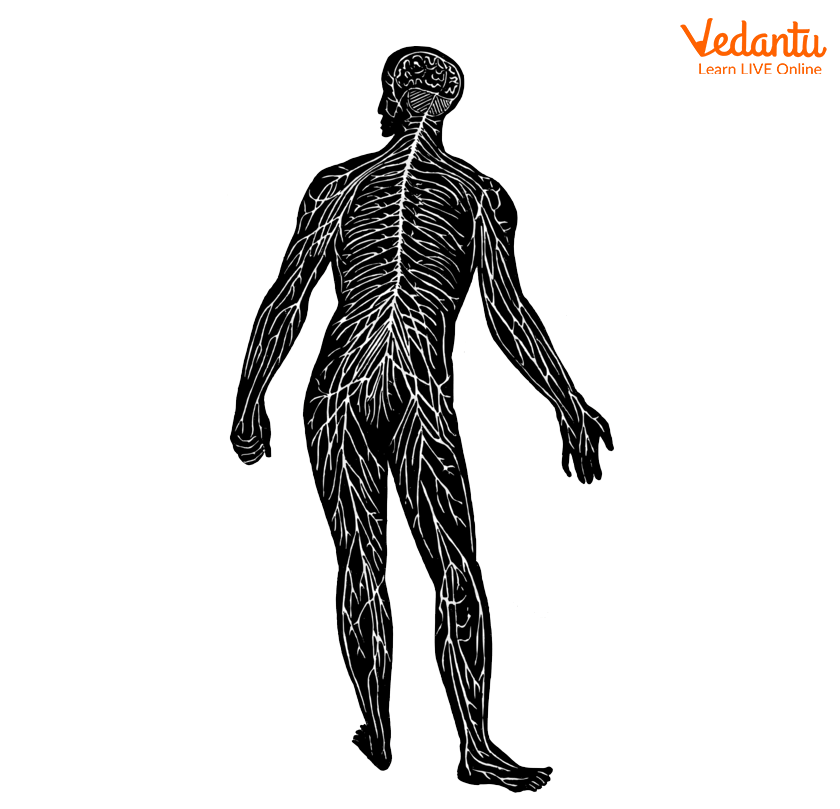
Nerves in the Body
For example, if you touch a hot object with your hand, then that information is sent to your brain, which registers and understands the action, and the nerve signals travel back from the brain to your hand, causing you to draw back your hand.
Shape of a Nerve Cell
Neurons or nerve cells are the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. They send or receive messages from one part of the body to another. They are spread throughout the body and irregular in shape. They are of different sizes and shapes depending on their location and function.
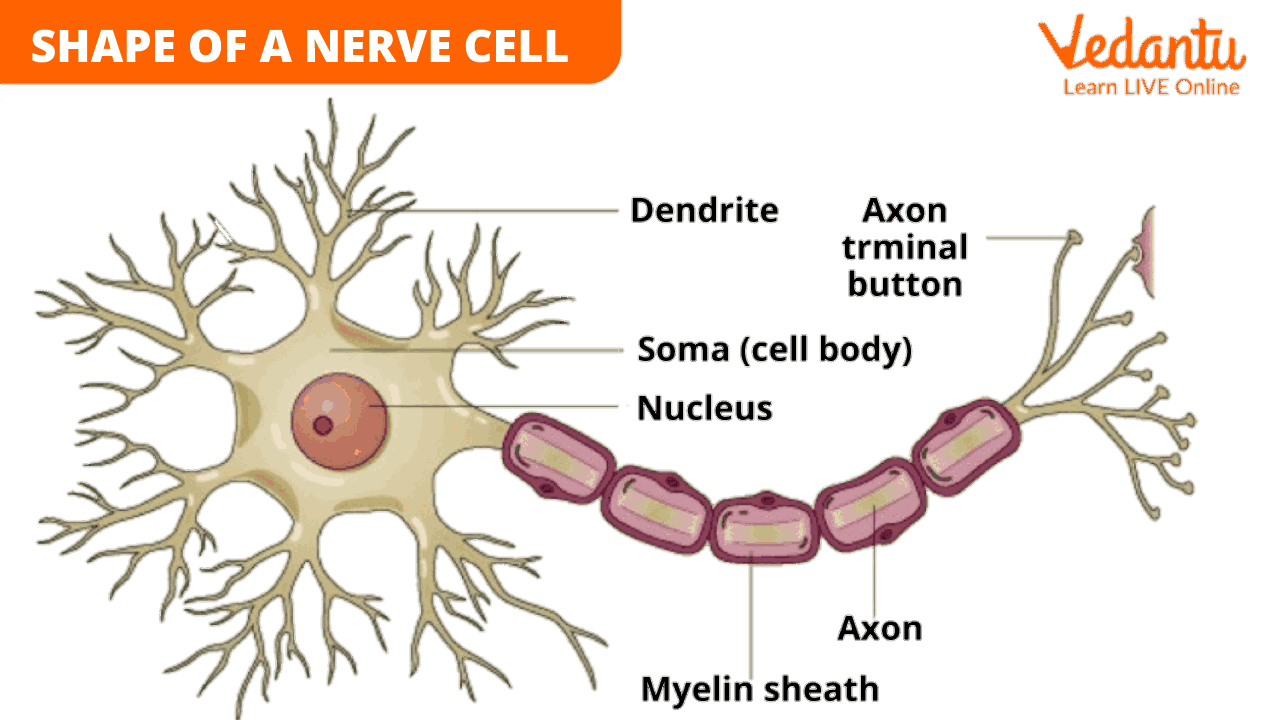
Structure of a Neuron
Parts of a Neuron
Dendrite - They are branch-like extensions of a nerve cell that receive messages from other nerve cells and further transmit them to the cell body.
Cell Body - The part of a nerve cell that contains the nucleus and other parts is called the cell body.
Synapse - It is the junction between the terminal of one neuron and the dendrites of another. Quite literally, it is a point between the ending of one neuron and the beginning of another.
Difference Between Neuron and Nerve
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system(CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord. It is the central processing unit of the body. The main functions of the CNS are-
To collect sensory input from the body and the surroundings
To register and process the sensory information
To respond appropriately to the action
Brain
The brain is an organ that is the centre of the nervous system in a human. It is located in the head and it is the largest and most complex organ of the body. It works like a computer that stores, sends, receives, and processes all the information from our body and the environment. Three parts of the brain-
Forebrain - The frontal part of the brain
Midbrain - The central but smaller part of the brain
Hindbrain - The central region of the brain
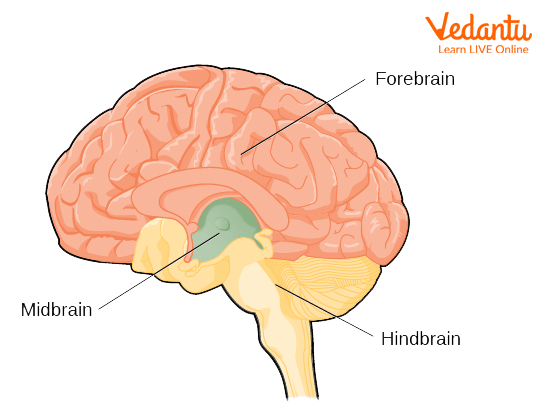
Parts of the Brain
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord extends downwards from below the brain. It consists of nerve fibres and a group of nerves that carry messages from the brain to the rest of your body.
The spinal cord is responsible for reflex actions (response to any action or occurrence around us) and the conduction of nerve signals to and from the brain.
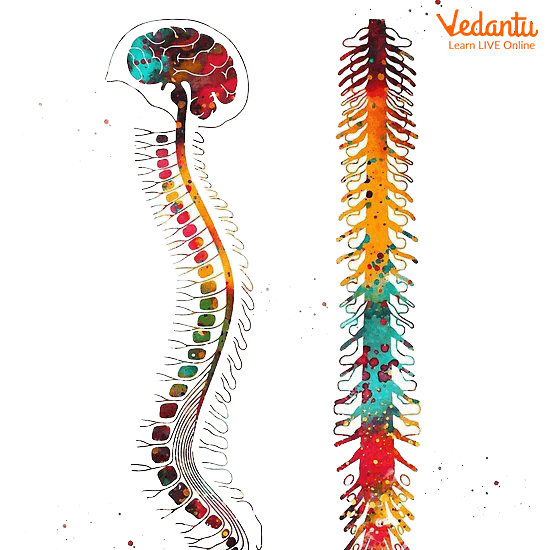
Spinal Cord
Transmission of Nerve Signals
Let’s understand how a nerve signal passes through the synapse.
A nerve signal passes from one neuron to the other through the synapse. A synapse is a junction between the ending of one neuron and the beginning of another.
When an outside action occurs, the nerve signal from that part of the body is transmitted to the central nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. The nerve signal is registered and processed in the brain after which appropriate action is sent back to the particular body part or sensory organ.
Nerve signals are like electric signals that are sent from one part to another. It first passes through the cell body after it goes to the axon, myelin sheath, and finally reaches the nerve endings after which it is transmitted to the next neuron through the synapse.
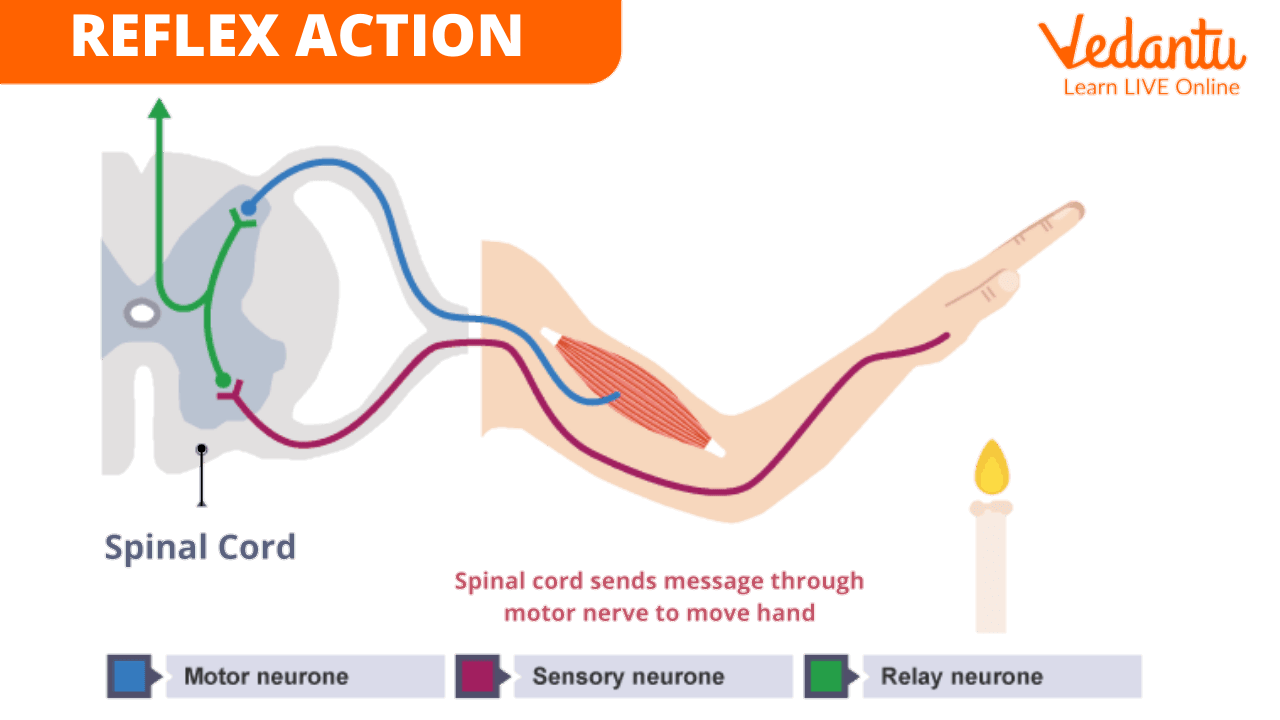
Reflex Action Movement
Conclusion
The nervous system and everything it includes is extremely important and vital for our body. It is responsible for our actions, emotions, surroundings, memory, etc. It helps to maintain control and coordination in our body. The nervous system is the control system of all our actions, thinking, and behaviour.
FAQs on How Do Nerve Signals Transmit Through Our Body?
1. What is a synapse and what is its primary function in the nervous system?
A synapse is a specialised junction where a nerve signal is passed from one neuron to another, or from a neuron to a target cell like a muscle or gland. Its primary function is to permit the unidirectional transmission of nerve impulses, ensuring that information flows in the correct direction through a neural circuit.
2. How does an electrical nerve signal cross a chemical synapse?
When an electrical impulse (action potential) reaches the end of the first neuron (the presynaptic terminal), it triggers the release of chemical messengers called neurotransmitters into the gap known as the synaptic cleft. These neurotransmitters travel across the cleft and bind to receptors on the next neuron (the postsynaptic neuron), converting the chemical signal back into an electrical signal to continue the impulse.
3. What are the key components of a chemical synapse?
A chemical synapse consists of three main parts:
- Presynaptic Terminal: The axon terminal of the sending neuron, which contains vesicles filled with neurotransmitters.
- Synaptic Cleft: The microscopic gap (about 20-40 nanometres wide) between the two neurons that neurotransmitters diffuse across.
- Postsynaptic Membrane: The surface of the receiving neuron's dendrite or cell body, which contains specific receptors that bind to the neurotransmitters.
4. What are neurotransmitters, and can you give some examples?
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers used by the nervous system to transmit signals across a synapse. They are released from the presynaptic neuron and bind to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron. Common examples include:
- Acetylcholine (ACh): Involved in muscle contraction and memory.
- Dopamine: Associated with reward, motivation, and motor control.
- Serotonin: Plays a role in mood, sleep, and appetite.
- GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid): The primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain.
5. What is the difference between a chemical synapse and an electrical synapse?
The main difference lies in their transmission method. A chemical synapse uses neurotransmitters to send a signal across a physical gap (the synaptic cleft), which causes a slight delay but allows for complex signal modulation. In contrast, an electrical synapse has a direct physical connection (a gap junction) between neurons, allowing ions to flow instantly from one cell to the next. Electrical synapses are much faster but less common and offer less control.
6. Why is synaptic transmission typically unidirectional?
Synaptic transmission is unidirectional because of its specific anatomy. Neurotransmitters are stored and released only from the presynaptic terminal (the sending neuron), while the receptors for these chemicals are located only on the postsynaptic membrane (the receiving neuron). This strict arrangement ensures that signals can only travel from the presynaptic to the postsynaptic neuron, preventing the nerve impulse from flowing backwards and causing chaos in the neural circuit.
7. What happens to neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft after a signal is transmitted?
To stop the signal and reset the synapse for the next one, neurotransmitters must be cleared from the synaptic cleft quickly. This occurs via one of three primary mechanisms:
- Reuptake: The presynaptic neuron reabsorbs the neurotransmitter using transporter proteins.
- Enzymatic Degradation: An enzyme present in the cleft breaks down the neurotransmitter (e.g., acetylcholinesterase breaks down acetylcholine).
- Diffusion: The neurotransmitter simply drifts away from the synaptic space.
8. How does a synapse prevent a nerve impulse from being continuously fired?
A synapse prevents continuous firing primarily through the rapid removal of neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft after they have delivered their message. This termination of the chemical signal (via reuptake, enzymatic degradation, or diffusion) immediately stops the stimulation of the postsynaptic neuron. Additionally, some synapses use inhibitory neurotransmitters that make the receiving neuron less likely to fire, providing another crucial layer of control.
9. What is the significance of the synaptic delay?
The synaptic delay is the brief period (about 0.5 milliseconds) it takes for a signal to cross a chemical synapse. This delay is due to the time needed for neurotransmitter release, diffusion, and binding. While it makes chemical transmission slower than direct electrical transmission, this delay is highly significant because it allows for neural integration. This is the process where a single neuron can sum up multiple incoming excitatory and inhibitory signals over a short time before 'deciding' whether to fire an impulse, forming the basis of complex information processing in the brain.









