




Overview of Sense of Smell
The five senses—sight, taste, touch, hearing, and smell—gather information about our surroundings that the brain can understand and recognise. Based on prior experience (and subsequent learning), as well as by putting together the information from each sensory organ, we make sense of any information. For example, whenever we smell any familiar thing, we can recognise it.
The ability to smell comes from the olfactory sensory neurons, which are present inside the nose. Today we will discuss the sense of smell which is also a very important sense in our body, with the aid of some sense of smell pictures for Kids.
What is the Sense of Smell?
Your nose and brain enable you to experience smell like those of roses, perfume, freshly baked bread, and cookies. The discovery and perception of substances in the atmosphere constitute the phenomenon of olfaction. The olfactory epithelium, a membrane, is where chemical particles enter the nostril and dissolve in mucus. The olfactory epithelium of humans is situated around 7 cm upwards in the nose from the nostril.
As you are aware, a stuffy nose and a cold make it difficult to smell well. This is because smell molecules cannot get to the olfactory receptors.
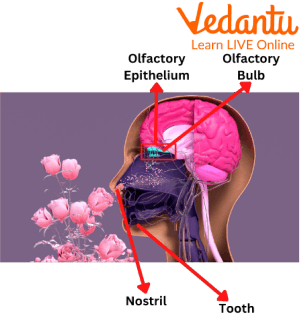
The Olfactory System
Smelling and Tasting
The most well-known example of how something can impact taste is having a cold. When our ears are congested and our nostrils are blocked, we are also unable to taste food.
About 80% of what we taste results from our sense of smell. Without scent, there are five unique flavours humans can taste: sweet, salty, sour, bitter, and the recently found "umami", or savoury flavour. The only other flavours we can taste originate from fragrance. This explains why most foods taste bland or insipid when our noses are closed, as when we have a cold. We also have a heightened sense of smell when we're hungry.
You can sense the fragrances of what is going on in your environment using your nose. The nose enables you to sense what is happening through smelling, just like your eyes and ears provide information through seeing and hearing. Many components deeply buried inside your head and nasal cavities help it accomplish this.
The olfactory epithelium is higher on the roof of your nasal cavity, which is the area behind your nose. Olfaction is a technical term that refers to smell. Special receptors in the olfactory epithelium are sensitive to odour molecules carried via the air.
There are approximately 10 million olfactory receptors in your nose. These can detect particular odour molecules. An odour can activate a variety of receptors, according to research. Any one of the approximately 10,000 odours is recognised by the brain by analysing the interaction of receptors.
Tasting and the Tongue
Have you ever wondered why the meals you love the taste so good? You should be grateful to your taste buds for allowing you to enjoy the richness of ice cream and the saltiness of pretzels.
Your tongue has taste buds, which are sensory organs that let you experience the flavours of sweet, salty, sour, and bitter. How do the taste buds function? So, extend your tongue and inspect yourself in the mirror.
Look at all those lumps! They are known as papillae, most of which have taste receptors. The microvilli on taste buds are extremely sensitive tiny hairs. You can tell if something is sweet, sour, bitter, or salty because those little hairs tell the brain how it tastes.

Tongue Map of Taste Buds
Summary
From the topic of the sense of smell for kids, we have learnt that taste and smell are examples of chemical senses. A smell is perceived when atmospheric substances pass through the nose and activate the olfactory (smell) nerve. The mouth's taste buds react to molecules dissolved in saliva to produce the sensation of taste or gustation. Salty, sweet, sour, and bitter are the four basic tastes. Most people refer to the "taste" of meals as flavour. It combines odour, taste, heat, temperature, and texture. We hope you enjoyed reading this article; in case of any other doubts, feel free to ask in the comments.
FAQs on Sense of Smell for Kids
1. How do smell and taste interact to produce flavour?
Smell and taste are closely linked. The tongue's taste buds identify taste, and the nerves in the nose identify the smell.
Both sensations are communicated to the brain, which integrates the information so flavours can be recognised and appreciated.
2. Why is taste a valuable sense?
One of the five senses that humans have is taste. Because it lets the individual select the proper diet, which is needed for one's existence, maintenance, and function, it is crucial to our ability to survive.
3. Which area of the brain controls taste and smell?
Pituitary lobe interprets the signals that come to you through your five senses—sight, touch, smell, hearing, and taste.









