ICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 3 Selina Concise Solutions - Free PDF Download
Syllabus of class 10th ICSE board is not easy as pie as we all know ICSE board is tough in comparison to ICSE board, so to be erudite in your subject you need a proper guidance of that particular subject. For those students who are really keen to learn and understand concepts, Selina published a book of ICSE chapter wise solutions in a very illustrative and descriptive way. They keep every important point in their mind while preparing for a book like your exam pattern, important concepts which need to be highlighted again and again, etc. Their book is so useful to ICSE board students that you can blindly trust their concepts and solutions and by referring to this book you will be able to score good marks in your academics.
Access ICSE Selina Solutions for Grade 10 Biology Chapter No. 3 - Genetics- Some Basic Fundamentals
Progress Check
1. Mention if the following statements are True (T) or False (F)
Genetics and heredity are the same thing T/F
Ans: The above statement- “Genetics and heredity are the same thing” is False. This is because Genetics deals with the study of both heredity and variation. But heredity is known as the transmission of traits from one generation to the next.
"Like begets like", this applies only to animals T/F
Ans: The above statement- “Like begets like”, this applies only to animals is True.
The entire human population shows variations. T/F
Ans: The above statement- The entire human population shows variations is True.
2. Which of the following in humans are established genetic traits (Tick mark the correct ones) in the box provided
Traits are the qualities or attributes that individuals acquire from their ancestors
Capacity to be a good cricketer-
Ans: It is not a genetic trait.
Curly hair
Ans: It is a genetic trait.
Left-handedness
Ans: It is a genetic trait.
Quality of voice
Ans: It is not a genetic trait
Red-green color blindness
Ans: It is a genetic trait.
3. Mention the following:
Total number of pairs of chromosomes in each body cell in humans……....
Ans: Humans have 23 chromosome pairs. There are a total of 46 chromosomes. Chromosomes are thread-like structures.
Number of pairs of autosomes in humans……
Ans: Number of pairs of autosomes in humans is 22, where one pair (XX or XY) are allosomes or sex chromosomes.
4. A certain couple got only four daughters in a row and no son. Does it mean that the husband does not produce Y-bearing sperms? explain.
Ans:
There are two types of chromosomes in male sperm cells: X chromosomes and Y chromosomes.
A female's egg cells have two X chromosomes.
The type of male chromosome that fuses with the female chromosome determines the gender of the child.
The resulting zygote will have X and Y chromosomes (XY) and grow into a male offspring when a sperm with Y chromosomes combines with the egg having X chromosome.
When an X-chromosome sperm combines with an egg, the resulting zygote has X and X chromosomes (XX) and develops into a female kid (daughter).
As a result, having only female offspring does not indicate the possibility that the father does not produce Y-bearing sperms.
Progress Check
1. Write the basic unit of heredity?
Ans: Gene is the basic unit of heredity. Genes are made up of DNA that is useful in carrying information from one generation to the next.
2. Define the following terms:-
Allele
Ans: An allele is defined as the alternative form of genes that govern the same feature, such as blood type or colour blindness, and exist at a certain place on a chromosome. Alleles are often referred to as allelomorphs.
Dominant Gene
Ans: In a heterozygous condition, the gene that is able to express itself is known as the dominant gene, while the one that does not express itself is known as the recessive gene.
For example, let T represent plant height. The plant with TT will now be tall, whereas tt will be short. In Tt pairing the alleles are distinct, T allele suppresses the expression of the t, resulting in a tall plant.
Genotype
Ans: The genotype of an organism is the particular mix of alleles for a given gene. It is the genetic expression of the gene. As an example, the genotype of a short plant is tt.
Phenotype
Ans: The physical expression of the gene that is observable is known as phenotype. For example: tall, dwarf.
Recessive Gene
Ans: In a heterozygous condition, the gene that is not able to express itself is known as the Recessive gene.
For example: Let T represent plant height. The plant with TT will now be tall, whereas tt will be short. But in the Tt where the alleles are different, T (dominant) will express and mask the t (recessive) resulting in a tall plant.
3. Mention the number of paired homozygous chromosomes in
Human Female
Ans: The number of paired homozygous chromosomes in Human female is 23 pairs- 22 autosomes and 1 pair sex chromosome (allosomes).
Human Male
Ans: The number of paired homozygous chromosomes in Human male is 22 pairs and one pair of sex chromosomes. One sex chromosome (allosomes) pair in male is in heterozygous condition XY.
4. Can there be a heterozygous recessive? Explain
Ans: No, since recessive genes are not expressed when they are combined with dominant genes. It is expressed only when a recessive gene is present with another recessive gene. Heterozygous is a condition where both the alleles present at the same locus are different, Tt. As a result, the dominant allele will exhibit its expression while the recessive will be suppressed.
5. List any four traits in humans which you can easily study just by observing and making family charts.
Ans: The four traits in humans which we can easily study just by observing and making family charts are-
Eye colour.
Right handedness or left handedness.
Red – green colour blind.
Rh blood group – positive or negative.
Progress Check
1. Who discovered for the first time the basic principles of genetics?
Ans: Gregor John Mendel developed the basic idea of genetics for the first time in the mid-nineteenth century. He tested his theory on garden peas (Pisum sativum). Mendel is now regarded as the father of genetics.
2. Give the common and scientific names of the organism on which Gregor Mendel had worked.
Ans: The common and scientific names of the organism on which Gregor Mendel had worked is
Common name – Garden pea
Scientific name – Pisum sativum
3. Define the following terms:
Monohybrid Cross
Ans: A genetic cross between homozygous individuals with distinct alleles for a single gene locus of interest is known as monohybrid cross. Example- A cross between pure tall (TT) and a dwarf (tt) pea plant.
Dihybrid Cross
Ans: A dihybrid cross is a cross between two parents who differ in two alternative features of two distinct characters. The resulting hybrids are called dihybrid. A cross between a tall and purple flower bearing pea plant and a dwarf plant having white flowers.
Filial Generation
Ans: The term "filial generation" refers to the offspring of the parents’ generation. In other terms, it refers to the F1 generation, which is created when two true-breeding parental forms are crossed.
4. Write the two characters of pea pod with their alternative traits.
Ans: The two characters of pea pod with their alternative traits are-
Pea Pod Color- Green color pod is dominant and yellow color pod is recessive
Pod Shape- Inflated pod shape is dominant and constricted pod shape is recessive.
A. Multiple Choice Type
1. Which one of the following is the phenotypic monohybrid ratio in F2 generation?
(a) 3 : 1 (b) 1 : 2 : 1 (c) 2 : 2 (d) 1 :3
Ans: (a) 3 : 1
Monohybrid Cross: It is defined as the cross in which one character is involved.
For example: When a homozygous tall pea plant TT is crossed with dwarf pea plant tt, the phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation is 3:1.
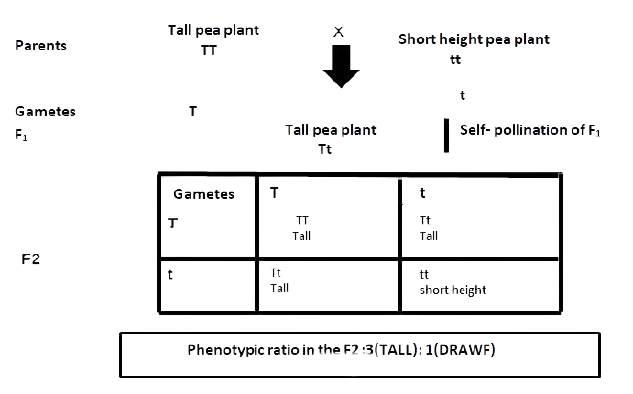
2. If a pure tall plant is crossed with a pure dwarf plant the offspring will be
(a) all tall (b) all dwarf (c) 3 tall 1 dwarf (d) 50% tall 50% dwarf
Ans: (a) all tall
Only tall plants develop in the first generation. However, 25% of the plants emerge as dwarfs in the second generation.
3. The 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 dihybrid ratio is due to:
(a) Segregation (b) crossing over (c) independent assortment (d) homologous pairing
Ans: (c) independent assortment
The law of independent assortment is responsible for the given ratio 9:3:3:1. The law of independent assortment states that genes on the same chromosome separate independently to one another during the gamete formation. In a dihybrid cross, two characters or genes on the same chromosome segregate independently and each of the gametes have a 50 % chance to receive either of them. This results in the 9:3:3:1 in the F2 generation.
4. A plant with green pods and smooth seeds with genotype Ggss will give rise to the following gametes:
(a) Gg and Ss (b) Gs and ss (c) Gs and gs (d) Gg and gs
Ans: (c) Gs and gs
The genotype Ggss plant is heterozygous for trait G but homozygous for s. As a result, two types of gametes will emerge: Gs and gs.
“Gs and gs” is the right answer.
B. Very Short Answer Type
1. Match the term column I with their explanation in column II.
Column I | Column II |
a. Genetics | (i) Chromosomes similar size and shape |
b. Autosomes | (ii) The alternative forms of a gene |
c. Recessive gene | (iii) Study of laws of inheritance of characters |
d. Allele | (iv) A gene that can express only when in a similar pair. |
e. Homologous chromosomes | (v) Chromosomes other than the pair of sex chromosomes. |
Ans:
Column I | Column II |
a. Genetics | (iii) Study of laws of inheritance of characters |
b. Autosomes | (v) Chromosomes other than the pair of sex chromosomes. |
c. Recessive gene | (iv) A gene that can express only when in a similar pair |
d. Allele | (ii) The alternative forms of a gene |
e. Homologous chromosomes | (i) Chromosomes similar size and shape |
2. Name any two genetic diseases in humans.
Ans: The two genetic diseases in humans are 1. Haemophilia 2. Thalassemia
3. Which one of the following is homozygous dominant and which one homozygous recessive in regards to tongue rolling: Rr, rr, RR?
Ans: RR is homozygous dominant pair, rr is homozygous recessive pair and Rr is heterozygous dominant
C. Short Answer Type
1. Differentiate between:
Genotype and phenotype
Ans: (a) The difference between genotype and phenotype are-
Genotype | Phenotype |
Genetic makeup an individual is called genotype. | The observable characteristics of an individual are called phenotype |
Genotype of an individual always remains constant. | Phenotype of an individual does not remain constant. |
It is not affected by environmental conditions. | Phenotype of an individual varies with changing environmental conditions. |
Character and Trait
Ans: The difference between character and trait is:
Character | Trait |
Any heritable feature is character | The alternative forms of a character are called traits. |
For example - Such as colours of eyes – Brown or blue. Here colour of eye is character. | For example - Such as colours of eyes – Brown or blue. Here colour brown or blue is a trait. |
Monohybrid and dihybrid cross (phenotypic ratio)
Ans:
Dihybrid Cross | Monohybrid Cross |
The phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation is 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 | The phenotypic ratio in the F2 generation is 3:1 |
2. Among lion, tiger and domestic cat, all the three have the same number of 38 chromosomes, yet they have different appearances. How do you account for such differences?
Ans: Although the lion, tiger, and domestic cat all have the same number of chromosomes, yet their appearances differ due to the genes placed on the chromosomes (DNA Segments) that govern inherited features.
3. List any three features of garden peas with their dominant and recessive traits.
Ans: The features are as below:
Features | Dominant $\times $ Recessive |
1. Plant height | Tall $\times $ Dwarf |
2. Flower colour | Purple $\times $ White |
3. Flower position | Axial $\times $ Terminal |
4. Seed shape | Round $\times $ Wrinked |
4. Explain why generally only the male child suffers from colour blindness and not females?
Ans: Color blindness is a hereditary disease. Recessive genes on the 'X' chromosome are responsible for this blindness. Male has only one X chromosome, hence colour blindness expresses even in heterozygous condition. While in the female heterozygous colour blindness remains as carrier and expresses only in the homozygous recessive.
The following examples demonstrate how color blindness is inherited in a sex-related manner.
Case 1: When father is carrier

Case 2: When mother is color blind

D. Descriptive Type
1. Define the following terms:
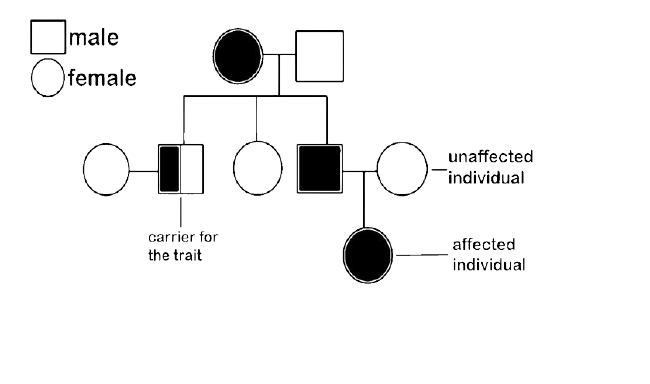
Pedigree Chart
Ans: A pedigree chart is a diagram that depicts the occurrence and appearance of phenotypes of a gene or organism, as well as their predecessors, from one generation to the next.
Variations
Ans: In genetics, variation refers to an individual who differs from others of his or her species in some way.
Mutation
Ans: Mutation occurs when the base pair sequence of our DNA changes as a result of numerous environmental influences such as UV radiation or errors during DNA replication.
2. State the three Mendel’s Laws of inheritance.
Ans: The three Mendel’s laws of inheritance are-
Law of Dominance: Out of a pair of opposing traits present together, only one is able to express itself while the other is suppressed. The dominant character is the one who expresses, whereas the recessive character is the one who does not. Only when both recessives are present in a pair can the recessive feature express itself.
Law of Segregation: During the gamete formation, the two members/alleles of a pair separate. They don't mix; instead, they segregate and divide into various gametes. At the time of zygote development, the gametes fuse together at random.
Law of Independent Assortment: When two pairs of genes with opposing characteristics exist, the members of one pair's distribution into gametes is independent of the distribution of the other pair's members.
3. Does the sex of the child depend on the father or it is just a matter of chance. Discuss.
Ans: No, the child's sex is not determined by the parents; it is just a matter of chance. The type of sperm that fertilises the egg determines the child's sex. Although the egg only has one chromosome, half of the sperm discharged into the female are X-bearing and the other half are Y-bearing. The group of sperm that unites with the ovum is just a matter of luck.
4. Distinguish between the following pairs:
Karyotype and Karyokinesis
Ans: The difference between Karyotype and Karyokinesis is-
Karyotype | Karyokinesis |
Karyotype is a test that is used to examine chromosomes present in a sample of cell | Karyokinesis is defined as the division of nucleus that results in daughter cell |
Autosomes and Sex Chromosomes
Ans: The differences between autosomes and sex chromosomes:
Autosomes | Sex chromosomes |
1. They determine the somatic traits. | 1. They determine the sex of an organism. |
2. They are numbered from 1 to 22. | 2. They are numbered by the letters XO, XY, ZO, ZW. |
3. They show Mendelian inheritance. | 3. They do not show Mendelian inheritance. |
4. Humans show 22 pairs of autosomes. | 4. Humans show only 1 pair of sex chromosome. |
Homozygous and Heterozygous Chromosomes
Ans: The differences between homozygous and heterozygous chromosomes is:
Homozygous Chromosomes | Heterozygous Chromosomes |
It has two same copies of the same allele coding for a particular trait. | It contains two different copies of alleles coding for a particular trait. |
Structured/Application and Skill Type
In a certain species of animals, black fur (B) is dominant over brown fur (b). Predict the genotype and phenotype of the offspring, when both parents are 'Bb' or have heterozygous black fur.
Ans:
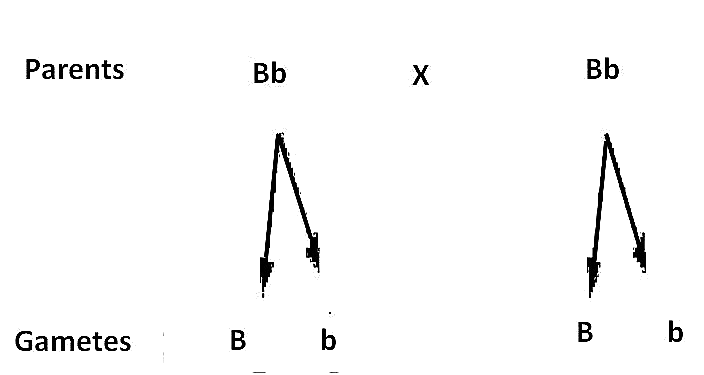
Gametes | B | b |
B | BB | Bb |
b | Bb | bb |
Genotype - 1(Homozygous Black Fur): 2 (Heterozygous Black Fur) : 1 (Homozygous Brown Fur)
Phenotype - 3 (Black Fur): 1(Brown Fur)
2. Two pairs (A and B) of rabbits were crossed as given below:
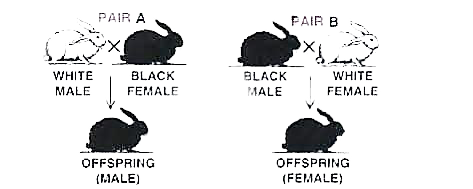
Can you tell which coat colour (black or white) is dominant?
Ans: Black fur is dominant as in F1 generation Black colour expresses itself.
Is the coat colour sex-linked?
Ans: No, the coat colour is not sex-linked. This is because the inheritance of the coat color from parents to off springs is sex independent that is the male and female offspring have equal change to inherit the trait.
3. Make a Punnett square for finding out the proportion of different genotypes in the progeny of a genetic cross between
A pure tall (TT) pea plant with a pure dwarf (tt) pea plant.
Ans: (a)
Parents TT x Tt
↓
F1 generation Tt(Hybrid red flower)
Gamets T t
F2 generation -
Gametes | T | t |
T | TT | Tt |
t | Tt | Tt |
Genotype - 1(Homozygous tall) :2 (Heterozygous tall):1 (Homozygous dwarf)
Phenotype - 3 (Tall) :1(Dwarf)
Red flower variety of pea (RR) with white flower variety of pea (rr).
Ans:
Parents RR x rr
↓
Rr (Hybrid red flower)
Gamets R r
F2 Generation -
Gametes | R | r |
R | RR | Rr |
r | Rr | rr |
Genotype - 1(Homozygous red): 2 (Heterozygous red):1 (Homozygous white)
Phenotype - 3 (Red): 1(White)
4. A family consists of two parents and their five children and the pedigree chart shown below shows the inheritance of the trait colour blindness in them.
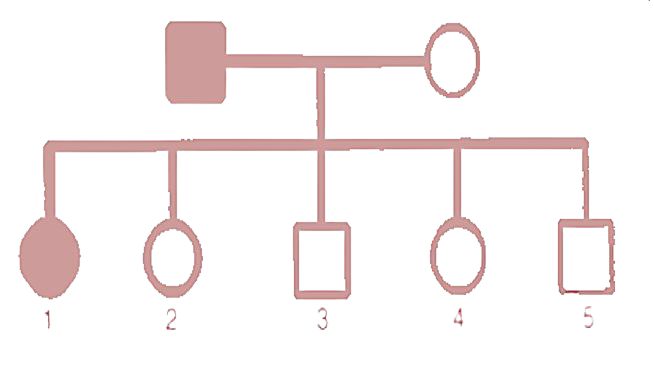
Who is colour blind in the parents - the Father or the Mother?
Ans: By seeing the pedigree chart we can say that the father is colour blind.
How many daughters and how many sons have been born in the family?
Ans: There are three daughters and two sons born in the family.
What does child 1 indicate about this trait?
Ans: The child 1 is a daughter that indicates she is colour blind.
On which chromosome is the gene of this trait located?
Ans: On the X chromosome the gene of this trait is located.
Name one other trait in humans which follows a similar pattern of inheritance.
Ans: The other trait in humans which follows a similar pattern of inheritance is Haemophilia.
Introduction to the Chapter
Selina solutions plays a very crucial role in preparation for class 10th ICSE board exam as it gives you a path to give your best during exam preparation in every aspect as it develops better understanding of different concepts which will help you in preparation of different competitive exams like NTSE and various olympiads, this shows what a pivotal role Selina solution is playing in students life and this is the reason it is considered as one of the best solution book for ICSE class 7th students. And keeping all these important points in mind vedantu provides a pdf of Selina concise solution and you can download it from vedantu learning app site and go through it in both online and offline mode. It helps those students who really want to command the maths of class 10th. Vedantu believes in educating those students who really have fervidity towards learning and do well in their exams and we as a family of vedantu try to inchance your interest towards your learning as well as grasping skills as we trust in the power of learning.
Class 10th is considered as a base for higher classes which really matter for a brighter future as well all want to be topper of our class or school and for this you need proper guidance and support and we provide this guidance to you, so start preparing for your dream with vedantu, we dream what you all dream.
Link of concise Selina class 10th biology solution of chapter 3 genetics is being provided below by vedantu and by downloading this pdf you will be able to go through all solved questions of genetics as they cover at least four to five questions during your exams. As the genetics topic is not only important as per exam point of view but also plays a major role in other entrance examinations like NEET and other graduate level entrance examinations. Experienced subject experts put all their efforts together for your dreams and make your path easier. By solving this solution pdf you can self analyse yourself i.e where you stand in this race of success. Each solution is precisely and accurately prepared so that students don't get any difficulty in getting the concepts. There are so many correlated concepts in the chapter and all of them are very well illustrated so that students don't find any difficulty in getting the concepts.
Apart from this, solution pdf also teaches students how to present their knowledge in a very descriptive and illustrative way so that they can write a perfect solution matter in their school level exam as all such queries of students are considered during preparation of solution and we are glad to speak that this solution pdf from Selina has very positive feedback from students of class 10th. Students who refer to this solution pdf have really scored well in their competitive as well as other entrance examinations. If we really rely on trusted material we all can make change in our education and vedantu do the same for ICSE class 10th students as they provide the best solution pdf of Selina publisher. Each ICSE board student will find it very useful as they all want accurate and descriptive solutions for their related chapters or concepts and they get the same in a very easy way from vedantu, so below is the the accurate answer of all questions of chapter genetics in pdf form and along with this you can also get notes of this chapter from vedantu site to make your concept more stronger or to get command in that particular topic.
Chapter - 3 - Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals of Class 10 Biology is one of the most crucial chapters in the subject. In this chapter, you get to learn about genetics, the law of inheritance, sex determination and a lot more. With a vast array of subtopics, it creates a base for the subsequent chapters. So, if you understand this chapter with utmost sincerity, it will be much easier for you to learn the concepts in the upcoming chapters.
Concepts in Class 10 Biology Chapter - 3 - Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals
Let us quickly look at the various topics that entail chapter 3. They are as follows:
What is Genetics?
Variations in Populations
Chromosomes – The Carriers of Heredity
The two main categories of Chromosomes – Autosomes and Sex chromosomes
Sex determination – Son or Daughter
Chromosomes – Carriers of Genes
Genes and Their Alleles
Genotype and Phenotype
From parents to children – Tongue rolling – An example of Inheritance
Sex-Linked Inheritance
Mendel’s experiment on Inheritance
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance
Advantages of studying via Selina Concise Solutions for ICSE Class 10 Biology PDF
The Selina Concise solutions for ICSE Class 10 Biology pdf offers a wide range of benefits. These are:
The Selina Solutions pdf provides you with step-by-step answers with detailed explanations to help you understand the concepts better.
The pdf consists of tables that are used for appropriate questions to make them easy to learn and comprehend.
The solutions in this reliable pdf are entirely based on the content from the Selina textbook, which is recommended by the ICSE to prepare for board exams.
In this pdf, you will find the answers to structural and skill-type questions along with the relevant diagrams. These diagrams have neat and clean labels for clear and effective learning.
For better learning, the concepts are explained in a simple language. It avoids misunderstanding and boosts the learning process.
All the solutions are designed by field professionals to ensure an effective understanding of the basics.
If you have missed any classes, the Selina solutions for ICSE Class 10 Biology pdf will help you get back on track with its simplified answers.
Since Selina is considered the best book for ICSE preparations, it is better to have all the textbook answers with yourself to score better in the final examinations.
FAQs on Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 3 - Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals
1. How do I get access to solutions to textbook questions?
The most convenient way to make the solutions accessible to you is the Vedantu website. There is plenty of study material for all the subjects for all the classes on the site. Unlike many other resources, Vedantu offers its study material to students for free. You don’t have to pay a single penny to download the pdf format of the solutions to textbook questions. Moreover, you can find revision notes, quizzes, puzzles, sample papers, important concepts, and much more on the Vedantu mobile application.
2. Do Selina Solutions cover all the important topics for chapter 3?
The Concise Selina solutions for ICSE class 10 biology Chapter 3 covers the entire syllabus with detailed explanations of every concept. It consists of topics and subtopics such as genetics, sex determination, genotype, phenotype, Mendel’s law of inheritance, etc. The Selina solutions feature simple and easy-to-understand language, making it easier for students to gain knowledge about any topic. With this pdf on your mobile phone, you can look at the solutions whenever you are having problems in solving a question.
3. What study material is necessary for the ICSE Biology exam?
With all the theories in Biology, you will need plenty of study material to prepare for the ICSE Biology exam. Make sure to write down notes during classes that can help you in quick revisions before the exam. Solving sample papers and previous year’s question papers is also an excellent way to boost your preparations. You can download the Concise Selina Solutions for ICSE Class 10 Biology to keep the answers available to you 24*7, whether online or offline.
4. Can I skip unimportant topics for the Class 10 Biology exam?
Class 10 Biology is the base for further studies in subsequent classes. Also, most of the concepts are inter-connected, which means you cannot move on to the next one without understanding a particular topic. It is advised not to leave out any concept in biology, even if they seem unimportant. Moreover, the ICSE exams are hard and unpredictable. Since you don’t know the type of questions, it is better to cover the entire curriculum without missing a single detail. It will ensure excellent marks, leading to an outstanding overall score.
5. What is the best reference book for the ICSE Biology exam?
ICSE recommends studying from Selina as it is one of the best reference books for the biology exam. ICSE prepares its question papers based on the information provided in the Selina Textbook. Students can learn biological concepts with ease since these textbooks feature simple language and deep explanations. The book can also clear your doubts with its uncomplicated illustrations and examples. However, if you go through more reference books, along with Selina, your chances of a perfect score in the ICSE exam will increase significantly.







































