ICSE Class 10 Mathematics Chapter 20 Selina Concise Solutions - Free PDF Download
ICSE Class 10 Math Chapter 20 deals with finding surface area and cylindrical volume, cones and spheres, solid conversion, solid mixture, and other miscellaneous issues. For the purpose of clarifying the doubts of students, the ICSE Class 10 Math Ch 20 Selina Solutions for Class 10 Mathematics is prepared by our experts which are built after deep research. It also provides students with instructions to confidently solve problems. ICSE Class 10 Math Chapter 20 solutions are available on our website. We will cover the important formulas involved in solving problems related to cylinder cone and sphere Class 10. Chapter 20 Math ICSE Class 10 is one of the important topics as this will be applicable in higher classes as well as during engineering majors.
Chapter 20 in the Class 10 ICSE syllabus is the area and volume of cylinders, cones, and spheres. This chapter is the one that has got too many formulae and theorems to remember. Before you start your preparation for the examination, mark this chapter to be an important chapter. Since this involves a lot of formulae, this chapter could have many types of indirect questions. All these indirect types of questions need more practice. Without practice, students would not figure out the question type itself. This will lead to a waste of time in the examination which will eventually lead to scoring minimum marks. All you have to do is give more practice to this concept.
Access ICSE Selina Solutions for 10 Mathematics Chapter 20 - Cylinder, Cone and Sphere (Surface Area and Volume)
Exercise 20A
1. The height of a circular cylinder is 20cm and the radius of its base is 7cm. Find:
Volume
Ans: Volume of cylinder, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{7}^{2}}\times 20$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=22\times 7\times 20$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=3080\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the volume of the circular cylinder is $3080\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
Total Surface Area
Ans: Total surface area of cylinder, $\text{S}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}\left( \text{h}+\text{r} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}=2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 7\left( 20+7 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}=2\times 22\times 27$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}=1188\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the total surface area of the circular cylinder is $1188\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
2. The inner radius of a pipe is 2.1cm. How much water can 12m of this pipe hold?
Ans: Amount of water a pipe can hold is equal to the volume of the pipe.
Height of the cylinder, $\text{h}=12\text{m}=1200\text{cm}$
Volume of metal pipe, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{2.1}^{2}}\times 1200$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=22\times 0.3\times 2.1\times 1200$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=16632\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the amount of water the pipe can hold is $16632\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
3. A cylinder of circumference 8cm and length 21cm rolls without sliding for $4\dfrac{1}{2}$ seconds at the rate of 9 complete rounds per second. Find
The distance travelled by the cylinder in $4\dfrac{1}{2}$ seconds
Ans: Circumference of cylinder, $\text{P}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}$
$\Rightarrow 8=2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times \text{r}$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=\dfrac{14}{11}\text{cm}$
Distance covered in 1 revolution = 8cm
Distance covered in 9 revolutions = 72cm
So the distance covered in 1sec=72cm
Distance covered in $4\dfrac{1}{2}$sec=$72\times \dfrac{9}{2}=324\text{cm}$
Therefore the distance covered in $4\dfrac{1}{2}$ seconds is 324cm.
The area covered by the cylinder in $4\dfrac{1}{2}$seconds
Ans: Curved surface area, $\text{C}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rh}$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{14}{11}\times 21$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=2\times 2\times 2\times 21$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=168\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Area covered in one revolution is $168\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Area covered in 9 revolutions = $168\times 9=1512\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
So the area covered in 1 second = $1512\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Area covered in $4\dfrac{1}{2}$ seconds = $1512\times \dfrac{9}{2}=6804\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
4. How many cubic meters of earth must be dug out to make a well 28m deep and 2.8m in diameter? Also, find the cost of plastering its inner surface at 4.50rs per sq.meter.
Ans: Radius of well, $\text{r}=\dfrac{2.8}{2}=1.4\text{m}$
Volume of well, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{1.4}^{2}}\times 28$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=22\times 0.2\times 1.4\times 28$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=172.48{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Curved surface area of well, $\text{C}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rh}$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 1.4\times 28$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=2\times 22\times 0.2\times 28$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=246.4{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Cost of plastering is $246.4\times 4.5=1108.8$
Therefore, the volume of well is $172.48{{\text{m}}^{3}}$and cost of plastering is $1108.8\text{rs}.$
5. What length of solid cylinder 2cm in diameter must be taken to recast into a hollow cylinder of external diameter 20cm, 0.25cm thick and 15cm long?
Ans: External radius of the cylinder $=\dfrac{20}{2}=10\text{cm}$
Internal radius of the cylinder$=10-0.25=9.75\text{cm}.$
Volume of hollow cylinder, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ h}\left( {{\text{R}}^{2}}-{{\text{r}}^{2}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 15\times \left( {{10}^{2}}-{{9.75}^{2}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 15\times 4.94$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=232.77\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
The radius of the cylindrical recast, $\text{r }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{2}{2}=1\text{cm}$
Let the length of the solid cylinder is $\text{h }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }$
Volume of solid cylinder, $\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{(1)}^{2}}\text{h }\!\!'\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of solid cylinder = Volume of hollow cylinder
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{(1)}^{2}}\text{h }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=232.77$
$\Rightarrow \text{h }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=232.77\times \dfrac{7}{22}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=74.06\text{cm}$
Thus the length of the solid cylinder is 74.06cm
6. A cylinder has a diameter of 20cm. The area of a curved surface is $100\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{2}}.$ Find:
The height of the cylinder is correct to one decimal place.
Ans: Radius of cylinder, $\text{r}=\dfrac{20}{2}=10\text{cm}$
Curved surface area of the cylinder, $\text{C}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rh}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\dfrac{\text{C}}{2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\dfrac{100}{2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 10}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\dfrac{100\times 7}{2\times 22\times 10}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=1.6\text{cm}$
Thus the height of the cylinder is 1.6cm.
The volume of the cylinder correct to one decimal place
Ans: Volume of cylinder, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{10}^{2}}\times 1.6$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=502.9\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the volume of the cylinder is $502.9\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
7. A metal pipe has a bore(inner diameter) of 5cm. The pipe is 5mm thick all round. Find the weight, in kilogram, of 2 meters of the pipe if $1\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{3}}$of the metal weighs 7.7g.
Ans: Inner radius of the pipe, $\text{r}=\dfrac{5}{2}=2.5\text{cm}$
Height of the cylinder, $\text{h}=2\text{m}=200\text{cm}$
Thickness of the pipe, $\text{t}=5\text{mm}=0.5\text{cm}$
Outer radius of the pipe = inner radius of the pipe + thickness of the pipe
$\Rightarrow \text{R}=\text{r}+\text{t}$
$\Rightarrow \text{R}=2.5+0.5=3\text{cm}$
Volume of pipe, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ h}\left( {{\text{R}}^{2}}-{{\text{r}}^{2}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 200\times \left( {{3}^{2}}-{{2.5}^{2}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 200\times 2.75$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=1728.57\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Weight of the metal, $\text{m}=1728.57\times 7.7=13309.98\text{gm}=13.31\text{kg}$
Therefore the weight of the metal is 13.31kg.
8. A cylindrical container with with diameter of base 42cm contains sufficient water to submerge a rectangular solid of iron with dimensions $22\mathbf{cm}\times 14\mathbf{cm}\times 10.5\mathbf{cm}.$Find the rise in the level of the water when the solid is submerged.
Ans: Radius of the cylindrical container, $\text{r}=\dfrac{42}{2}=21\text{cm}$
Volume of the rectangular solid,
${{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=22\times 14\times 10.5=3234\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of water in cylindrical container, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{21}^{2}}\times \text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=1386\text{h }\!\!~\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
From the given information, we know that Volume of water in cylindrical container = Volume of rectangular solid
$\Rightarrow 1386\text{h}=3234$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\dfrac{3234}{1386}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=2.33\text{cm}$
Therefore the water level is raised by 2.33cm when the solid is submerged.
9. A cylindrical container with internal radius of its base 10cm, contains water up to a height of 7cm. Find the area of the wet surface of the cylinder.
Ans: Area of wet surface of the cylinder = Total surface area of the container
Area of wet surface of the cylinder, $\text{S}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}\left( 2\text{h}+\text{r} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 10\times \left( 2\left( 7 \right)+10 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 10\times 24$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}=754.29\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore, area of wet surface is $754.29\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
10. Find the total surface area of an open pipe of length 50cm, external diameter 20cm and internal diameter 6cm.
Ans: External radius of pipe, $\text{R}=\dfrac{20}{2}=10\text{cm}$
Internal radius of pipe, $\text{r}=\dfrac{6}{2}=3\text{cm}$
Surface area of the open sides, ${{\text{A}}_{1}}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ h}\left( \text{R}+\text{r} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{A}}_{1}}=2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 50\times \left( 10+3 \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{A}}_{1}}=4085.7\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Surface area of lower and upper parts, ${{\text{A}}_{2}}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\left( {{\text{R}}^{2}}-{{\text{r}}^{2}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{A}}_{2}}=2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times \left( {{10}^{2}}-{{3}^{2}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{A}}_{2}}=572\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Total surface area,$\text{A}={{\text{A}}_{1}}+{{\text{A}}_{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=4085.7+572=4657.7\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the total surface area of the open pipe is $4657.7\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
11. The height and the radius of the base of a cylinder are in the ratio 3:1. If its volume is $1029\mathbf{\Pi c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{3}};$find its total surface area.
Ans: Ratio between the height and radius is given as 3:1.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{h}}{\text{r}}=\dfrac{3}{1}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=3\text{r}$
Volume of water in cylindrical container, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}=1029\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\left( 3\text{r} \right)=1029\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{3}}=\dfrac{1029}{3}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{3}}=343$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=7$
$\text{h}=3\text{r}=3\left( 7 \right)=21$
Total surface area of cylinder, $\text{S}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}\left( \text{h}+\text{r} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}=2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 7\times \left( 21+7 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}=2\times 22\times 28$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}=1232\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore, the total surface area is $1232\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
12. The radius of a solid right circular cylinder increases by 20% and its height decreases by 20%. Find the percentage change in its volume.
Ans: Let the radius and height of the cylinder be 100cm.
Volume of cylinder, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{100}^{2}}\times 100$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=1000000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
According to the question, radius is increased by 20% and height is decreased by 20%.
New radius, ${{\text{r}}_{1}}=120$and new height, ${{\text{h}}_{1}}=80$
Volume of the new cylinder, ${{\text{V}}_{1}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{2}{{\text{h}}_{1}}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{1}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{120}^{2}}\times 80$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{1}}=1152000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Change in volume$={{\text{V}}_{1}}-\text{V}=1152000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }-1000000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }=152000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }$
Percent change in volume$=\dfrac{152000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{1000000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}\times 100$
$=15.2$
Therefore the percent change in volume is increased by $15.2\text{ }\!\!%\!\!\text{ }.$
13. The radius of a solid right circular cylinder decreases by 20% and its height increases by 10%. Find the percentage change in its
Volume
Ans: Let the radius and height of the cylinder be 100.
Volume of cylinder, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{100}^{2}}\times 100$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=1000000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
According to the question, radius is decreased by 20% and height is increased by 10%.
New radius, ${{\text{r}}_{1}}=80$and new height, ${{\text{h}}_{1}}=110$
Volume of the new cylinder, ${{\text{V}}_{1}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{2}{{\text{h}}_{1}}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{1}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{80}^{2}}\times 110$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{1}}=704000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Change in volume$={{\text{V}}_{1}}-\text{V}=704000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }-1000000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }=-296000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }$
Percent change in volume$=\dfrac{-296000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{1000000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}\times 100$
$=-29.6$
Therefore the percent change in volume is decreased by
Curved surface area
Ans: Curved surface area of cylinder, $\text{C}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rh}$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\left( 100 \right)\left( 100 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=20000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
New curved surface area, ${{\text{C}}_{1}}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}{{\text{h}}_{1}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{C}}_{1}}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\left( 80 \right)\left( 110 \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{C}}_{1}}=17600\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Change in the curved surface area$={{\text{C}}_{1}}-\text{C}$
$=17600\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }-20000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }$
$=-2400\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }$
Percent change in curved surface area$=\dfrac{-2400\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{20000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}\times 100$
$=-12\text{ }\!\!%\!\!\text{ }$
Therefore the percentage change in curved surface area is decreased by $12\text{ }\!\!%\!\!\text{ }.$
14. Find the minimum length in cm and correct to the nearest whole number of the thin metal sheet required to make a hollow and closed cylindrical box of diameter 20cm and height 35cm. Given that the width of the metal sheet is 1m. Also, find the cost of the sheet at the rate of 56rs per meter. Find the area of the metal sheet required, if 10% of it is wasted in cutting, overlapping,etc.
Ans: Radius of the cylindrical box$=\dfrac{20}{2}=10\text{cm}$
Width of the metal sheet$=1\text{m}=100\text{cm}$
From the question, we know that
Area of the rectangular metal sheet = Total surface of the cylindrical box
$\Rightarrow \text{l}\times \text{b}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}\left( \text{r}+\text{h} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}\times 100=2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 10\left( 10+35 \right)$
$\Rightarrow 100\text{l}=2828.57$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=28\text{cm}$
Area of rectangular metal sheet, $\text{A}=\text{l}\times \text{b}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=28\times 100=2800\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}^{{}}=0.28{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Cost of the sheet$=0.28\times 56=15.68\text{rs}$
Let $\text{A }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }$be the area of the required sheet.
According to the question, 10% of required area of the sheet is waste in cutting
$\Rightarrow \text{A }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }-0.1\text{A }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=2800$
$\Rightarrow 0.9\text{A }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=2800$
$\Rightarrow \text{A }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=3111\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the minimum length of the thin metal sheet is 28cm, cost of the sheet is 15.68rs and the area of metal sheet required is $3111\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
15. 3080$\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{3}}$of water is required to fill a cylindrical vessel completely and $2310\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{3}}$water is required to fill it up to 5cm below the top. Find:
Height of the Vessel
Ans: Let the radius and height of the cylindrical vessel be r and h respectively.
Volume of cylindrical vessel = volume of the water filled in the vessel
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}=3080$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}=3080\times \dfrac{7}{22}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}=980$-------(1)
Given that volume of water when filled till 5cm below the top as $2310\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\left( \text{h}-5 \right)=2310$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}\left( \text{h}-5 \right)=735$-------(2)
Dividing equ (1) by (2)
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{h}}{\text{h}-5}=\dfrac{980}{735}$
$\Rightarrow 735\text{h}=980\text{h}-4900$
$\Rightarrow 980\text{h}-735\text{h}=4900$
$\Rightarrow 245\text{h}=4900$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=20\text{cm}$
Therefore the height of the vessel is 20cm
Radius of the Vessel
Ans: Substituting ‘h’ value in (1)
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}\left( 20 \right)=980$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}=49$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=7\text{cm}$
Therefore the radius of the vessel is 7cm.
Wetted surface area of the vessel when it is half filled with water
Ans: Surface area of cylinder$=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}+2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rh}$
But here only the bottom of the cylinder gets wet and height of wetted cylinder when it is half filled=10cm
Surface area of wetted cylinder when half filled$=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}+2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rh}$
$=\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{7}^{2}}+2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 7\times 10$
$=154+440=594\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the wetted surface area of the vessel when it is half filled with water is $594\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
16. Find the volume of the largest cylinder formed when a rectangular piece of paper 44cm by 33cm is rolled along it
Shorter Side
Ans: When the paper is rolled along its shorter side or breadth, the height of the cylinder will be 44cm and the circumference of the cylinder formed will be 33cm.
We know that circumference of the cylinder, $\text{C}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}$
$\Rightarrow 2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}=33$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=\dfrac{33}{2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=\dfrac{33\times 7}{2\times 22}$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=5.25\text{cm}$
Volume of cylinder formed, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{5.25}^{2}}\times 44$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=3811.5\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the volume of the cylinder formed when rolled along its shorter side is $3811.5\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
Longer Side
Ans: When the paper is rolled along its longer side or breadth, the height of the cylinder will be 33cm and the circumference of the cylinder formed will be 44cm.
We know that circumference of the cylinder, $\text{C}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}$
$\Rightarrow 2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}=44$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=\dfrac{44}{2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=\dfrac{44\times 7}{2\times 22}$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=7\text{cm}$
Volume of cylinder formed, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{7}^{2}}\times 33$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=5082\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the volume of the cylinder formed when rolled along its longer side is $5082\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
17. A metal cube of 11cm is completely submerged in water contained in a cylindrical vessel with diameter 28cm. Find the rise in the level of water.
Ans: Radius of the cylindrical vessel, $\text{r}=\dfrac{28}{2}=14\text{cm}$
From the question, we know that
Volume of the metal cube = Volume of water displaced in the cylinder
$\Rightarrow {{11}^{3}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}={{11}^{3}}\times \dfrac{1}{{{14}^{2}}}\times \dfrac{7}{22}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\dfrac{{{11}^{3}}}{2\times 14\times 22}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=2.16\text{cm}$
Therefore the rise in the level of water is 2.16cm.
18. A circular tank of diameter 2m is dug and the earth removed is spread uniformly all around the tank to form an embankment 2m in width and 1.6m in height. Find the depth of the circular tank.
Ans: Let us consider the depth of the circular tank be h.
Radius of the cylindrical tank, $\text{r}=\dfrac{2}{2}=1\text{m}$
Volume of the cylindrical tank, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{(1)}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ h }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Radius of the outer surface, $\text{R}=2+1=3\text{m}$
Volume of the embankment$=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{2}}\text{H}-\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{H}$
$=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ H}\left( {{\text{R}}^{2}}-{{\text{r}}^{2}} \right)$
$=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times 1.6\left( {{3}^{2}}-{{1}^{2}} \right)$
$=12.8\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of tank = Volume of embankment
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ h }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{3}}=12.8\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=12.8\text{m}$
Therefore the depth of the circular tank is 12.8m.
19. The sum of the inner and outer curved surfaces of a hollow metallic cylinder is $1056\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{2}}$and the volume of the material in it is $1056\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{3}}.$ Find its internal and external radii. Given that the height of the cylinder is 21cm.
Ans: According to the question, the sum of the inner and outer curved surface of a hollow metallic cylinder is $1056\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
\[\text{2 }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ Rh+2 }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rh=1056}\]
\[\Rightarrow 2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 21\times \left( R+r \right)=1056\]
$\Rightarrow R+r=\dfrac{1056}{132}$
$\Rightarrow {R+r}=8$-------(1)
Given the volume of the material as $1056\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{R}^{2}}h-\Pi {{r}^{2}}h=1056$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{22}{7}\times 21\times \left( {{R}^{2}}-{{r}^{2}} \right)=1056$
$\Rightarrow {{R}^{2}}-{{r}^{2}}=\dfrac{1056}{66}$
$\Rightarrow \left( R+r \right)\left( R-r \right)=16$
From (1)
$\Rightarrow R-r=2$-------(2)
Solving (1) and (2), we get
R=5 and r=3
Therefore the internal and external radii of the cylinder is 3cm and 5cm respectively.
20. The difference between the outer curved surface area and the inner curved surface area of a hollow cylinder is $352\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{2}}.$ If its height is 28cm and the volume of the material in it is $704\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{3}};$find its external curved surface area.
Ans: Let the inner and outer radius of the cylinder be r and R.
According to the question, The difference between the outer and the inner surface area of a cylinder is $352\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
$\Rightarrow 2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ Rh}-2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rh}=352$
$\Rightarrow 2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 28\times \left( \text{R}-\text{r} \right)=352$
$\Rightarrow \text{R}-\text{r}=\dfrac{352\times 7}{44\times 28}$
$\Rightarrow \text{R}-\text{r}=2$-------(1)
Also given that the volume of the material is $704\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{2}}\text{h}-\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}=704$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{22}{7}\times 28\times \left( {{\text{R}}^{2}}-{{\text{r}}^{2}} \right)=704$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{R}+\text{r} \right)\left( \text{R}-\text{r} \right)=\dfrac{704}{88}$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{R}+\text{r} \right)\left( \text{R}-\text{r} \right)=8$
From (1)
$\Rightarrow \text{R}+\text{r}=4$-------(2)
Solving (1) and (2), we get
R=3 and r=1
External curved surface area of the cylinder, $\text{C}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ Rh}$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 3\times 28$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=2\times 22\times 3\times 4$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=528\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore, the external curved surface area of the hollow cylinder is $528\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
21. The sum of the height and the radius of a solid cylinder is 35cm and its total surface area is 3080$\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{2}};$find the volume of the cylinder.
Ans: Let the radius and height be r and h respectively.
From the question, we know that $\text{r}+\text{h}=35$-------(1)
Also given the total surface area of the cylinder as $3080\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow 2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}\left( \text{h}+\text{r} \right)=3080$
$\Rightarrow 2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times \mathbf{r}=\dfrac{3080}{35}$
$\Rightarrow \mathbf{r}=\dfrac{3080\times 7}{2\times 22\times 35}$
$\Rightarrow \mathbf{r}=14$
Substitute r value in (1), we get
$\Rightarrow 14+\text{h}=35$
$\Rightarrow \mathbf{h}=21$
We know that volume of cylinder, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \mathbf{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{14}^{2}}\times 21$
$\Rightarrow \mathbf{V}=22\times {{14}^{2}}\times 3$
$\Rightarrow \mathbf{V}=12936\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the volume of the cylinder is $12936\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
22. The total surface area of a solid cylinder is $616{{\mathbf{m}}^{2}}.$ If the ratio between its curved surface area and total surface area is 2:1; find the volume of the cylinder.
Ans: Let us consider the radius and height of the cylinder is r and h.
Given the total surface area of cylinder as $616{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow 2\mathbf{\Pi r}\left( \mathbf{h}+\mathbf{r} \right)=616$-------(1)
Curved surface area of cylinder, $\text{C}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rh}$
Also given that the ratio between the curved surface area and total surface area as 1:2
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}\left( \text{h}+\text{r} \right)}{2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rh}}=\dfrac{2}{1}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{h}+\text{r}}{\text{h}}=\dfrac{2}{1}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}+\text{r}=2\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\text{r}$
Substitute h value in (1)
$\Rightarrow 2\mathbf{\Pi r}\left( \mathbf{r}+\mathbf{r} \right)=616$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}\left( 2{{\text{r}}^{2}} \right)=616\times \dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{7}{22}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}=49$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=7$
Volume of cylinder, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 7\times 7\times 7$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=1078\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
23. A cylindrical vessel of height 24cm and diameter 40cm is full of water. Find the exact number of small cylindrical bottles, each of height 10cm and diameter 8cm, which can be filled with this water.
Ans: Radius of the large cylindrical vessel, $\text{R}=\dfrac{40}{2}=20\text{cm}$
Volume of the the large cylindrical vessel, ${{\text{V}}_{1}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{2}}\text{H}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{1}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{20}^{2}}\times 24$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{1}}=9600\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Radius of the small cylindrical vessel, $\text{r}=\dfrac{8}{2}=4\text{cm}$
Volume of the the small cylindrical vessel, ${{\text{V}}_{2}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{H}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{2}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{4}^{2}}\times 10$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{2}}=160\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
The number of small cylindrical vessels which can be filled is
$=\dfrac{9600\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{160\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}$
$=60$
Therefore, 60 small cylinders can be filled.
24. Two solid cylinders, one with diameter 60cm and height 30cm and the other with radius 30cm and height 60cm, are melted and recasted into a third solid cylinder of height 10cm. Find the diameter of the cylinder formed.
Ans: Radius of first cylinder, ${{\text{r}}_{1}}=\dfrac{60}{2}=30\text{cm}$
Volume of first cylinder, ${{\text{V}}_{1}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{2}{{\text{h}}_{1}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{1}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{30}^{2}}\times 30$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{1}}=27000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }$
Radius of second cylinder, ${{\text{r}}_{2}}=\dfrac{60}{2}=30\text{cm}$
Volume of second cylinder, ${{\text{V}}_{2}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{2}{{\text{h}}_{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{2}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{30}^{2}}\times 60$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{2}}=54000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }$
Volume of the new cylinder, $\text{V}={{\text{V}}_{1}}+{{\text{V}}_{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}=27000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }+54000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }$
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\times 10=81000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}=8100$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=90\text{cm}$
$\Rightarrow \text{d}=2\text{r}=180\text{cm}$
Therefore, the diameter of the cylinder formed is 180cm.
25. The total surface area of a hollow cylinder, which is open from both the sides, is $3575\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{2}};$area of its base ring is $357.5\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{2}}$ and its height is 14cm. Find the thickness of the cylinder.
Ans: Let the inner and outer radius of the cylinder be r and R.
Let the thickness be $\text{t}=\text{R}-\text{r}$
Total surface area of the hollow cylinder$=3575\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow 2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ Rh}+2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rh}+2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\left( {{\text{R}}^{2}}-{{\text{r}}^{2}} \right)=3575$
$\Rightarrow 2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ h}\left( \text{R}+\text{r} \right)+2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\left( \text{R}+\text{r} \right)\left( \text{R}-\text{r} \right)=3575$
$\Rightarrow 2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\left( \text{R}+\text{r} \right)\left[ \text{h}+\text{R}-\text{r} \right]=3575$
$\Rightarrow 2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\left( \text{R}+\text{r} \right)\left[ 14+\text{t} \right]=3575$-------(1)
Area of base ring$=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\left( {{\text{R}}^{2}}-{{\text{r}}^{2}} \right)=357.5\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\left( \text{R}+\text{r} \right)\left( \text{R}-\text{r} \right)=357.5$-------(2)
Dividing (1) by (2)
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\left( \text{R}+\text{r} \right)\left[ 14+\text{t} \right]}{\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\left( \text{R}+\text{r} \right)\left( \text{R}-\text{r} \right)}=\dfrac{3575}{357.5}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{2\left( 14+\text{t} \right)}{\text{t}}=10$
$\Rightarrow 28+2\text{t}=10\text{t}$
$\Rightarrow 8\text{t}=28$
$\Rightarrow \text{t}=\dfrac{7}{2}=3.5$
Therefore the thickness of the cylinder is 3.5cm.
26. The given figure shows a solid formed of a solid cube of side 40cm and a solid cylinder of radius 20cm and height 50cm attached to the cube as shown. Find the volume and the total surface area of the whole solid.(Take $\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }=3.14$)
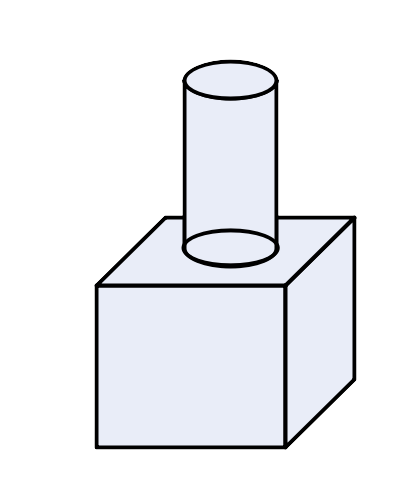
Ans: Volume of cube, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}={{\text{l}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}={{40}^{3}}=64000\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of solid, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{s}}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{s}}}=3.14\times {{20}^{2}}\times 50$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{s}}}=62800\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Total volume of solid, $\text{V}={{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}+{{\text{V}}_{\text{s}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=64000+62800=126800\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Total surface area of solid, $\text{S}=6{{\text{l}}^{2}}+2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rh}$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}=6\times {{40}^{2}}+2\times 3.14\times 20\times 50$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}=9600+6280$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}=15880\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the total volume of the solid is $126800\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$and the total surface area of the solid is $15880\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
27. Two right circular solid cylinders have radii in the ratio 3:5 and heights in the ratio 2:3. Find the ratio between their:
Curved Surface Areas
Ans: Let the radii of the two cylinders be ${{\text{r}}_{1}}$and ${{\text{r}}_{2}}$
Let the heights of the two cylinders be ${{\text{h}}_{1}}$and ${{\text{h}}_{2}}$
Given in the question, ratio between their radii is 3:5
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{r}}_{1}}}{{{\text{r}}_{2}}}=\dfrac{3}{5}$
ratio between their heights is 2:3
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{h}}_{1}}}{{{\text{h}}_{2}}}=\dfrac{2}{3}$
Curved surface area of cylinder is $2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rh}$
Ratio between the curves surface area is
$=\dfrac{2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}{{\text{h}}_{1}}}{2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{2}}{{\text{h}}_{2}}}$
$=\dfrac{{{\text{r}}_{1}}}{{{\text{r}}_{2}}}\times \dfrac{{{\text{h}}_{1}}}{{{\text{h}}_{2}}}$
$=\dfrac{3}{5}\times \dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{2}{5}$
Volumes
Ans: Ratio between their volumes is
$=\dfrac{2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{2}{{\text{h}}_{1}}}{2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{2}{{\text{h}}_{2}}}$
$={{(\dfrac{{{\text{r}}_{1}}}{{{\text{r}}_{2}}})}^{2}}\times \dfrac{{{\text{h}}_{1}}}{{{\text{h}}_{2}}}$
$={{(\dfrac{3}{5})}^{2}}\times \dfrac{2}{3}$
$=\dfrac{6}{25}$
Therefore, the ratio of their curved surface area and volume is 2:5 and 6:25 respectively.
28. A closed cylindrical tank, made of thin iron sheet, has diameter 8.4m and height 5.4m. How much metal sheet, to the nearest ${{\mathbf{m}}^{2}},$is used in making this tank, if $\dfrac{1}{15}$of the sheet actually used was wasted in making the tank?
Ans: Radius of the cylindrical tank, $\text{r}=\dfrac{8.4}{2}=4.2\text{m}$
Total surface area of the cylindrical tank$=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}\left( \text{h}+\text{r} \right)$
$=2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 4.2\left( 5.4+4.2 \right)$
$=44\times 0.6\times 9.6$
$=253.44{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Area of sheet wasted in making the tank
$=\dfrac{1}{15}\times 253.44$
$=16.896{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Total metal sheet required$=253.44+16.896=270.336$
Therefore $271{{\text{m}}^{2}}$of metal sheet is required in making the tank.
Exercise 20B
1. Find the volume of a cone whose slant height is 17cm and radius of base is 8cm.
Ans: Slant height of the cone is given by ${{\text{l}}^{2}}={{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\sqrt{{{\text{l}}^{2}}-{{\text{r}}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\sqrt{{{17}^{2}}-{{8}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\sqrt{289-64}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=15\text{cm}$
Volume of cone, $\text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{8}^{2}}\times 15$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=1005.7\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the volume of the cone is $1005.7\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
2. The curved surface area of a cone is $12320\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{2}}.$ If the radius of its base is $56\mathbf{cm},$find its height.
Ans: Given the curved surface area
We know that curved surface area of a cone as $\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rl}$
$\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rl}=12320$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=12320\times \dfrac{7}{22}\times \dfrac{1}{56}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=70\text{cm}$
We know that slant height of cone, ${{\text{l}}^{2}}={{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{70}^{2}}={{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{56}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{h}}^{2}}=4900-3136$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{h}}^{2}}=1764$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=42$
Therefore, the height of the cone is 42cm.
3. The circumference of the base of a 12m high conical tent is 66m. Find the volume of the air contained in it.
Ans: Given the circumference of a cone as 66m
$\Rightarrow 2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}=66$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=66\times \dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{7}{22}$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=10.5\text{m}$
Volume of the air contained in a cone is equal to the volume of the cone
Volume of cone, $\text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{21}{2}\times \dfrac{21}{2}\times 12$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=11\times 21\times 6$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=1386{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the volume of the air contained in a conical tent is $1386{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
4. The radius and the height of a right circular cone are in the ratio $5:12$and its volume is $2512~\mathbf{cubic}~\mathbf{cm}.$Find the radius and slant height of the cone.(Take $\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }=3.14)$
Ans: Given in the question that the ratio between radius and height is 5:12
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{r}}{\text{h}}=\dfrac{5}{12}$
Let us consider the radius and height be $5\text{x}$ and $12\text{x}$
We know that the slant height of the cone, ${{\text{l}}^{2}}={{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{{{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{{{(12\text{x})}^{2}}+{{(5\text{x})}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{144{{\text{x}}^{2}}+25{{\text{x}}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{169{{\text{x}}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=13\text{x}$
Given the volume of the cone is $2512{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}=2512$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{(5\text{x})}^{2}}\times 12\text{x}=2512$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{3}}=2512\times 3\times \dfrac{7}{22}\times \dfrac{1}{25}\times \dfrac{1}{12}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{x}}^{3}}\simeq 8$
$\Rightarrow \text{x}=2$
Radius of the right circular cone$=5\text{x}=10\text{m}$
Slant height of the right circular cone$=13\text{x}=26\text{m}$
Therefore, the radius and slant height of the right circular cone are 10m and 26m respectively.
5. Two right circular cones x and y are made. x having three times the radius of y and y having half the volume of x. Calculate the ratio between the heights of x and y.
Ans: Let the radius of the circular cone y be r
Then the radius of x will be 3r(given in question)
Let the volume of the circular cone x be V
Then the volume of y will be $\dfrac{\text{V}}{2}$
Let the height of cone x and y be ${{\text{h}}_{\text{x}}}$and ${{\text{h}}_{\text{y}}}$ respectively.
Volume of the cone, $\text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
Volume of cone x, $\text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{(3\text{r})}^{2}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{x}}}\Rightarrow {{\text{h}}_{\text{x}}}=\dfrac{3\text{V}}{\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }9{{\text{r}}^{2}}}$
Volume of cone y, $\dfrac{\text{V}}{2}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}{{\text{h}}_{\text{y}}}\Rightarrow {{\text{h}}_{\text{y}}}=\dfrac{3\text{V}}{2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}}$
Ratio of the heights of cones is $\dfrac{{{\text{h}}_{\text{x}}}}{{{\text{h}}_{\text{y}}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{h}}_{\text{x}}}}{{{\text{h}}_{\text{y}}}}=\dfrac{3\text{V}}{9\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}}\times \dfrac{2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}}{3\text{V}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{h}}_{\text{x}}}}{{{\text{h}}_{\text{y}}}}=\dfrac{2}{9}$
Thus, the ratio of height of cone x and cone y is 2:9.
6. The diameters of two cones are equal. If their slant heights are in the ratio 5:4, find the ratio of their curved surface areas.
Ans: Given the diameter of two cones as equal which means their radius will also be equal and let the radius be r.
Given the ratio of slant heights of the cones as 5:4
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{l}}_{1}}}{{{\text{l}}_{2}}}=\dfrac{5}{4}$
Let the slant heights be $5\text{x}$ and $4\text{x}$
Curved surface area of the first cone$=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}{{\text{l}}_{1}}$
Curved surface area of the second cone$=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}{{\text{l}}_{2}}$
Dividing the curved surface area of the first cone by second cone we get
$=\dfrac{\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}{{\text{l}}_{1}}}{\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}{{\text{l}}_{2}}}=\dfrac{{{\text{l}}_{1}}}{{{\text{l}}_{2}}}=\dfrac{5}{4}$
Therefore the ratio of the curved surface area is equal to the ratio of their slant height which is equal to 5:4.
7. There are two cones. The curved surface area of one is twice that of the other. The slant height of the latter is twice that of the former. Find the ratio of their radii.
Ans: Let the slant height of the second cone be l.
According to the question, the slant height of the first cone is twice that of the second cone which is equal to 2l.
Let the curved surface area of the first cone be C.
Curved surface area of the second cone will be twice that of the first cone which is 2C.
Curved surface area of first cone, $\text{C}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}\left( 2\text{l} \right)$
Curved surface area of second cone, $\text{C}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{2}}\text{l}$
Curved surface area of first cone is twice that of the second cone
$\Rightarrow 2\left( \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}\left( 2\text{l} \right) \right)=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{2}}\text{l}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{r}}_{1}}}{{{\text{r}}_{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{4}$
Therefore, the ratio of the first and second cone is 1:4.
8. A heap of wheat is in the form of a cone of diameter 16.8m and height 3.5m. Find its volume. How much cloth is required to just cover the heap.
Ans: Given diameter of cone$=16.8\text{m}$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=\dfrac{\text{d}}{2}=\dfrac{16.8}{2}=8.4\text{m}$
Given height, $\text{h}=3.5\text{m}$
Volume of cone, $\text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{8.4}^{2}}\times 3.5$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=22\times 8.4\times 2.8\times 0.5$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=258.72{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Slant height of the cone, ${{\text{l}}^{2}}={{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{{{3.5}^{2}}+{{8.4}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{82.81}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=9.1\text{m}$
Amount of cloth required to cover the heap is nothing but the curved surface area of the cone.
Curved surface area of the cone, $\text{C}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rl}$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 8.4\times 9.1$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=22\times 1.2\times 9.1$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=240.24{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the volume of the cone is $258.72{{\text{m}}^{3}}$ and the amount of cloth required to cover the heap is $240.24{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
9. Find what length of canvas, 1.5m in width, is required to make a conical tent 48m in diameter and 7m in height? Given that 10% of the canvas is used in folds and stitchings. Also, find the cost of the canvas at the rate of 24rs per meter.
Ans: Given the diameter of the tent, $\text{d}=48\text{m}$
Therefore radius of the tent, $\text{r}=\dfrac{\text{d}}{2}=\dfrac{48}{2}=24\text{m}$
Slant height of the cone, ${{\text{l}}^{2}}={{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{{{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{{{7}^{2}}+{{24}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{625}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=25\text{m}$
Curved surface area of the cone, $\text{C}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rl}$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 24\times 25$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=\dfrac{13200}{7}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
According to the question, 10% of the canvas is used in folds and stitching
$=10\text{ }\!\!%\!\!\text{ }\times \dfrac{13200}{7}=\dfrac{1320}{7}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Total canvas required to make conical tent$=\dfrac{13200}{7}+\dfrac{1320}{7}=\dfrac{14520}{7}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Area of the canvas, $\text{l}\times \text{b}=\dfrac{14520}{7}$
$\Rightarrow \text{b}=\dfrac{14520}{7\times 1.5}$
$\Rightarrow \text{b}=\dfrac{9680}{7}$
$\Rightarrow \text{b}=1382.86\text{m}$
Cost of the canvas$=1382.86\times 24=33188.64$
Therefore the cost of the canvas is 33188.64 rupees.
10. A solid cone of height 8cm and base radius 6cm is melted and recast into identical cones, each of height 2cm and diameter 1cm. Find the number of cones formed.
Ans: We know that volume of cone, $\text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{6}^{2}}\times 8$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times 8\times 12$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=96\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Given diameter of small cones as 1cm
Radius, $\text{r }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{\text{d}}{2}=\dfrac{1}{2}\text{cm}$
Volume of small cones, $\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}{{\text{ }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{\left( \dfrac{1}{2} \right)}^{2}}\times 2$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{6}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Number of small cones formed$=\dfrac{96\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{\dfrac{\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{6}}$
$=96\times 6=576$
Therefore, the total number of small cones formed is 576.
11. The total surface area of a right circular cone of slant height 13cm is $90\mathbf{\Pi c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{2}}.$ Calculate
Its Radius in cm
Ans: Given the total surface area as $90\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
We know that total surface area of a right circular cone is $\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}\left( \text{l}+\text{r} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}\left( \text{l}+\text{r} \right)=90\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}\left( 13+\text{r} \right)=90$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}+13\text{r}-90=0$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}+18\text{r}-5\text{r}-90=0$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}\left( \text{r}+18 \right)-5\left( \text{r}+18 \right)=0$
$\Rightarrow \left( \text{r}-5 \right)\left( \text{r}+18 \right)=0$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=5\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ or }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }-18$
We know that radius cannot be negative, so the radius of the right circular cone is 5.
Slant height of the cone, ${{\text{l}}^{2}}={{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{13}^{2}}={{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{5}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{h}}^{2}}=169-25$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{h}}^{2}}=144$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=12$cm
Its volume in cm(take $\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }=3.14$)
Ans: Volume of the right circular cone, $\text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times 3.14\times {{5}^{2}}\times 12$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=3.14\times 25\times 4$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=314\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the radius and the volume of the right circular cone is $5\text{cm}$ and $314\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$ respectively.
12. The area of the base of a conical solid is $38.5\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{2}}$ and its volume is $154\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{3}}.$ Find the curved surface area of the solid.
Ans: Given the area of the base of the conical solid as $38.5\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
We know that area of the bases of the conical solid is $\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}=38.5$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}=38.5\times \dfrac{7}{22}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}=12.25$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=3.5\text{cm}$
Also given the volume of the cone as $154\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of cone, $\text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow 154=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{(3.5)}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=154\times 3\times \dfrac{7}{22}\times \dfrac{1}{3.5\times 3.5}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=7\times 3\times 2\times \dfrac{1}{3.5}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=12\text{cm}$
Slant height of the cone, ${{\text{l}}^{2}}={{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{l}}^{2}}={{12}^{2}}+{{3.5}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{l}}^{2}}=144+12.25$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{l}}^{2}}=156.25$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=12.5\text{cm}$
Curved surface area of the solid, $\text{C}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rl}$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 3.5\times 12.5$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=11\times 12.5$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=137.5\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the curved surface area of the solid is $137.5\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
13. A vessel, in the form of an inverted cone, is filled with water to the brim. Its height is 32cm and diameter of the base is 25.2cm. Six equal solid cones are dropped in it, so that they are fully submerged. As a result, one-fourth of water in the original cone overflows. What is the volume of each of the solid cones submerged?
Ans: Given the diameter of the base is 25.2cm
Radius, $\text{r}=\dfrac{\text{d}}{2}=\dfrac{25.2}{2}=12.6\text{cm}$
Volume of the water in conical vessel, $\text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{12.6}^{2}}\times 32$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=5322.24\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Given in the question that one fourth of water overflows on submerging six equal solid cones. So the new volume is
$\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{4}\times 5322.24$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=1330.56\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of each cone, $\text{V}''=\dfrac{1}{6}\times \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}''=\dfrac{1}{6}\times 1330.56$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}''=221.76\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore, the volume of each of the solid cone is $221.76\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
14. The volume of a conical tent is $1232{{\mathbf{m}}^{3}}$ and the area of the base floor is $154{{\mathbf{m}}^{2}}$. Calculate the
Radius of the floor,
Ans: Given the area of the base of the conical tent as $154{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
We know that area of the base of conical tent$=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}=154$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}=154\times \dfrac{7}{22}$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=7\text{m}$
Therefore the radius of the floor is 7m.
Height of the tent,
Ans: Given the volume of cone as $1232{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
We know that volume of cone, $\text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}=1232$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=1232\times 3\times \dfrac{7}{22}\times \dfrac{1}{{{7}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\dfrac{56\times 3}{7}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=24\text{m}$
Therefore the height of the tent is 24m.
Length of the canvas required to cover this conical tent if its width is 2m
Ans: Slant height of the cone, ${{\text{l}}^{2}}={{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{l}}^{2}}={{24}^{2}}+{{7}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{l}}^{2}}=576+49$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{l}}^{2}}=625$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=25\text{m}$
Let $\text{l }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }$ be the length and $\text{l}$ is the slant height
Area of the canvas, $\text{A}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rl}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }\times \text{b}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 7\times 25$
$\Rightarrow \text{l }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{22\times 25}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=275\text{m}$
Therefore, the length of canvas required is 275m.
Exercise 20C
1. The surface area of the sphere is $2464\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{2}},$ find its volume.
Ans: We know that surface area of sphere, $\text{A}=4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow 4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}=2464$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}=2464\times \dfrac{1}{4}\times \dfrac{7}{22}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}=28\times 7$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}=196$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=14$
Volume of sphere, $\text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{14}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4\times 22\times 2\times 14\times 14}{3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=11498.66\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
2. The volume of the sphere is $38808\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{3}};$ find its diameter and the surface area.
Ans: Volume of sphere, $\text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow 38808=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{3}}=\dfrac{38808\times 3\times 7}{4\times 22}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{3}}=9261$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=21\text{cm}$
Diameter of sphere$=2\text{r}=2\times 21=42\text{cm}$
Surface area of sphere$=4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$=4\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{21}^{2}}$
$=4\times 22\times 3\times 21$
$=5544\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the diameter of sphere is $42\text{cm}$ and surface area of sphere is $5544\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
3. A spherical ball of lead has been melted and made into identical smaller balls with radius equal to half the radius of the original one. How many such balls can be made?
Ans: Volume of spherical ball, $\text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
According to the given question, the radius of the smaller ball is half the radius of the original ball.
Let the radius of the original ball be r.
Radius of the smaller ball be $\text{r }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{\text{r}}{2}$
Volume of the smaller spherical ball, $\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}{{\text{ }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{(\dfrac{\text{r}}{2})}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}}{6}$
Number of smaller balls formed from the bigger ball $=\dfrac{\text{V}}{\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}$
$=\dfrac{4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}}{3}\times \dfrac{6}{\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}}$
$=\dfrac{4\times 6}{3}=8$
Therefore, the total number of small balls that can be formed are 8.
4. How many balls each of radius 1cm can be made by melting a bigger ball whose diameter is 8cm?
Ans: Given the diameter of the bigger ball as 8cm
Radius of the bigger ball, $\text{r}=\dfrac{\text{d}}{2}=\dfrac{8}{2}=4\text{cm}$
Volume of the bigger ball, $\text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{4}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{256\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of smaller ball, $\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{1}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Total number of balls that can be formed from the bigger ball$=\dfrac{\text{V}}{\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}$
$=\dfrac{256\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\times \dfrac{3}{4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}$
$=64$
Therefore, 64 smaller balls can be formed from the bigger ball.
5. Eight metallic spheres; each of radius 2 mm, and melted and cast into a single sphere. Calculate the radius of the new sphere.
Ans: Given the radius of metallic sphere as 2mm$=\dfrac{2}{10}\text{cm}$
Volume of one small sphere, $\text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{\left( \dfrac{1}{5} \right)}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{375}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of 8 spheres, $\text{V}=8\times \dfrac{4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{375}=\dfrac{32\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{375}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Let the radius of the single big sphere be R
Volume of new sphere, $\text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{3}}$
Here volume of 8 spheres is equal to the volume of new sphere
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{32\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{375}=\dfrac{4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{3}}}{3}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{R}}^{3}}=\dfrac{32\times 3}{375\times 4}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{R}}^{3}}=\dfrac{8}{125}$
$\Rightarrow \text{R}=\dfrac{2}{5}=0.4\text{cm}=4\text{mm}$
Therefore the radius of the new sphere is 4mm.
6. The volume of one sphere is 27 times that of another sphere. Calculate the ratio of their
Radii
Ans: Let the radius of the first sphere be ${{\text{r}}_{1}}$ and the radius of the second sphere be ${{\text{r}}_{2}}.$
Volume of the first sphere, ${{\text{V}}_{1}}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{3}$
Volume of the second sphere, ${{\text{V}}_{2}}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{3}$
(i) According to the question volume of one sphere is 27 times the other
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{3}=27\times \dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{3}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}_{1}}^{3}=27{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{3}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}_{1}}=3{{\text{r}}_{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{r}}_{1}}}{{{\text{r}}_{2}}}=\dfrac{3}{1}$
Therefore the ratio of their radii is 3:1.
Surface Areas
Ans: Surface area of first sphere, ${{\text{A}}_{1}}=4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{2}$
Surface area of second sphere, ${{\text{A}}_{2}}=4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{2}$
Ratio of their surface area$=\dfrac{4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{2}}{4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{2}}$
$=\dfrac{{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{2}}{{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{2}}={{(\dfrac{3}{1})}^{2}}=\dfrac{9}{1}$
Therefore the ratio of their surface areas is 9:1.
7. If the number of square centimeters on the surface of a sphere is equal to the number of cubic centimeters in its volume, what is the diameter of the sphere?
Ans: Let the radius of the sphere be r.
Surface area of the sphere$=4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
Volume of spherical ball, $\text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
Given in the question that the number of square centimeters on the surface of the sphere is equal to the number of cubic centimeters in its volume.
$\Rightarrow 4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow 3=\dfrac{{{\text{r}}^{3}}}{{{\text{r}}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=3\text{cm}$
We know that diameter, $\text{d}=2\text{r}$
$\Rightarrow \text{d}=2\times 3$
$\Rightarrow \text{d}=6\text{cm}$
Therefore the diameter of the sphere is 6cm.
8. A solid metal sphere is cut through its center into 2 equal parts. If the diameter of the sphere is $3\dfrac{1}{2}\mathbf{cm},$ find the total surface area of each part correct to two decimal places.
Ans: Given the diameter of the sphere as $3\dfrac{1}{2}\text{cm}$
Radius, $\text{r}=\dfrac{\text{d}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=\dfrac{\dfrac{7}{2}}{2}=\dfrac{7}{4}\text{cm}$
Given in the question that the solid metal sphere is cut through its center which means both the parts of the sphere are equal which forms two hemispheres of equal radius.
Total surface area of each hemisphere, $\text{A}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}+\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=3\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=3\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{7}{4}\times \dfrac{7}{4}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=\dfrac{3\times 11\times 7}{2\times 4}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=28.88\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the total surface area of each hemisphere is $28.88\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
9. The internal and external diameters of a hollow hemispherical vessel are 21cm and 28cm respectively. Find
Internal curved surface area
Ans: Given the external diameter as 28cm
External radius, $\text{R}=\dfrac{28}{2}=14\text{cm}$
Given the internal diameter as 21cm
Internal radius, $\text{r}=\dfrac{21}{2}=10.5\text{cm}$
(i) Internal curved surface area, ${{\text{A}}_{\text{i}}}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{A}}_{\text{i}}}=2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 10.5\times 10.5$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{A}}_{\text{i}}}=3\times 22\times 10.5$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{A}}_{\text{i}}}=693\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the internal curved surface area of the hemispherical vessel is $693\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
External Curved surface area
Ans: External curved surface area, ${{\text{A}}_{\text{e}}}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{A}}_{\text{e}}}=2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 14\times 14$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{A}}_{\text{e}}}=2\times 22\times 2\times 14$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{A}}_{\text{e}}}=1232\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the external curved surface area of the hemispherical vessel is $1232\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
Total Surface Area
Ans: Total surface area of hemispherical vessel, $\text{A}={{\text{A}}_{\text{i}}}+{{\text{A}}_{\text{e}}}+\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\left( {{\text{R}}^{2}}-{{\text{r}}^{2}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=693+1232+\dfrac{22}{7}\left( {{14}^{2}}-{{10.5}^{2}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=1925+\dfrac{22}{7}\left( 196-110.25 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=1925+\dfrac{22}{7}\left( 85.75 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=1925+269.5$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=2194.5\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the total surface area is $2194.5\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
Volume of Material of the Vessel
Ans: Volume of the material of the vessel, $\text{V}=\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\left( {{\text{R}}^{3}}-{{\text{r}}^{3}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{2}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times \left( {{14}^{2}}-{{10.5}^{2}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{2}{3}\times 269.5$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=179.67\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the volume of the material of the vessel is $179.67\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
10. A solid sphere and a solid hemisphere have the same total surface area. Find the ratio between their volumes.
Ans: Let the radius of sphere and hemisphere be ${{\text{r}}_{1}}$ and ${{\text{r}}_{2}}.$
Total surface area of sphere $=4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{2}$
Total surface area of hemisphere $=3\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{2}$
Given in the question that the total surface area of the sphere and hemisphere are equal.
$\Rightarrow 4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{2}=3\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{2}}{{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{2}}=\dfrac{3}{4}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{r}}_{1}}}{{{\text{r}}_{2}}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$
Volume of sphere $=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{3}$
Volume of hemisphere $=\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{3}$
Ratio between their volumes $=\dfrac{\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{3}}{\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{3}}$
$=\dfrac{2{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{3}}{{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{3}}$
$=2\times {{(\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2})}^{3}}$
$=2\times \dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{8}=\dfrac{3\sqrt{3}}{4}$
Therefore the ratio of volume of the volumes of sphere and hemisphere is $3\sqrt{3}:4.$
11. Metallic spheres of radii 6cm, 8cm and 10cm respectively are melted and recast into a single solid sphere. Take $\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }=3.1,$ find the surface area of the solid sphere formed.
Ans: Let the radius of the new sphere be R.
Volume of the new sphere=Sum of volumes of all spheres
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{3}}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{3}+\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{3}+\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{3}}^{3}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{R}}^{3}}={{\text{r}}_{1}}^{3}+{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{3}+{{\text{r}}_{3}}^{3}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{R}}^{3}}={{6}^{3}}+{{8}^{3}}+{{10}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{R}}^{3}}=216+512+1000$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{R}}^{3}}=1728$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{R}}^{3}}={{12}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{R}=12\text{cm}$
Surface area of the new sphere$=4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{2}}$
$=4\times 3.1\times 12\times 12$
$=1785.6\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore, the surface area of the solid sphere is $1785.6\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
12. The surface area of a solid sphere is increased by 21% without changing its shape. Find the percentage increase in its
Radius
Ans: Let the radius of the sphere be $\text{r}$ and the new radius be ${{\text{r}}_{1}}.$
(i) Total surface area of sphere $=4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
Given in the question that the total surface area of sphere is
$\Rightarrow 4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{2}=4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}+\dfrac{21}{100}\times 4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow 4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{2}=\dfrac{121}{100}\times 4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}_{1}}^{2}=\dfrac{121{{\text{r}}^{2}}}{100}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}_{1}}=\dfrac{11\text{r}}{10}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}_{1}}=\text{r}+\dfrac{\text{r}}{10}$
Therefore the change in the radius of sphere is $\dfrac{\text{r}}{10}.$
Percentage change in radius $=\dfrac{\dfrac{\text{r}}{10}}{\text{r}}\times 100$
$=10\text{ }\!\!%\!\!\text{ }$
Therefore the percentage change in radius is 10%.
Volume
Ans: Volume of sphere, $\text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
Radius of the new sphere is increased by 10%.
${{\text{r}}_{1}}=\dfrac{11\text{r}}{10}$
New volume of the sphere will be
${{\text{V}}_{1}}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{3}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{1}}=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{(\dfrac{11}{10}\text{r})}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{1}}={{(\dfrac{11}{10})}^{3}}\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{1}}=\dfrac{1331}{1000}\text{V}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{1}}=\text{V}+\dfrac{331}{1000}\text{V}$
Percentage change in volume $=\dfrac{\dfrac{331\text{V}}{1000}}{\text{V}}\times 100$
$=\dfrac{331}{1000}\times 100$
$=33.1\text{ }\!\!%\!\!\text{ }$
Therefore the percentage change in volume is 33.1%.
Exercise 20D
1. A solid sphere of radius 15cm is melted and recast into solid right circular cones of radius 2.5cm and height 8cm. Calculate the number of cones recast.
Ans: Volume of solid sphere, $\text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{15}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=4500\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of each cone, $\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{2}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{2.5}^{2}}\times 8$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{50\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Number of cones recasted $=\dfrac{\text{V}}{\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}$
$=\dfrac{4500\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{\dfrac{50\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}}$
$=90\times 3=270$
Therefore the number of cones that can be recast is 270.
2. A hollow sphere of internal and external diameters 4cm and 8cm respectively is melted into a cone of base diameter 8cm. Find the height of the cone.
Ans: External radius of sphere, $\text{R}=\dfrac{8}{2}=4\text{cm}$
Internal radius of sphere, $\text{r}=\dfrac{4}{2}=2\text{cm}$
Volume of metal used in hollow sphere $=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\left( {{\text{R}}^{3}}-{{\text{r}}^{3}} \right)$
$=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\left( {{4}^{3}}-{{2}^{3}} \right)$
$=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\left( 64-8 \right)$
$=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 56$
$=\dfrac{704}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Radius of cone, $\text{r }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{8}{2}=4\text{cm}$
Let the height of the cone is h.
Volume of cone, $\text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 4\times 4\times \text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{352\text{h}}{21}$
We know that volume of cone is equal to volume of metal used in hollow sphere
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{352\text{h}}{21}=\dfrac{704}{3}$
$\Rightarrow 352\text{h}=4928$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=14\text{cm}$
Therefore the height of the cone is 14cm.
3. The radii of the internal and external surfaces of a metallic spherical shell are 3cm and 5cm respectively. It is melted and recast into a solid right circular cone of height 32cm. Find the diameter of the base of the cone.
Ans: Volume of spherical shell, $\text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\left( {{\text{R}}^{3}}-{{\text{r}}^{3}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times \left( {{5}^{3}}-{{3}^{3}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times 98$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{392\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Let the radius of the circular cone be $\text{r }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }$
Volume of cone, $\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}{{\text{ }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times \text{r}{{\text{ }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}^{2}}\times 32$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{32}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}{{\text{ }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}^{2}}$
Given in the question that $\text{V}=\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{32}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}{{\text{ }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}^{2}}=\dfrac{392\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}$
$\Rightarrow 32\text{r}{{\text{ }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}^{2}}=392$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}{{\text{ }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}^{2}}=12.25$
$\Rightarrow \text{r }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=3.5\text{cm}$
Diameter of the cone, $\text{d }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=2\text{r }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }$
$\Rightarrow \text{d }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=2\left( 3.5 \right)=7\text{cm}$
Therefore the diameter of the cone is 7cm.
4. Total volume of three identical cones is the same as that of a bigger cone whose height is 9cm and diameter 40cm. Find the radius of the base of each smaller cone, if height of each is 108cm.
Ans: Let the radius of the smaller cone be $\text{r}$ and the radius of the bigger cone be $\text{R}.$
Radius of the bigger cone, $\text{R}=\dfrac{40}{2}=20\text{cm}$
Volume of bigger cone, $\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{2}}\text{h}{{\text{ }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}^{{}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{20}^{2}}\times 9$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=1200\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of the smaller cone, $\text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{\text{r}}^{2}}\times 108$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=36\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
According to the question, the volume of three smaller cones is equal to the volume of a bigger cone.
$\Rightarrow 3\text{V}=\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }$
$\Rightarrow 3\times 36\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{\text{r}}^{2}}=1200\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}=\dfrac{400}{36}$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=\dfrac{20}{6}$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=3.33\text{cm}$
Therefore the radius of base of each cone is 3.33cm.
5. A solid rectangular block of metal 49cm by 44cm by 18cm is melted and formed into a solid sphere. Calculate the radius of the sphere.
Ans: Volume of the solid rectangular block $=49\times 44\times 18=38808\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of sphere, $\text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{88}{21}{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
Given in the question that the volume of sphere is equal to the volume of the solid rectangular block
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{88}{21}{{\text{r}}^{3}}=38808$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{3}}=38808\times \dfrac{21}{88}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{3}}=9261$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=21\text{cm}$
Therefore, the radius of the sphere is 21cm.
6. A hemispherical bowl of internal radius 9cm is full of liquid. This liquid is to be filled into conical shaped small containers each of diameter 3cm and height 4cm. How many containers are necessary to empty the bowl?
Ans: Volume of hemispherical bowl, $\text{V}=\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \mathbf{V}=\dfrac{2}{3}\times \mathbf{\Pi }\times {{9}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \mathbf{V}=486\mathbf{\Pi c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{3}}$
Given the diameter of conical shaped container as 3cm
Then the radius, $\text{r }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{3}{2}\text{cm}$
Volume of the conical container, $\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}{{\text{ }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times \dfrac{3}{2}\times \dfrac{3}{2}\times 4$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=3\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Total number of containers $=\dfrac{\text{V}}{\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}$
$=\dfrac{486\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}$
$=162$
Therefore a total of 162 containers are required to empty the bowl.
7. A hemispherical bowl of diameter 7.2cm is filled completely with chocolate sauce. This sauce is poured into an inverted cone of radius 4.8cm. Find the height of the cone if it is completely filled.
Ans: Given the diameter of the hemispherical bowl as 7.2cm
Radius of the hemispherical bowl, $\text{r}=\dfrac{7.2}{2}=3.6\text{cm}$
Volume of chocolate sauce in hemispherical bowl, $\text{V}=\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{2}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{3.6}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=31.1\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }$
Volume of cone, $\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{4.8}^{2}}\times \text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=7.68\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ h}$
Now we know that the volume of cone is equal to the volume of chocolate sauce in hemispherical bowl
$\Rightarrow 7.68\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ h}=31.1\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\dfrac{31.1}{7.68}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=4.05\text{cm}$
Therefore the height of the cone when completely filled is 4.05cm.
8. A solid cone of radius 5cm and height 8cm is melted and made into small spheres of radius 0.5cm. Find the number of spheres formed.
Ans: Volume of cone, $\text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{5}^{2}}\times 8$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{200\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of one sphere, $\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}{{\text{ }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{0.5}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{6}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Number of sphere, $\text{n}=\dfrac{\text{V}}{\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=\dfrac{\dfrac{200\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}}{\dfrac{\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{6}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=\dfrac{200\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\times \dfrac{6}{\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=400$
Therefore a total of 400 spheres are formed.
9. The total area of a solid metallic sphere is $1256\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{2}}.$ It is melted and recast into solid right circular cones of radius 2.5cm and height 8cm. Calculate:
The radius of solid sphere,
Ans: We have to find the radius of solid sphere
Given the total area of a solid metallic sphere as $1256\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow 4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}=1256$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}=\dfrac{1256}{4\times 3.14}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}=\dfrac{1256}{12.56}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}=100$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=10\text{cm}$
Therefore the radius of the solid metallic sphere is 10cm.
The number of cones recast.(take $\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }=3.14$)
Ans: We know that Volume of metallic sphere, $\text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{10}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of cone, $\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{2.5}^{2}}\times 8$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{50\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Number of cones recasted, $\text{n}=\dfrac{\text{V}}{\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=\dfrac{4000\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\times \dfrac{3}{50\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=80$
Therefore the number of cones that can be re-casted from the metallic sphere is 80.
10. A solid metallic cone, with radius 6cm and height 10cm, is made of the same heavy metal A. In order to reduce its weight, a conical hole is made in the cone as shown and it is completely filled with a lighter metal B. The conical hole has a diameter of 6cm and depth 4cm. Calculate the ratio of the volume of metal A to the volume of metal B in the solid.
Ans: Volume of the cone made from metal A, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{A}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{A}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{6}^{2}}\times 10$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{A}}}=120\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of the cone made from metal B, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{B}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{B}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{3}^{2}}\times 4$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{B}}}=12\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Final volume of the cone made from metal B $=120\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }-12\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }=108\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }$
Ratio of volume of sphere made from metal A and B $=\dfrac{108\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{12\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}=\dfrac{9}{1}$
Therefore the ratio of the volume of the sphere made from metal A and B is 9:1.
11. A hollow sphere of internal and external radii 6cm and 8cm respectively is melted and recast into small cones of base radius 2cm and height 8cm. Find the number of cones.
Ans: Volume of the hollow cylinder, $\text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\left( {{\text{R}}^{3}}-{{\text{r}}^{3}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times \left( {{8}^{3}}-{{6}^{3}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times 296$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1184\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of each small cone, $\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{2}^{2}}\times 8$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{32\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Number of cones, $\text{n}=\dfrac{\text{V}}{\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=\dfrac{1184\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\times \dfrac{3}{32\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=\dfrac{1184}{32}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=37$
Therefore, the number of cones that can be re-casted from the hollow cylinder are 37.
12. The surface area of a solid metallic sphere is $2464\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{2}}.$ It is melted and recast into solid right circular cones of radius 3.5cm and height 7cm. Calculate:
The radius of the sphere
Ans: (i) We have to find the radius of solid sphere
Given the total area of a solid metallic sphere as $2464\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow 4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}=2464$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}=\dfrac{2464}{4\times \dfrac{22}{7}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}=\dfrac{17284}{88}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}=196$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=14\text{cm}$
Therefore the radius of the solid metallic sphere is 14cm.
The number of cones recast. (Take $\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{22}{7}$)
Ans: We know that Volume of metallic sphere, $\text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{14}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{10976\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of cone, $\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{3.5}^{2}}\times 7$
$\Rightarrow \text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{85.75\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Number of cones recasted, $\text{n}=\dfrac{\text{V}}{\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=\dfrac{10976\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\times \dfrac{3}{85.75\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=128$
Therefore the number of cones that can be recasted from the metallic sphere is 128.
Exercise 20E
1. A cone of height 15cm and diameter 7cm is mounted on a hemisphere of same diameter. Determine the volume of the solid thus formed.
Ans: Given the diameter of cone, $\text{d}=7\text{cm}$
Radius of the cone will be, $\text{r}=\dfrac{\text{d}}{2}=\dfrac{7}{2}\text{cm}$
Volume of the solid formed will be the sum of the volume of the cone and the volume of the hemisphere.
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}+\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{7}{2}\times \dfrac{7}{2}\times 15+\dfrac{2}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{7}{2}\times \dfrac{7}{2}\times \dfrac{7}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=192.5+89.83$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=282.33\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Thus the volume of the solid formed is $282.33\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
2. A buoy is made in the form of a hemisphere surmounted by a right cone whose circular base coincides with the plane surface of the hemisphere. The radius of the base of the cone is 3.5m and its volume is two-third of the hemisphere. Calculate the height of the cone and the surface area of the buoy, correct to two places of decimal.
Ans: Volume of hemisphere, $\text{V}=\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{2}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{3.5}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{85.75\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Given in the question that the volume of the cone is two by third times the volume of the hemisphere.
Volume of conical part $=\dfrac{2}{3}\times $ Volume of the hemisphere
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}=\dfrac{2}{3}\times \dfrac{85.75\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}=\dfrac{2\times 85.75}{3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\dfrac{2\times 85.75}{3\times 3.5\times 3.5}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\dfrac{171.5}{36.75}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=4.67\text{m}$
We know that slant height of the cone, ${{\text{l}}^{2}}={{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{l}}^{2}}={{4.67}^{2}}+{{3.5}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{l}}^{2}}=21.81+12.25$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{34.06}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=5.83\text{m}$
Surface area of buoy, $\text{A}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}+\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rl}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 3.5\times 3.5+\dfrac{22}{7}\times 3.5\times 5.83$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=77+64.13$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=141.13{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the height of the buoy is $4.67\text{m}$ and the surface area is $141.13{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
3. From a rectangular solid of metal 42cm by 30cm by 20cm, a conical cavity of diameter 14cm and depth 24cm is drilled out. Find:
The Surface Area of Remaining Solid
Ans: (i) Total surface area of cuboid $=2\left( \text{lb}+\text{bh}+\text{hl} \right)$
$=2\left( 42\times 30+30\times 20+20\times 42 \right)$
$=2\left( 1260+600+840 \right)$
$=2\left( 2700 \right)$
$=5400\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Radius of cone, $\text{r}=\dfrac{\text{d}}{2}=\dfrac{14}{2}=7\text{cm}$
Area of the base $=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$=\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{7}^{2}}=154\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Slant height of the cone, ${{\text{l}}^{2}}={{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{l}}^{2}}={{24}^{2}}+{{7}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{576+49}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=25\text{cm}$
Curved surface area of cone, $\text{A}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rl}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 7\times 25$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=550\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Surface area of remaining solid $=5400+550-154=5796\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the remaining area of solid is $5796\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
The volume of remaining solid
Ans: Volume of rectangular solid, $\text{V}=42\times 30\times 20=25200\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Radius of conical cavity, $\text{r}=\dfrac{\text{d}}{2}=\dfrac{14}{2}=7\text{cm}$
Volume of the conical cavity $=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{7}^{2}}\times 24$
$=1232\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of remaining solid $=25200-1232=23968\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the volume of the remaining solid is $23968\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
The weight of the material drilled out if it weighs 7gm per $\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{3}}$
Ans: Weight of the material drilled $=1232\times 7\text{g}$
$=8624\text{g}=8.624\text{kg}$
Therefore the weight of the material drilled out is $8.624\text{kg}.$
4. A cubical block of side 7cm is surmounted by a hemisphere of the largest size. Find the surface area of the resulting solid.
Ans: Radius of the hemisphere, $\text{r}=\dfrac{7}{2}\text{cm}$
Curved surface area of the hemisphere $=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$=2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{7}{2}\times \dfrac{7}{2}$
$=77\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Surface area of the remaining solid = Surface area of top face of the cube - Area of the base of the sphere
$={{7}^{2}}-\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{(\dfrac{7}{2})}^{2}}$
$=49-\dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{7}{2}\times \dfrac{7}{2}$
$=49-38.5=10.5\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Surface area of the cube $=5\times {{7}^{2}}=245\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Surface area of the resulting solid $=245+10.5+77=332.5\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the surface area of the resulting solid is $332.5\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
5. A vessel is in the form of an inverted cone, Its height is 8cm and the radius of its top, which is open, is 5cm. It is filled with water up to the rim. When lead shots, each of which is a sphere of radius 0.5cm, are dropped into the vessel, one fourth of the water flows out. Find the number of lead shots dropped in the vessel.
Ans: Volume of cone, $\text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{5}^{2}}\times 8$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{200\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Given in the question that the volume of water that has flowed out is one by four times the volume of cones.
Volume of the water flowed out, $\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{1}{4}\times \dfrac{200\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}=\dfrac{50\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of lead shots, $\text{V}''=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{(\text{r }\!\!'\!\!\text{ })}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}''=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{0.5}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}''=\dfrac{\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{6}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Number of lead shots dropped in the vessel, $\text{n}=\dfrac{\text{V }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }}{\text{V}''}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=\dfrac{50\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\times \dfrac{6}{\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=100$
Therefore the number of lead shots dropped in the vessel is 100.
6. A hemi-spherical bowl has negligible thickness and the length of its circumference is 198cm. Find the capacity of the bowl.
Ans: Let the radius of the bowl be r.
Circumference of the bowl is given as 198cm
$\Rightarrow 2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}=198$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=198\times \dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{7}{22}$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=\dfrac{63}{2}\text{cm}$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=31.5\text{cm}$
Capacity of the hemispherical bowl $=\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$=\dfrac{2}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{31.5}^{3}}$
$=65488.5\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the capacity of the hemispherical bowl is $65488.5\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
7. Find the maximum volume of a cone that can be carved out of a solid hemisphere of radius r cm.
Ans: For the volume of the cone to be largest, h=r
Volume of the cone, $\text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{\text{r}}^{2}}\times \text{r}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
Therefore the maximum volume of a cone that can be carved out of a solid hemisphere is $\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}.$
8. The radii of the bases of two solid right circular cones of same height are ${{\mathbf{r}}_{1}}$ and ${{\mathbf{r}}_{2}}$ respectively. The cones are melted and recast into a solid sphere of radius $\mathbf{R}$. Find the height of each cone in terms of ${{\mathbf{r}}_{1}},{{\mathbf{r}}_{2}}$ and $\mathbf{R}.$
Ans: Let the height of the solid circular cone be h.
Volume of the first solid circular cone, ${{\text{V}}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{2}\text{h}$
Volume of the second solid circular cone, ${{\text{V}}_{2}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{2}\text{h}$
Given in the question that the volume of the sphere is the sum of the volumes of first and second cones.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{3}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{2}\text{h}+\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{2}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow 4{{\text{R}}^{3}}=\text{h}\left( {{\text{r}}_{1}}^{2}+{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{2} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\dfrac{4{{\text{R}}^{3}}}{\left( {{\text{r}}_{1}}^{2}+{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{2} \right)}$
Therefore the height of each cone in terms of ${{\text{r}}_{1}},\text{ }\!\!~\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{2}}$ and $\text{R}$ is $\text{h}=\dfrac{4{{\text{R}}^{3}}}{\left( {{\text{r}}_{1}}^{2}+{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{2} \right)}$.
9. A solid metallic hemisphere of diameter 28cm is melted and recast into a number of identical solid cones, each of diameter 14cm and height 8cm. Find the number of cones so formed.
Ans: Given the diameter of hemisphere as 28cm
Radius is half of diameter which is equal to 14cm
Volume of the solid hemisphere, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{h}}}=\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{h}}}=\dfrac{2}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{14}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{h}}}=\dfrac{5488\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Given the diameter of cone as 14cm
Radius is half of diameter which is equal to 7cm
Volume of each cone, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{7}^{2}}\times 8$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=\dfrac{392\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Number of cones formed, $\text{n}=\dfrac{{{\text{V}}_{\text{h}}}}{{{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=\dfrac{5488\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\times \dfrac{3}{392\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=\dfrac{5488}{392}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=14$
Therefore the number of cones formed is 14.
10. A cone and a hemisphere have the same base and the same height. Find the ratio between their volumes.
Ans: Let the radius of base and height be r and h respectively.
Given in the question that the radius and height are the same.
Volume of cone, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
Volume of the hemisphere, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{h}}}=\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
To find the ratio
$\dfrac{{{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}}{{{\text{V}}_{\text{h}}}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}}{\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}}{{{\text{V}}_{\text{h}}}}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
Therefore the ratio between the volume of the cone and the hemisphere is 1:2.
Exercise 20F
1. From a solid right circular cylinder with height 10cm and radius of the base 6cm, a right circular cone of the same height and same base is removed. Find the volume of the remaining solid.
Ans: Volume of the cylindrical part, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{cy}}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
Volume of the conical part, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{co}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
Volume of the remaining solid, $\text{V}={{\text{V}}_{\text{cy}}}-{{\text{V}}_{\text{co}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}-\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{2}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 6\times 6\times 10$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{5280}{7}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=754.28\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the volume of the remaining solid is $754.28\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
2. From a solid cylinder whose height is 16cm and radius is 12cm, a conical cavity of height 8cm and base radius 6cm is hollowed out. Find the volume and total surface area of the remaining solid.
Ans: Volume of the cylindrical part, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{cy}}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
Volume of the conical part, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{co}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
Volume of the remaining solid, $\text{V}={{\text{V}}_{\text{cy}}}-{{\text{V}}_{\text{co}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{H}-\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{12}^{2}}\times 16-\dfrac{1}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{6}^{2}}\times 8$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=7241.14-301.71$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=6939.43\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Slant height of the conical cavity, ${{\text{l}}^{2}}={{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{{{8}^{2}}+{{6}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{64+36}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=10\text{cm}$
Curved surface area of the solid cylinder $=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ RH}$
Curved surface area of cone $=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rl}$
Base area of the cylinder $=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{2}}$
Area of circular cylinder $=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\left( {{\text{R}}^{2}}-{{\text{r}}^{2}} \right)$
Total surface area of remaining solid, $\text{A}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ RH}+\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rl}+\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{2}}+\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\left( {{\text{R}}^{2}}-{{\text{r}}^{2}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 12\times 16+\dfrac{22}{7}\times 6\times 10+\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{12}^{2}}+\dfrac{22}{7}\left( {{12}^{2}}-{{6}^{2}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=\dfrac{8448}{7}+\dfrac{1320}{7}+\dfrac{3168}{7}+\dfrac{2376}{7}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=\dfrac{15312}{7}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=2187.42\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the volume of the remaining solid is $6939.43\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$ and the area is $2187.42\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
3. A circus tent is cylindrical to a height of 4m and conical above it. If its diameter is 105m and its slant height is 80m, calculate the total area of the canvas required. Also, find the total cost of canvas used at 15rs per meter if the width is 1.5m.
Ans: Given the diameter of the cylindrical part of tent as 105m
Radius of the cylindrical part of the tent, $\text{r}=\dfrac{105}{2}\text{m}$
Total curved surface area of tent $=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rh}+\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rl}$
$=2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{105}{2}\times 4+\dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{105}{2}\times 80$
$=22\times 15\times 4+22\times 15\times 40$
$=1320+13200=14520{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Area of canvas
$\Rightarrow \text{l }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }\times \text{b}=14520$
$\Rightarrow \text{l }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{14520}{1.5}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=9680\text{m}$
Total cost of canvas at 15rs per meter $=9680\times 15=145200\text{rs}$
Therefore the total cost of canvas is $145200\text{rs}.$
4. A circus tent is cylindrical to a height of 8m surmounted by a conical part. If total height of the tent is 13m and the diameter of its base is 24m; calculate:
Total surface area of tent
Ans: Height of the conical part of the tent, $\text{h}=13-8=5\text{m}$
Given diameter of base of tent as 24m
Radius, $\text{r}=\dfrac{24}{2}=12\text{m}$
Slant height, ${{\text{l}}^{2}}={{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{{{5}^{2}}+{{12}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{25+144}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=13\text{m}$
(i) Total surface area of tent, $\text{A}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rH}+\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rl}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 12\left( 2\times 8+13 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=\dfrac{22\times 12\times 29}{7}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=1093.71{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the total surface area of tent is $1093.71{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Area of canvas required to make this tent allowing 10% of the canvas used for folds and stitching.
Ans: Area of the canvas required$=$Surface area of tent+Area of canvas used in folding and stitching
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=1093.71+\dfrac{\text{A}}{10}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{9\text{A}}{10}=1093.71$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=\dfrac{10937.1}{9}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=1215.23{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the area of the canvas required is $1215.23{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
5. A cylindrical boiler, 2m high, is 3.5m in diameter. It has a hemispherical lid. Find the volume of its interior, including the part covered by the lid.
Ans: Given the diameter, $\text{d}=3.5\text{m}$
So the radius, $\text{r}=\dfrac{3.5}{2}\text{m}$
Total volume of the boiler, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}+\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\left( \text{h}+\dfrac{2}{3}\text{r} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{3.5}{2}\times \dfrac{3.5}{2}\left( 2+\dfrac{2}{3}\times \dfrac{3.5}{2} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{11\times 3.5}{4}\times \dfrac{9.5}{3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=9.625+3.16$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=12.785{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the volume covered by the lid is $12.785{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
6. A vessel is a hollow cylinder fitted with a hemispherical bottom of the same base. The depth of the cylindrical part is $4\dfrac{2}{3}\mathbf{m}$ and the diameter of the hemisphere is 3.5m. Calculate the capacity and the internal surface area of the vessel.
Ans: Given diameter as 3.5m
So radius, $\text{r}=\dfrac{3.5}{2}\text{m}$
Height of the cylindrical part $=4\dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{14}{3}\text{m}$
Capacity of the vessel, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}+\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{3.5}{2}\times \dfrac{3.5}{2}\times \dfrac{14}{3}+\dfrac{2}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{3.5}{2}\times \dfrac{3.5}{2}\times \dfrac{3.5}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{11\times 3.5\times 3.5}{3}+\dfrac{11\times 3.5\times 3.5}{3\times 2\times 2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=44.91+11.22$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=56.13{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Internal curved surface area of vessel, $\text{A}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rh}+2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{3.5}{2}\times \dfrac{14}{3}+2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{3.5}{2}\times \dfrac{3.5}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=\dfrac{2\times 22\times 3.5}{3}+\dfrac{11\times 3.5}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=51.33+19.25$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=70.58{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the capacity of the vessel is $56.13{{\text{m}}^{3}}$ and the curved surface area is $70.58{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
7. A wooden toy is in the shape of a cone mounted on a cylinder as shown alongside. If the height of the cone is 24cm, the total height of the toy is 60cm and the radius of the base of the cone is twice the radius of the base of the cylinder which is 10cm, find the total surface area of the toy.(Take $\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }=3.14$)
Ans: According to the question, the radius of the base of the cone is twice that of the radius of the base of the cylinder.
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=2\times 5=10\text{cm}$
Curved surface area of the solid cylinder $=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ RH}$
Curved surface area of cone $=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rl}$
Base area of the cylinder $=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
Slant height of the cone, ${{\text{l}}^{2}}={{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{{{24}^{2}}+{{10}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=26\text{cm}$
Total surface area of the toy, $\text{A}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ RH}+\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rl}+\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 5\times 36+\dfrac{22}{7}\times 10\times 26+\dfrac{22}{7}\times 10\times 10$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=1131.42+817.14+314.28$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=2262.84\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the total surface area of toy is $2262.84\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
8. A cylindrical container with diameter of base 42cm contains sufficient water to submerge a rectangular solid of iron with dimensions $22\mathbf{cm}\times 14\mathbf{cm}\times 10.5\mathbf{cm}.$ Find the rise in level of the water when the solid is submerged.
Ans: Diameter of the cylindrical container is given as 42cm
Radius of the cylindrical container, $\text{r}=\dfrac{42}{2}=21\text{cm}$
Volume of iron, $\text{V}=22\times 14\times 10.5=3234\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Let the rise in level of water when solid is submerged be h.
Volume of water in the container will be equal to volume of the metal
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}=3234$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=3234\times \dfrac{7}{22}\times \dfrac{1}{21}\times \dfrac{1}{21}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\dfrac{22638}{9702}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=2.33\text{cm}$
Therefore the rise in the level of water when the solid is submerged is 2.33m.
9. Spherical marbles of diameter 1.4cm are dropped into a beaker containing some water and are fully submerged. The diameter of the beaker is 7cm. Find how many marbles have been dropped in it if the water rises by 5.6cm?
Ans: Given the diameter of the spherical marble as 1.4cm.
Radius of the marble, $\text{r}=\dfrac{1.4}{2}=0.7\text{cm}$
Volume of each spherical marble, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{m}}}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{m}}}=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{0.7}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{m}}}=\dfrac{1.372\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Radius of the beaker, $\text{R}=\dfrac{7}{2}=3.5\text{cm}$
Volume of the water in the beaker, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{b}}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{b}}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{(3.5)}^{2}}\times 5.6$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{b}}}=68.6\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Number of marbles dropped, $\text{n}=\dfrac{{{\text{V}}_{\text{b}}}}{{{\text{V}}_{\text{m}}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=\dfrac{68.6\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{\dfrac{1.372\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=\dfrac{68.6\times 3}{1.372}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=150$
Therefore the total number of marbles dropped in the water for the water to rise by 5.6cm is 150.
10. The cross section of a railway tunnel is a rectangle 6m broad and 8m high surrounded by a semi-circle as shown in the figure. The tunnel is 35m long. Find the cost of plastering the internal surface of the tunnel(excluding the floor) at the rate of 2.25rs per ${{\mathbf{m}}^{2}}.$
Ans: From the figure given the diameter of semi circle as 6m
Radius, $\text{r}=\dfrac{6}{2}=3\text{m}$
Circumference of the semi circle, $\text{C}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 3$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=9.43\text{m}$
Internal surface area of the tunnel, $\text{A}=2\left( \text{l}\times \text{h} \right)+\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rl}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=2\left( 35\times 8 \right)+9.43\times 35$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=560+330.05$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=890.05{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Rate of plastering the internal surface of the tunnel $=2.25\times 890.05=2002.6$
Therefore the rate of plastering is 2002.6rs.
11. The horizontal cross section of a water tank is in the shape of a rectangle with a semi-circle at one end, as shown in the following figure. The water is 2.4m deep in the tank. Calculate the volume of water in the tank in gallons.(1 gallon=4.5 liters)
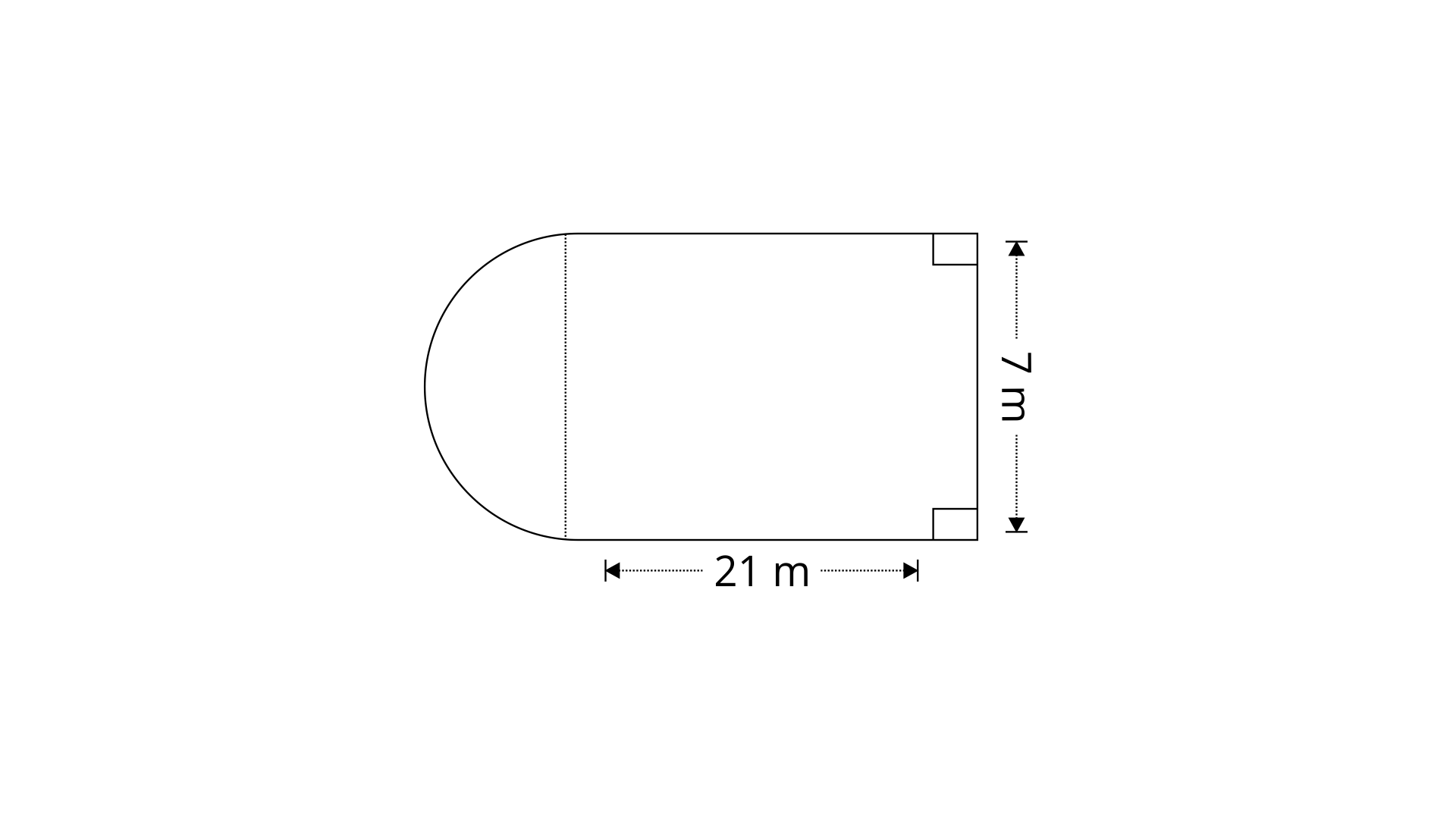
Ans: Given the diameter of the semicircle as 7m
Radius, $\text{r}=\dfrac{7}{2}=3.5\text{m}$
Area of cross section = Area of rectangle + Area of the semicircle
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=\text{lb}+\dfrac{1}{2}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=21\times 7+\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 3.5\times 3.5$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=147+19.25$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=166.25{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Volume of water filled in gallons, $\text{V}=166.25\times 2.4{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=399{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=399\times {{100}^{3}}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{399\times {{100}^{3}}}{1000}\text{l}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{399\times 1000}{4.5}\text{g}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=88666.67\text{g}$
Therefore the volume of water filled in gallons is 88666.67 gallons.
12. The given figure shows the cross section of a water channel consisting of a rectangle and a semicircle. Assuming that the channel is always full, find the volume of water discharged through it in one minute if water is flowing at the rate of 20cm per second. Give your answer in cubic meters correct to one place of decimal.
Ans: Radius of semicircle, $\text{r}=\dfrac{21}{2}\text{cm}$
Area of cross section of water channel = Area of Rectangle + Area of the semi circle
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=\text{lb}+\dfrac{1}{2}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=21\times 7+\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{(\dfrac{21}{2})}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=147+173.25$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=320.25\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Given in the question that the water is flowing at the rate of 20cm per second.
Therefore the length of the water column $=20\times 60=1200\text{cm}$
Volume of water discharged, $\text{V}=320.25\times 1200$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=384300\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=0.3843{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}\simeq 0.4{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the amount of water displaced is $0.4{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
13. An open cylindrical vessel of internal diameter 7cm and height 8cm stands on a horizontal table. Inside this is placed a solid metallic right circular cone, the diameter of which is $3\dfrac{1}{2}\mathbf{cm}$ and height 8cm. Find the volume of the water required to fill the vessel.
If this cone is replaced by another cone, whose height is $1\dfrac{3}{4}\mathbf{cm}$ and the radius of whose base is 2cm, find the drop in the water level.
Ans: Given diameter is 7cm.
Radius, $\text{r}=\dfrac{7}{2}\text{cm}$
Radius of the circular cone, $\text{R}=\dfrac{3\dfrac{1}{2}}{2}=\dfrac{7}{4}\text{cm}$
Volume of remaining portion where water needs to be filled
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}-\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{7}{2}\times \dfrac{7}{2}\times 8-\dfrac{1}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{7}{4}\times \dfrac{7}{4}\times 8$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=308-25.67$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=282.33\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Height of the new cone, $\text{h }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=1\dfrac{3}{4}=\dfrac{7}{4}\text{cm}$
Volume of water, $\text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{2}}\text{h}-\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{(\text{R }\!\!'\!\!\text{ })}^{2}}\text{h }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{(\dfrac{7}{4})}^{2}}\times 8-\dfrac{1}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{2}^{2}}\times \dfrac{7}{4}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{77}{3}-\dfrac{22}{3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{55}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Let the height of the water that is dropped down be H.
Volume of water in cylinder = Volume of water that dropped down
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{H}=\dfrac{55}{3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{H}=\dfrac{55\times 7}{3\times 22\times {{(\dfrac{7}{2})}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{H}=\dfrac{10}{21}\text{cm}$
Therefore the height of the water that is dropped down below is $\dfrac{10}{21}\text{cm}.$
14. A cylindrical can, whose base is horizontal and of radius 3.5cm, contains sufficient water so that when a sphere is placed in the can, the water just covers the sphere. Given that the sphere just fits into the can, calculate:
The total surface area of the can in contact with water when the sphere is in it
Ans: Total surface area of the can is the sum of base area and the curved surface area
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}+2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rh}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{3.5}^{2}}+2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 3.5\times 7$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=38.5+154$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=192.5\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the total surface area of the can is $192.5\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
The depth of water in the can before the sphere was put into the can
Ans: Let the depth of the water be $\text{h }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }$
Volume of can is equal to the sum of volume of water and the volume of sphere
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }+\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\text{h }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }+\dfrac{4}{3}\text{r}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=7-\dfrac{4\times 3.5}{3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{7}{3}\text{cm}$
Therefore the depth of water in the can before the sphere was put in is $\dfrac{7}{3}\text{cm}.$
15. A hollow cylinder has a solid hemisphere inward at one end and on the other end it is closed with a flat circular plate. The height of water is 10cm when the flat circular plate is downward. Find the level of water, when it is inverted upside down, common diameter is 7cm and height of the cylinder is 20cm.
Ans: Let the height of the water level be h.
Volume of the cylinder, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{(\dfrac{7}{2})}^{2}}\times 10$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=\dfrac{245\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{2}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of hemisphere, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{h}}}=\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{h}}}=\dfrac{2}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{(\dfrac{7}{2})}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{h}}}=\dfrac{343\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{12}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of water in cylinder = Volume of water level - Volume of hemisphere
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{245\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{2}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}-\dfrac{343\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{12}$
$\Rightarrow {{(\dfrac{7}{2})}^{2}}\times \text{h}=\dfrac{245}{2}+\dfrac{343}{12}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=10+\dfrac{7}{3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\dfrac{37}{3}\text{cm}$
Therefore the height of water when hemisphere is facing downwards is $\dfrac{37}{3}\text{cm}.$
Exercise 20G
1. What is the least number of solid metallic spheres, each of 6cm diameter, that should be melted and recast to form a solid metal cone whose height is 45cm and diameter 12cm.
Ans: Volume of sphere, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{s}}}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{s}}}=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{3}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{s}}}=36\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of cone, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{(\text{r }\!\!'\!\!\text{ })}^{2}}\text{h }\!\!'\!\!\text{ }$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{6}^{2}}\times 45$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=540\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Number of solid metallic spheres needed to form the cone, $\text{n}=\dfrac{{{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}}{{{\text{V}}_{\text{s}}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=\dfrac{540\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{36\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=15$
Therefore the least number of solid metallic spheres needed to form the cone is 15
2. A largest sphere is to be carved out of a right circular cylinder of radius 7cm and height 14cm. Find the volume of the sphere to the nearest integer.
Ans: Radius of the largest sphere that can be carved from the cylinder should be equal to the radius of the cylinder.
Therefore the radius of the sphere = 7cm.
Volume of the given sphere, $\text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{7}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4312}{3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=1437.33$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}\simeq 1437\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the volume of the largest sphere that can be carved from the cylinder is $1437\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
3. A right circular cylinder having diameter 12cm and height 15cm is full of ice-cream. The ice-cream is to be filled in identical cones of height 12cm and diameter 6cm having a hemispherical shape on the top. Find the number of cones required.
Ans: Volume of cylinder, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{6}^{2}}\times 15$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=540\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of ice cream cone is equal to the sum of volume of cone and the volume of hemisphere
$\Rightarrow \text{V}={{\text{V}}_{\text{co}}}+{{\text{V}}_{\text{h}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{(\text{r }\!\!'\!\!\text{ })}^{2}}\text{h}+\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{(\text{r }\!\!'\!\!\text{ })}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{3}^{2}}\times 12+\dfrac{2}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{(3)}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=36\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }+18\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=54\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Number of cones formed, $\text{n}=\dfrac{{{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}}{\text{V}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=\dfrac{540\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{54\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=10$
Therefore the number of cones that can be formed is 10.
4. A solid is in the form of a cone standing on a hemi-sphere with both their radii being equal to 8cm and the height of the cone is equal to its radius. Find, in terms of $\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ },$ the volume of the solid.
Ans: Given in the question that the radius and height both are equal.
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\text{r}=8\text{cm}$
Volume of the solid formed, $\text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}+\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{8}^{2}}\times 8+\dfrac{2}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{8}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{512\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}+\dfrac{1024\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1536\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=512\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the volume of the solid formed is $512\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
5. The diameter of a sphere is 6cm. It is melted and drawn into a wire of diameter 0.2cm. Find the length of the wire.
Ans: Radius of sphere, $\text{r}=\dfrac{6}{2}=3\text{cm}$
Volume of sphere, $\text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{3}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=36\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Radius of the wire, $\text{R}=\dfrac{0.2}{2}=0.1\text{cm}$
Let the length of the wire be l.
Volume of wire, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{w}}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{2}}\text{l}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{w}}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{(0.1)}^{2}}\times \text{l}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{w}}}=0.01\text{l }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Given that the sphere is melted to form a wire. Therefore the volume of the sphere will be equal to the volume of the wire
$\Rightarrow 36\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }=0.01\text{l }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\dfrac{36}{0.01}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=3600\text{cm}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=36\text{m}$
Therefore the length of the wire is 36m.
6. Determine the ratio of volume of a cube to that of a sphere which will exactly fit inside the cube.
Ans: Let the edge of the cube be x.
Volume of cube $=\text{x}\times \text{x}\times \text{x}={{\text{x}}^{3}}$
For a sphere to completely fit inside a cube, its radius should be equal to half of the edge of the cube.
Therefore, $\text{r}=\dfrac{\text{x}}{2}$
Volume of the sphere $=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{(\dfrac{\text{x}}{2})}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{11}{21}{{\text{x}}^{3}}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Ratio of volume of the cube to the volume of sphere$=\dfrac{{{\text{x}}^{3}}}{\dfrac{11}{21}{{\text{x}}^{3}}}$
$=\dfrac{21}{11}=21:11$
Therefore the ratio of volume of the cube to the volume of the sphere is 21:11.
7. An iron pole consisting of a cylindrical portion 110cm high and of base diameter 12cm is surmounted by a cone 9cm high. Find the mass of the pole, given that $1\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{3}}$ of iron has $8\mathbf{gm}$ of mass. (Take $\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }=\dfrac{355}{113}$)
Ans: Total volume of the iron pole is the sum of the volume of the cylindrical portion and the conical portion.
Total volume of the iron pole, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}{{\text{h}}_{1}}+\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}{{\text{h}}_{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\left( {{\text{h}}_{1}}+\dfrac{1}{3}{{\text{h}}_{2}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{355}{113}\times {{6}^{2}}\left( 110+\dfrac{1}{3}\times 9 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{355}{113}\times 36\times 113$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=12780\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Total mass of the pole, $\text{m}=12780\times 8$
$\Rightarrow \text{m}=102240\text{gm}=102.24\text{kg}$
Therefore the total mass of the pole is $102.24\text{kg}.$
8. In the following diagram a rectangular platform with a semi-circular end on one side is 22 meters long from one end to the other end. If the length of the half circumference is 11meters, find the cost of constructing the platform, 1.5 meters high at the rate of 4rs per cubic meters.
Ans: Circumference of the semicircular portion, $\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}=11$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=11\times \dfrac{7}{22}$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=\dfrac{7}{2}\text{m}$
The breadth of the rectangular platform is twice of the radius of the semi-circular path
Therefore, $\text{b}=2\text{r}$
$\Rightarrow \text{b}=2\times \dfrac{7}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{b}=7\text{m}$
Actual length of the rectangular platform, $\text{l}=22-\dfrac{7}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\dfrac{37}{2}=18.5\text{m}$
Area of the platform, $\text{A}=\text{lb}+\dfrac{1}{2}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=18.5\times 7+\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{(\dfrac{7}{2})}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=129.5+19.25$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=148.75{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Volume of platform is the product of area of the platform and height
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=148.75\times 1.5=223.125{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Total cost of construction $=223.125\times 4=892.5\text{rs}$
Therefore the total cost of construction in rupees is 892.5.
9. The cross-section of a tunnel is a square of side 7m surmounted by a semi-circle as shown in the adjoining figure. The tunnel is 80m long. Calculate
Its Volume,
Ans: Radius of the semi-circle, $\text{r}=\dfrac{7}{2}\text{m}$
Area of cross-section, $\text{A}={{\text{a}}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}={{7}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{(\dfrac{7}{2})}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=49+\dfrac{1}{2}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{7}{2}\times \dfrac{7}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=49+\dfrac{77}{4}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=49+19.25$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=68.25{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
(i) Volume of tunnel, $\text{V}=\text{A}\times \text{l}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=68.25\times 80$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=5460{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the volume of the tunnel is $5460{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
The surface area of the tunnel(excluding the floor) and
Ans: Circumference of the tunnel, $\text{C}=\text{l}+\text{l}+\dfrac{1}{2}\times 2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=7+7+\dfrac{22}{7}\times \dfrac{7}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}=25\text{m}$
Surface area of the tunnel, $\text{S}=\text{C}\times \text{l}$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}=25\times 80$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}=2000{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the surface area of the tunnel is $2000{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
Its Floor Area.
Ans: Floor area, $\text{A}=\text{lb}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=7\times 80$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=560{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the floor area of the tunnel is $560{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
10. A cylindrical water tank of diameter 2.8m and height 4.2m is being fed by a pipe of diameter 7cm through which water flows at the rate of $4\mathbf{m}{{\mathbf{s}}^{-1}}.$ Calculate, in minutes, the time it takes to fill the tank.
Ans: Radius of the tank, $\text{r}=\dfrac{2.8}{2}=1.4\text{m}$
Volume of water filled in tank, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{1.4}^{2}}\times 4.2$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=8.232\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=8.232\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{100}^{3}}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Radius of pipe, ${{\text{r}}_{1}}=\dfrac{7}{2}\text{cm}$
Let the height of the water filled be ${{\text{h}}_{1}}$
Volume of water in the pipe, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{2}{{\text{h}}_{1}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{(\dfrac{7}{2})}^{2}}\times {{\text{h}}_{1}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{49{{\text{h}}_{1}}}{4}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of the water coming out of the pipe is equal to the volume of water filled in the tank.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{49{{\text{h}}_{1}}}{4}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }=8.232\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{100}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{h}}_{1}}=\dfrac{8.232\times 4\times {{100}^{3}}}{49}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{h}}_{1}}=6720\times 100\text{cm}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{h}}_{1}}=6720\text{m}$
Therefore time taken to fill the tank, $\text{t}=\dfrac{6720}{4\times 60}\text{mins}$
$\Rightarrow \text{t}=28$minutes
Therefore the time taken to fill the tank is 28minutes.
11. Water flows, at 9km per hour, through a cylindrical pipe of cross-sectional area $25\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{2}}.$ If this water is collected into a rectangular cistern of dimensions 7.5m by 5m by 4m; calculate the rise in level in the cistern in 1hour 15minutes.
Ans: Distance travelled by water in 1 hour 15minutes $=\left( 1+\dfrac{15}{60} \right)\times 9$
$=\dfrac{45}{4}\text{km}=11250\text{m}$
Volume of water, $\text{V}=25\times 11250$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{25}{10000}\times 11250$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=28.125{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Let the height of water in the tank be h.
Volume of water is equal to the volume of the water in tank
$\Rightarrow 28.125=7.5\times 5\times \text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\dfrac{28.125}{37.5}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=0.75\text{m}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=75\text{cm}$
Therefore the height of water in the cylindrical tank is 75cm.
12. The given figure shows the cross-section of a cone, a cylinder and a hemisphere all with the same diameter 10cm, and the other dimensions are as shown.
Calculate
The total Surface Area
Ans: Radius of base, $\text{r}=\dfrac{10}{2}=5\text{cm}$
Slant height of the cone, ${{\text{l}}^{2}}={{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{{{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{{{12}^{2}}+{{5}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{169}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=13\text{cm}$
(a) Total surface area of solid $\text{A}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rl}+2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rh}+2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}\left( \text{l}+2\text{h}+2\text{r} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 5\left( 13+2\left( 12 \right)+2\left( 5 \right) \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 5\left( 47 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{A}=738.57\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the total surface area of the solid is $738.57\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
The Total Volume of Solid and
Ans: Total volume of the solid, $\text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}+\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}+\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{\text{h}}{3}+\text{h}+\dfrac{2}{3}\text{r} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{5}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{12}{3}+12+\dfrac{2}{3}\left( 5 \right) \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 25\left( 4+12+3.33 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 25\left( 19.33 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=1518.78\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the volume of the solid is $1518.78\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
The density of the material if its total weight is 1.7kg.
Ans: Density, $\text{d}=\dfrac{\text{m}}{\text{v}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{d}=\dfrac{1.7\text{kg}}{1518.78\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{d}=\dfrac{1.7\times 1000\text{g}}{1518.78\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{d}=1.12\dfrac{\text{g}}{\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}}$
Therefore the density of the solid is $1.12\dfrac{\text{g}}{\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}}$.
13. A solid, consisting of a right circular cone standing on a hemisphere, is placed upright in a right circular cylinder, full of water, and touches the bottom. Find the volume of water left in the cylinder, given that the radius of the cylinder is 3cm and its height is 6cm; the radius of the hemisphere is 2cm and the height of the cone is 4cm. Give your answer to the nearest cubic centimeter.
Ans: Volume of water in cylinder, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{3}^{2}}\times 6$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=54\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of water displaced = Volume of cone + Volume of hemisphere
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{2}}\text{H}+\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{2}}\left( \text{H}+2\text{R} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{2}^{2}}\left( 4+2\left( 2 \right) \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times 32$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{32\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of water left in the cylinder = Volume of water in cylinder - Volume of water displaced
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=54\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }-\dfrac{32\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{130\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{3}\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{130}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=136.19\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}\simeq 136\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the volume of the water left in the cylinder is $136\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
14. A metal container in the form of a cylinder is surmounted by a hemisphere of the same radius. The internal height of the cylinder is 7m and the internal radius is 3.5m. Calculate:
The total area of the internal surface, excluding the base;
Ans: (i) Total surface area of the container(excluding base) = Curved surface area of the cylinder + Area of hemisphere
$\Rightarrow \text{S}.\text{A}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rh}+2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}.\text{A}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}\left( \text{h}+\text{r} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}.\text{A}=2\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 3.5\times \left( 7+3.5 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}.\text{A}=22\times 10.5$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}.\text{A}=231{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the total surface area of the container(excluding the base) is $231{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
The internal volume of the container in ${{\mathbf{m}}^{3}}.$
Ans: Volume of the container, $\text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}+\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\left( \text{h}+\dfrac{2}{3}\text{r} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{3.5}^{2}}\left( 7+\dfrac{2}{3}\times 3.5 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=11\times 3.5\times 9.33$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=359.2{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the volume of the container is $359.2{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
15. An exhibition tent is in the form of a cylinder surmounted by a cone. The height of the tent above the ground is 85m and the height of the cylindrical part is 50m. If the diameter of the base is 168m, find the quantity of the canvas required to make the tent. Allow 20% extra for fold and for stitching. Give your answer to the nearest ${{\mathbf{m}}^{2}}.$
Ans: Radius of base of the tent, $\text{r}=\dfrac{168}{2}=84\text{m}$
Height of the conical part, $\text{h}=85-50=35\text{m}$
Slant height of the conical part, ${{\text{l}}^{2}}={{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{{{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=\sqrt{{{35}^{2}}+{{84}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=91\text{m}$
Total surface area of the tent, $\text{S}.\text{A}=2\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rH}+\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rl}$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}.\text{A}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ r}\left( 2\text{H}+\text{l} \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}.\text{A}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 84\times \left( 2\times 50+91 \right)$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}.\text{A}=22\times 12\times 191$
$\Rightarrow \text{S}.\text{A}=50424{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
According to the question 20% extra is needed for folds and stitching.
Therefore total canvas required $=50424+\dfrac{20}{100}\times 50424$
$=50424+10084.8=60508.8{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
$\simeq 60509{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the total area of the canvas required is $60509{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
16. A test tube consists of a hemisphere and a cylinder of the same radius. The volume of the water required to fill the whole tube is $\dfrac{5159}{6}\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{3}},$ and $\dfrac{4235}{6}\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{3}}$ water is required to fill the tube to a level which is 4cm below the top of the tube. Find the radius of the tube and length of its cylindrical part.
Ans: Let the radius and height of the tube be r and h respectively.
Volume of water in test tube
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}+\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}=\dfrac{5159}{6}$
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{2}{3}\text{r}+\text{h} \right)=\dfrac{5159}{6}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}}{3}\left( 2\text{r}+3\text{h} \right)=\dfrac{5159}{6}$
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\left( 2\text{r}+3\text{h} \right)=\dfrac{5159}{2}$------------(1)
Volume of water filled upto 4cm,
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}+\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\left( \text{h}-4 \right)=\dfrac{4235}{6}$
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{2}{3}\text{r}+\text{h}-4 \right)=\dfrac{4235}{6}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}}{3}\left( 2\text{r}+3\text{h}-12 \right)=\dfrac{4235}{6}$
$\Rightarrow \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\left( 2\text{r}+3\text{h}-12 \right)=\dfrac{4235}{2}$--------------(2)
Subtract equation (2) from (1)
$\Rightarrow 12\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}=\dfrac{5159}{2}-\dfrac{4235}{2}$
$\Rightarrow 12\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}=462$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}=\dfrac{462}{12}\times \dfrac{7}{22}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}=12.25$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=3.5\text{cm}$
Substitute the value of r in 1
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{3.5}^{2}}\left( 2\times 3.5+3\text{h} \right)=\dfrac{5159}{2}$
$\Rightarrow 11\times 3.5\times \left( 7+3\text{h} \right)=\dfrac{5159}{2}$
$\Rightarrow 7+3\text{h}=\dfrac{5159}{2\times 11\times 3.5}$
$\Rightarrow 7+3\text{h}=67$
$\Rightarrow 3\text{h}=60$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=20\text{cm}$
Therefore the radius and height of the test tube is 3.5cm and 20cm respectively.
17. A solid is in the form of a right circular cone mounted on a hemisphere. The diameter of the base of the cone, which exactly coincides with the hemisphere, is 7cm and its height is 8cm. The solid is placed in a cylindrical vessel of internal radius 7cm and height 10cm. How much water, in $\mathbf{c}{{\mathbf{m}}^{3}},$ will it be required to fill the vessel completely?
Ans: Radius of the base of cone and hemisphere, $\text{r}=\dfrac{7}{2}=3.5\text{cm}$
Volume of the solid formed, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{s}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}+\dfrac{2}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{s}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\left( \text{h}+2\text{r} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{s}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{(3.5)}^{2}}\times \left( 8+2\times 3.5 \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{s}}}=\dfrac{11\times 3.5\times 15}{3}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{s}}}=192.5\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of the cylinder, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{R}}^{2}}\text{H}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times {{7}^{2}}\times 10$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=1540\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of water required to fill the vessel, $\text{V}={{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}-{{\text{V}}_{\text{s}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=1540-192.5$
$\Rightarrow \text{V}=1347.5\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Therefore the volume of water required to fill the vessel is $1347.5\text{c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}.$
18. Two solid spheres of radii 2cm and 4cm are melted and recast into a cone of height 8cm. Find the radius of the cone so formed.
Ans: Let the radius of the cone be r
Volume of the cone formed = sum of volumes of the volumes of both the spheres melted to form cones.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{3}+\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{3}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}=4{{\text{r}}_{1}}^{3}+4{{\text{r}}_{2}}^{3}$
$\Rightarrow 8{{\text{r}}^{2}}=4\left( {{2}^{3}}+{{4}^{3}} \right)$
$\Rightarrow 2{{\text{r}}^{2}}=8+64$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{r}}^{2}}=36$
$\Rightarrow \text{r}=6\text{cm}$
Therefore the radius of the cone formed is 6cm.
19. A certain number of metallic cones, each of radius 2cm and height 3cm, are melted and recast into a solid sphere of radius 6cm. Find the number of cones used.
Ans: Volume of each cone, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{\text{c}}}^{2}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{2}^{2}}\times 3$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}=4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Volume of the sphere, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{s}}}=\dfrac{4}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}_{\text{s}}}^{3}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{s}}}=\dfrac{4}{3}\times \text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }\times {{6}^{3}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{V}}_{\text{s}}}=288\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{3}}$
Number of cones used, $\text{n}=\dfrac{{{\text{V}}_{\text{s}}}}{{{\text{V}}_{\text{c}}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=\dfrac{288\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}{4\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }}$
$\Rightarrow \text{n}=72$
Therefore, the number of cones used is 72.
20. A conical tent is to accommodate 77 persons. Each person must have $16{{\mathbf{m}}^{3}}$ of air to breathe. Given the radius of the tent as 7m, find the height of the tent and also its curved surface area.
Ans: Given in the question that a conical tent can accommodate 77 persons and each person needs $16{{\text{m}}^{3}}$ of air to breathe.
$\Rightarrow 77\times 16=\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}\text{h}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\dfrac{77\times 16\times 3}{\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ }{{\text{r}}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=\dfrac{77\times 16\times 3\times 7}{22\times {{7}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \text{h}=24\text{m}$
Slant height of the conical tent, ${{\text{l}}^{2}}={{\text{h}}^{2}}+{{\text{r}}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{l}}^{2}}={{24}^{2}}+{{7}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow {{\text{l}}^{2}}=625$
$\Rightarrow \text{l}=25\text{m}$
Curved surface area of the tent, $\text{C}.\text{S}.\text{A}=\text{ }\!\!\Pi\!\!\text{ rl}$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}.\text{S}.\text{A}=\dfrac{22}{7}\times 7\times 25$
$\Rightarrow \text{C}.\text{S}.\text{A}=550{{\text{m}}^{2}}$
Therefore the slant height and the curved surface area of the conical tent is $25\text{m}$ and $550{{\text{m}}^{2}}.$
Why Learn This Chapter?
Students may wonder why they would have to study all these problems and memorize all the formulae and theorems. The truth is, getting a strong base in this chapter will help you in the long run. These shapes are the concept that you will deal with in your graduation and masters. It gives you the confidence to deal with all the engineering data. Practice will give the confidence to deal with the chapter. This chapter not only evaluates you academically but also your brain strength to hold the number of formulae. It will improvise you by giving you remarkable brain capacity.
What Is A Proper Study Plan?
To have proper preparation, students can download the updated syllabus that is given on the Vedantu website. Click the link below to download the syllabus. Analyze the importance given to every concept in this chapter and start your preparation. Since students in grade 10 are going to appear for the board exam, they need a proper plan to prepare. This study plan will help them keep track of their progress. This will also help them figure out where they lack and where they excel. The concepts they lack will need more focus. To do so, you can download the important questions PDF that is available on the Vedantu website.
Students can learn all the important questions from this concept and understand how questions are going to be in the final examination. These important questions are set by our subject experts. Students can also make use of Seline publisher’s textbook for the Class 10 ICSE board. This textbook contains all the important questions along with the solutions that are given in a detailed manner. Students can refer to this textbook for practicing all the sums from this concept. And students can approach the Vedantu website if there are any doubts about the concept.
FAQs on Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 20 - Cylinder, Cone and Sphere (Surface Area and Volume)
1. Can I prepare all the questions given in the Selina Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 20 - Cylinder, Cone and Sphere (Surface Area and Volume)?
Yes, students can prepare all the questions that are given in the NCERT textbook. This gives the confidence to face all the questions in the final exam. Practice every day. Students can also make use of the Selin concise textbook on the Vedantu website. This textbook follows all the guidelines given by the ICSE board. This also has all the problems with explained solutions. The explanations are in the most detailed manner possible. It will be useful for the students to understand where they make mistakes.
2. What is the purpose of this chapter in grade 10?
There are many benefits for the students in Class 10 to read this chapter. This chapter consists of a lot of formulae. These formulae will be useful for them in the long run. For higher classes, students will be using thing formulae. It will increase your brain capacity. Since you are going to memorize the formulae, you can improve your memory. This chapter will be useful for you if you are going to choose engineering as your career. Shapes and areas rule the engineering. Also gives you a strong foundation.
3. What is the proper preparation for grade 10?
To get proper preparation, students will have to get a study plan. This study plan must have a syllabus, important questions, and mock tests. The syllabus analysis must be the first step. You can refer to the Vedantu website for the updated Class 10 syllabus. Along with that learn all the important questions. The important questions PDF is available for free on the Vedantu website. After practicing the important questions, practice with the mock tests. These mock test question papers are set by subject experts with extensive teaching experience.
4. Why do I have to concentrate more on math in grade 10?
Concentrating more on the math subject in your grade 20 is important. Because grade 10 is the crucial academic part. It is the stage that will sculpt your future and will decide your future. So it is important to score better marks in the examination. This math subject will act as a mark booster. It is easy to score marks in math subjects with proper preparation. And with no preparation, it may fail you. So to score better marks, concentrate more on the math subject.
5. What is a total surface area according to Selina Concise Mathematics Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 20 - Cylinder, Cone and Sphere (Surface Area and Volume)?
The total surface area of a solid can be explained as the sum of the areas of all the faces or surfaces that enclose the solid. The faces include the tops and the bottoms along with the remaining surfaces. The sum of the areas of the rectangle and the two circles is the total surface area. This is an easy-to-understand and important definition.







































