




Functions of the Human Skeleton and Types of Bones Explained
The skeleton, made up of bones, is a solid framework to support and protect the body's soft organs. The skeleton supports the body as it resists the pull of gravity. When standing, the spine is supported by the massive bones of the lower limbs. The skeleton likewise shields the delicate bodily components.
The skeletal system, which is made up of the head, vertebral column, and rib cage, and the long bones, which are the limb bones, and the pectoral and pelvic girdles.
Vertebrates are creatures with a spinal column or backbone, including humans. They are supported by a strong internal framework built around a visible spine. The human skeletal system, which makes up 20% of the body weight, comprises bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons.
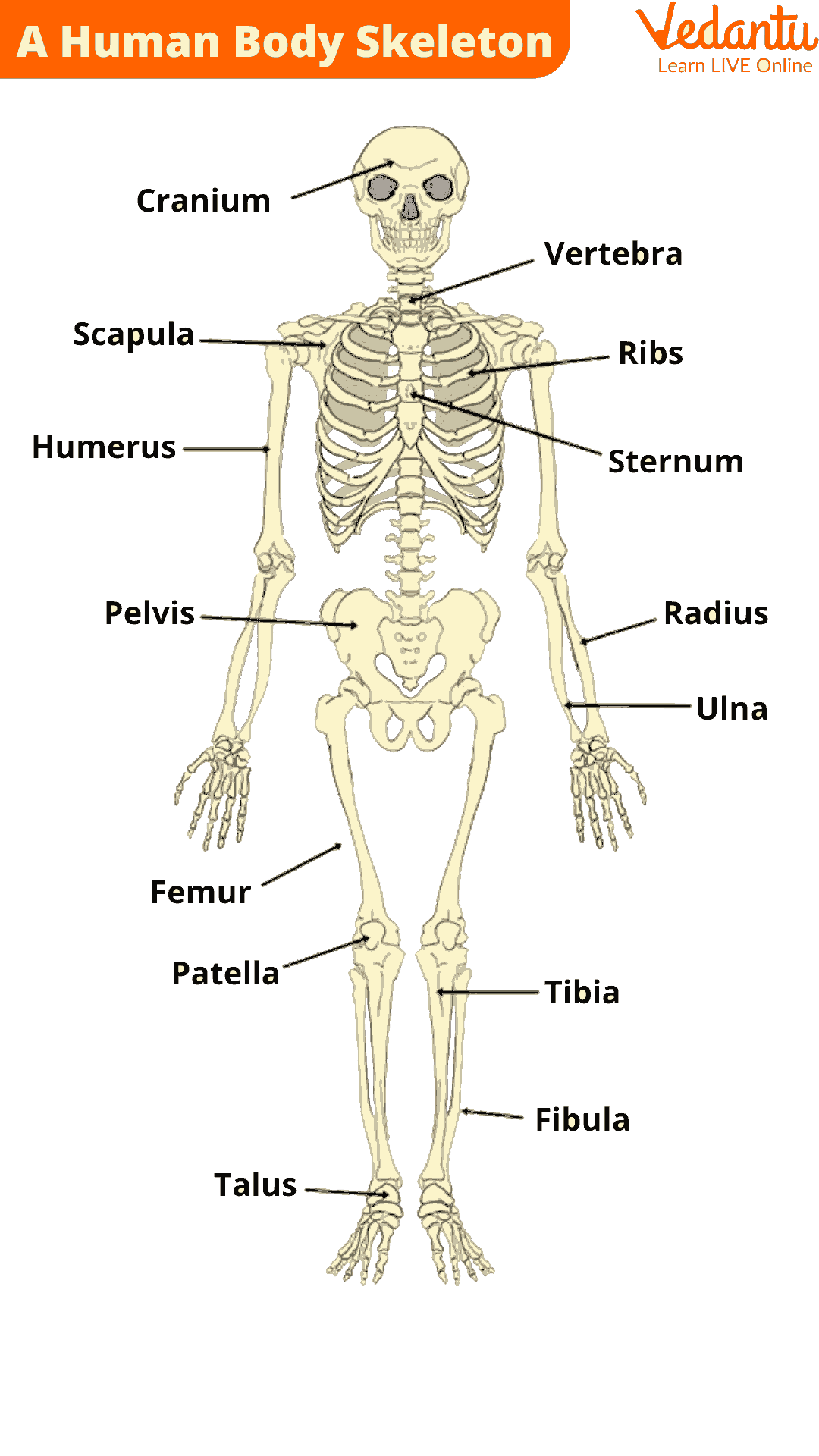
A Human Body Skeleton
Ligaments in the Human Body
Connective tissue with a lot of dense collagen fibres makes ligaments. They can be found in the body in various sizes and shapes. Arch-shaped ligaments are also visible.
Two bones are frequently joined by ligaments, especially in the joints. They hold the ends of two bones together or support the joint like strong, tightly linked belts or ropes. Doing this prevents the bones in the joint from twisting or separating too much and becoming dislocated.
Ligaments contribute to the body's stability, whether attached to bones or organs. These ligaments frequently flow across delicate organs like blood arteries or gland ducts. These structures are protected and kept from bending, twisting, or ripping.
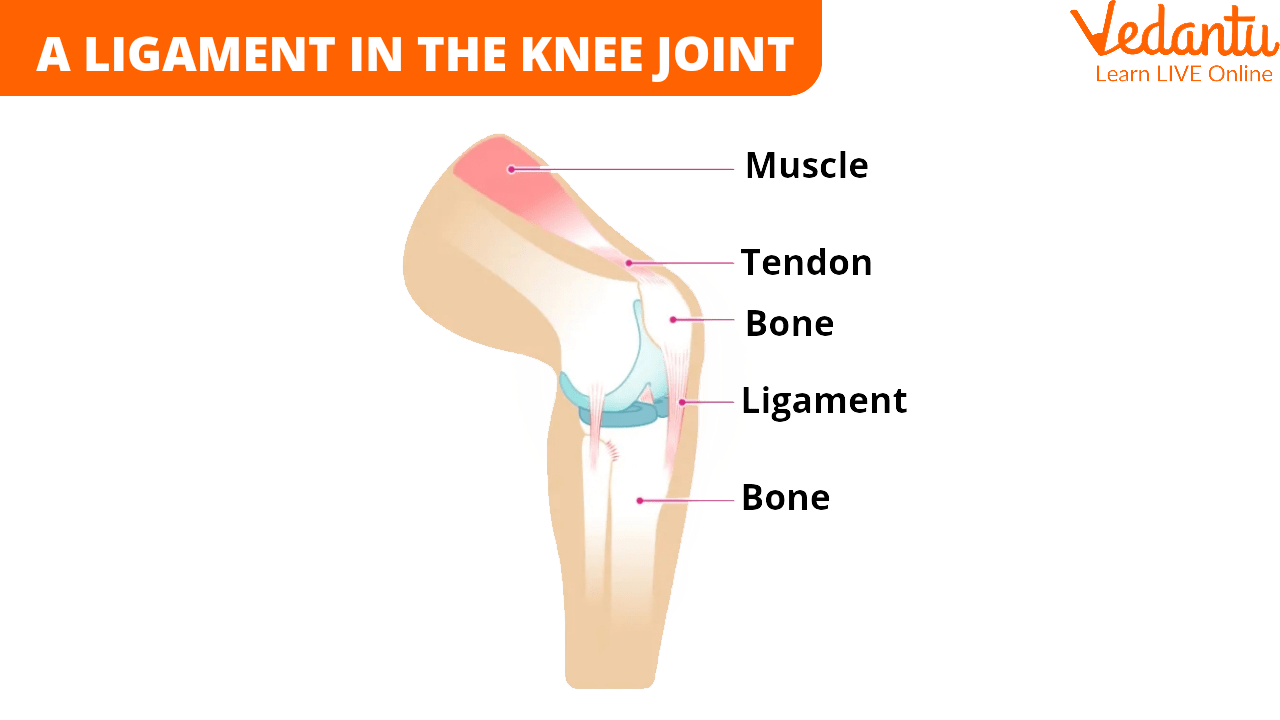
A Ligament in The Knee Joint
Why Do Bones Have Joints?
They make the skeleton flexible for it to move. Bones are not directly in contact with one another in a joint. They are covered by fluid, membranes, and joint cartilage.
The purpose of joints is to allow two bones to move relative to one another. The bones that meet at the joint must be connected to function. The attachment must be both strong enough to hold the joint in place and flexible enough to allow movement of the bones.
The presence of an articular capsule between the Bone-to-bone joint defines synovial joints. A layer of articular cartilage covers the bone surfaces at joints to provide protection. The ligaments surrounding synovial joints frequently support and reinforce, limiting movement to prevent harm.
Fluid Between Bones
A sticky fluid found between your joints is called synovial fluid, or joint fluid. When you move your joints, the fluid softens the ends of the bones and reduces contact. A series of tests called a synovial fluid analysis looks for conditions that impact the joints.
A collection of fluid inside your bones is called bone marrow oedema. It may occur as a result of an injury like a fracture. Alternatively, it can be connected to a medical issue like arthritis, an infection, or a tumour.
Common places for fluid are the knees, hips, and elbows. Joint effusion is the medical term for when too much fluid collects around a joint in your body. Our joints may appear swollen if one is experiencing this issue.
Conclusion
Our body's skeletal system serves as a support system. It protects organs, enables movement, creates blood cells, gives the body its structure, and stores minerals. The term "musculoskeletal system" is another name for the skeletal system.
In addition to sustaining the body's structure and enabling movements, bones are an essential component of the musculoskeletal system. Where two bones meet is called a joint. Without them, the movement would not be possible since they enable the skeleton to be flexible. Our bodies may move in numerous ways because of joints.
FAQs on Skeleton and Bones: Complete Study Guide
1. What is the human skeleton and what is its main purpose?
The human skeleton is the internal framework of the body, composed of all the bones. Its primary purpose is to provide structure and support, protect vital internal organs like the brain and heart, allow movement by acting as levers for muscles, store minerals like calcium, and produce blood cells in the bone marrow.
2. Are bones and the skeleton the same thing?
No, they are related but not the same. A bone is a single, hard organ that is part of the skeleton. The skeleton is the complete structure formed by all the individual bones (206 in an adult) and other connective tissues like cartilage, which work together as a system.
3. How many bones are in the human body, and why does this number change from childhood?
An adult human has 206 bones. However, babies are born with around 300 bones. This number decreases because many smaller bones, particularly in the skull and spine, are made of softer cartilage and gradually fuse together to form larger, stronger bones as a person grows.
4. What are the main types of bones found in the human body? Give examples.
Bones are classified into five main types based on their shape and function:
- Long Bones: Longer than they are wide, act as levers for movement. Examples include the femur (thigh bone) and humerus (upper arm bone).
- Short Bones: Roughly cube-shaped, provide stability. Examples are the carpals (wrist bones) and tarsals (ankle bones).
- Flat Bones: Thin, flattened, and often curved, they provide protection. Examples include the skull bones, ribs, and sternum (breastbone).
- Irregular Bones: Have complex shapes that don't fit other categories. Examples are the vertebrae in the spine and the hip bones.
- Sesamoid Bones: Small bones embedded within tendons, protecting them from stress. The patella (kneecap) is the largest example.
5. What is the difference between the axial and appendicular skeleton?
The human skeleton is divided into two main parts:
- The Axial Skeleton forms the central axis of the body and includes the bones of the skull, the vertebral column (spine), the ribs, and the sternum. Its main role is to protect vital organs.
- The Appendicular Skeleton consists of the bones of the limbs (arms and legs) and the girdles (shoulder and pelvic) that attach them to the axial skeleton. Its primary function is to facilitate movement.
6. What are joints and why are they important for the skeletal system?
A joint is a point in the body where two or more bones meet. Joints are crucial for the skeletal system because they are responsible for allowing movement and providing flexibility. Without joints, the skeleton would be a rigid, immovable structure. Different types of joints, like hinge joints (in the knee) and ball-and-socket joints (in the shoulder), allow for different ranges of motion.
7. How do bones, muscles, and joints work together to create movement?
Movement is a coordinated effort. Bones act as a rigid framework. Muscles are attached to bones by strong cords called tendons. When a muscle contracts, it pulls on the tendon, which in turn pulls the bone, causing it to move at a joint. The joints act as pivot points, allowing the bones to move smoothly in specific directions.
8. What is cartilage and where is it found?
Cartilage is a strong, flexible connective tissue that is softer than bone. It plays several important roles in the skeletal system. It is found:
- Covering the ends of bones at the joints to act as a cushion and reduce friction.
- Forming structures like the nose and the outer ears.
- Connecting the ribs to the sternum, allowing the chest to expand during breathing.
9. If bones are so hard, how do they repair themselves after a fracture?
Bones can repair themselves because they are living tissues with a rich blood supply and specialised cells. When a bone breaks, the body initiates a healing process. Blood vessels deliver cells that form a clot and then a soft callus around the break. Over several weeks, this callus is replaced with hard, new bone tissue (a process called ossification), which gradually remodels and strengthens until the bone is fully healed.









