




What Makes Dry Cells Essential in Everyday Life?
Many chapters of our science book show experiments where dry cell batteries were used to make a circuit. But we don't know how these batteries work or what makes them up. In this article, we'll also discuss dry batteries and how they work.
Dry cell batteries are those that have an electrolyte that has very little water in it. Also, they are different from lead-acid batteries, which use an electrolyte liquid.
Also, most dry cell batteries have electrolytes like semi-liquids or pastes with less water than liquid electrolyte batteries. Also, watch batteries, 9-volt batteries, "C" batteries, and "A" batteries are some of the most common dry batteries.
What is a Dry Cell?
A dry cell is a voltage-making cell in which the electrolyte is in the form of a moist paste. Because of this, the electrolyte doesn't leak out, and the device can be taken anywhere. This is used in flashlights, small radios, and other things. Dry cells are things like zinc-carbon batteries and alkaline batteries.
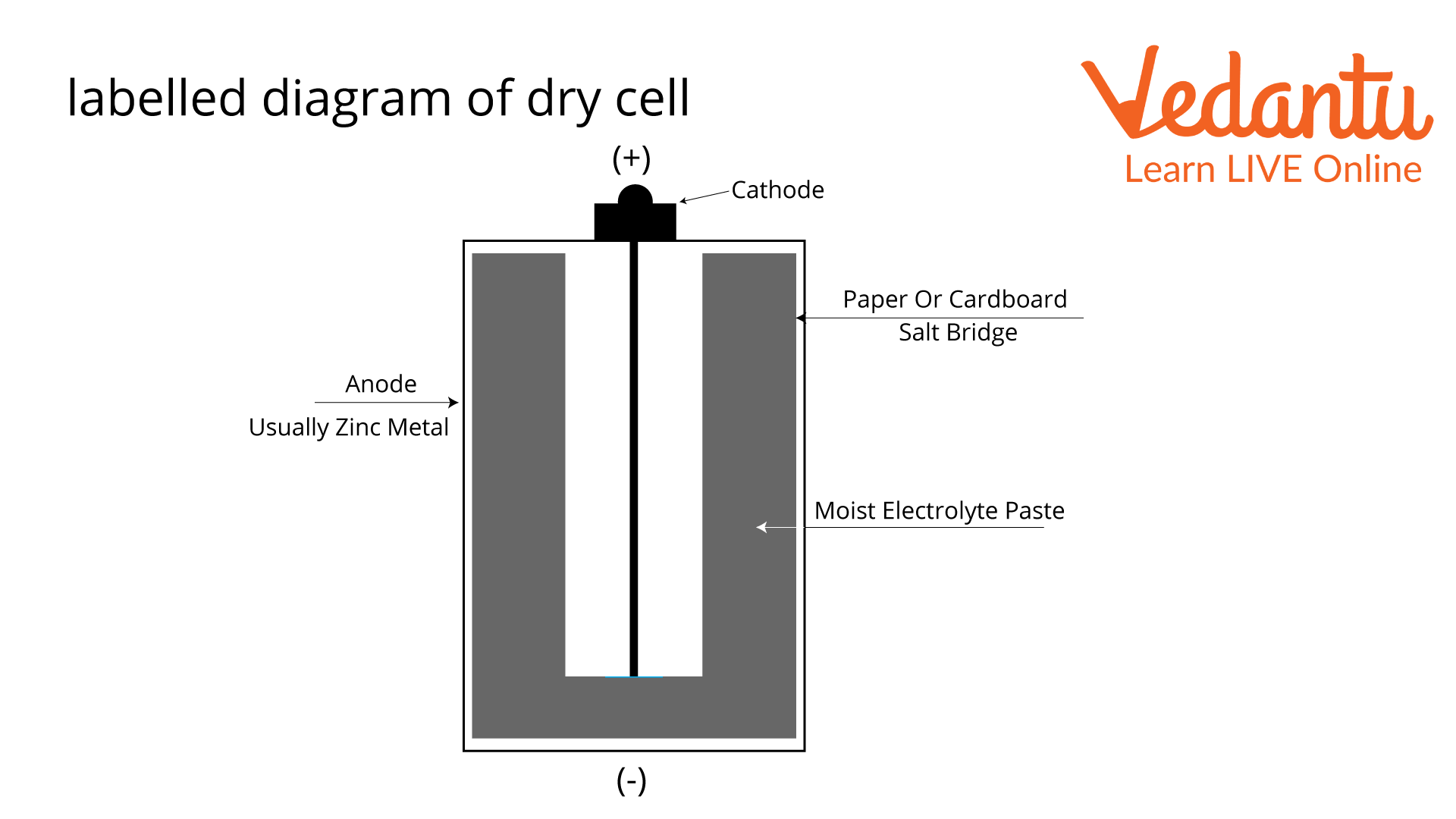
Labelled Diagram of Dry Cell
A dry cell comprises a metal electrode or graphite rod surrounded by a moist electrolyte paste and put inside a metal cylinder. Depending on the type of battery, different chemicals, like ammonium chloride and manganese dioxide, can be used to make this paste. The cathode and electrolyte paste is wrapped in paper or cardboard and put inside a zinc-made metal used in a dry cell called an anode.
The dry cell battery's anode has two ends, one of which is positive and the other negative. When a load is connected to the battery's terminals, the anode and paste go through a chemical reaction that makes about 1.5 volts of electricity. A pin or collector in the middle of the battery sends this charge to a circuit outside the battery. This circuit connects physically to the electronic device the battery is in, giving it the amount it needs to work.
Working Principle of Dry Cell
Depending on how the dry cell works, it can be called a primary or secondary cell. A primary cell cannot be used again or charged. Once the chemical reagents are used, the electrochemical reactions stop making electricity. On the other hand, a secondary cell can be used repeatedly by resetting the chemical reactions with a battery charge.
Uses of dry cell in daily life
The different uses of dry cell in daily life are as follows:
A lot of portable electronic devices use dry cells.
Chemical energy is turned into electrical energy in dry cells. Most of the time, they are used in portable electronics.
The alarm clock is portable, and only dry cells can be used to power it.
A dry cell is used every day in alarm clocks.
Conclusion
There are different kinds of dry cells. Some can be recharged, while others can only be used once. Batteries should be kept in a cool place because of the rate at which they lose power on their speeds up when the temperature is high. Whether or not a dry cell can be recharged, it is further broken down into primary and secondary cells.
FAQs on Uses of Dry Cell: Key Concepts and Applications
1. What is a dry cell and how does it generate electricity?
A dry cell is a type of electrochemical cell, commonly used as a portable source of electricity. It's called 'dry' because it uses an electrolyte in the form of a non-spillable paste, rather than a free-flowing liquid. It generates electricity by converting stored chemical energy into electrical energy through a chemical reaction between its components.
2. What are the common uses of a dry cell in our daily lives?
Dry cells are ideal for low-power, portable electronic devices due to their compact size and safety. Some common examples of their use include:
Remote controls for televisions and air conditioners
Wall clocks and alarm clocks
Flashlights and torches
Portable radios
Electronic toys and games
3. What are the main advantages of using a dry cell over a wet cell?
Dry cells offer several key advantages over wet cells, making them more suitable for consumer electronics. The main benefits are:
Portability: They are lightweight and compact, and can be used in any orientation without fear of spillage.
Safety: The paste-like electrolyte is sealed, significantly reducing the risk of leakage and corrosion.
Low Maintenance: Dry cells do not require any maintenance, such as topping up the electrolyte.
Longer Shelf Life: They lose their charge much more slowly when not in use compared to primary wet cells.
4. How is a dry cell explained in the context of Class 12 Chemistry?
In Class 12 Chemistry, under the chapter on Electrochemistry, a dry cell (specifically the Leclanché cell) is discussed as a prime example of a primary battery. It consists of a zinc container that acts as the anode (negative electrode), and a graphite or carbon rod that acts as the cathode (positive electrode). The cathode is surrounded by a powdered mixture of manganese dioxide (MnO₂) and carbon. The electrolyte is a moist paste of ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl) and zinc chloride (ZnCl₂).
5. Why is a dry cell called a 'primary' battery and can it be recharged?
A dry cell is called a primary battery because the electrochemical reaction that produces electricity is not reversible. Once the chemicals inside have been consumed to generate power, the cell is exhausted and cannot be recharged. Attempting to recharge a primary dry cell is dangerous and can lead to leakage or explosion, as the cell is not designed to reverse its chemical process.
6. What are the key chemical components inside a typical Leclanché dry cell and what role does each play?
Each component in a Leclanché dry cell has a specific electrochemical role:
Zinc Container: This acts as the negative electrode or anode, where oxidation occurs. The zinc metal loses electrons.
Graphite Rod: This is the positive electrode or cathode. It is inert and conducts the electrons for the reduction reaction to take place on its surface.
Manganese Dioxide (MnO₂): This chemical acts as a depolarizer around the cathode. It reacts with the hydrogen gas produced during the reaction, preventing a build-up of gas that would otherwise stop the cell from working.
Ammonium Chloride (NH₄Cl) Paste: This serves as the electrolyte, providing the ions needed to conduct electricity and complete the circuit inside the cell.
7. Why do dry cells eventually stop working, even if they are not used?
A dry cell has a limited shelf life and can stop working even without being used due to slow internal chemical reactions. The electrolyte, typically made of ammonium chloride, is acidic in nature. This acidic paste can slowly corrode the zinc casing over time, even when no current is being drawn. This corrosion thins the zinc anode, eventually causing the electrolyte to leak out and the cell to lose its power.
8. What happens at the anode and cathode during the discharge of a dry cell?
During the discharge of a Leclanché dry cell, specific electrochemical reactions occur at the electrodes. At the anode (the negative zinc casing), zinc is oxidised, releasing electrons:
Zn(s) → Zn²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻
At the cathode (the positive graphite rod), ammonium ions from the electrolyte are reduced in a complex reaction involving manganese dioxide:
2MnO₂(s) + 2NH₄⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ → Mn₂O₃(s) + 2NH₃(aq) + H₂O(l)
This flow of electrons from the anode to the cathode through an external circuit is what we use as electricity.









