




Common Uses of Concave and Convex Mirrors in Daily Life
Uses of Spherical Mirrors are central to many optical devices, making the topic essential for every JEE Main aspirant. These mirrors, defined as sections of a sphere's surface polished to reflect light, come in two forms: concave and convex. Understanding how they function and where they are applied provides a strong conceptual base for questions often tested in competitive exams.
If you’ve ever checked your appearance on a shiny spoon or noticed a wide view in a car’s side mirror, you have experienced spherical mirrors in real life. Their unique image-forming properties lead to widespread use across industries and daily life.
Core Concepts Behind Spherical Mirrors
A spherical mirror is a curved reflecting surface that is part of a sphere. Concave mirrors have their inner surface reflective, while convex mirrors reflect from the outer surface. This difference changes how they bend and focus light.
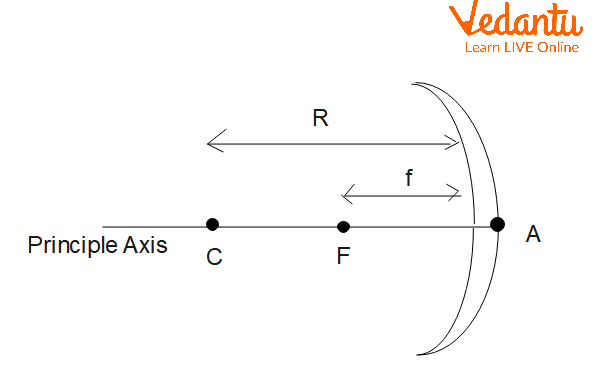
For any spherical mirror, key terms must be clear. The principal axis is a straight line through the mirror’s center. The center of curvature (C) is the sphere’s center, and the radius of curvature (R) is its distance from the mirror’s pole. The focus (F) is where parallel rays meet (concave) or appear to diverge from (convex), with focal length (f) given by f = R/2.
The fundamental equation relating object distance (u), image distance (v), and focal length (f) is the mirror formula: 1/f = 1/v + 1/u. Magnification (m) is calculated as m = -v/u, indicating how the image size compares to the object.
Concave and Convex Mirror Applications
Exam questions often ask you to match mirror type to use-case. Here, recognising image characteristics—magnified, diminished, inverted, upright—will help solve problems quickly.
Let’s break down prominent uses, focusing on why each mirror fits a particular task thanks to its optical nature.
- Concave mirrors are used in headlights to focus beams straight ahead.
- They serve as shaving and makeup mirrors by giving a magnified, upright image.
- Dentists use concave mirrors to inspect teeth, using their magnifying properties.
- Solar concentrators and reflecting telescopes use concave mirrors to collect and focus light.
- Convex mirrors are installed as vehicle side and rear-view mirrors for a wider field of view.
- ATM security and shop surveillance use convex mirrors for their ability to capture broad scenes.
You’ll notice the chosen mirror matches the practical optical need: detailed inspection demands magnification (concave), while wide-area monitoring calls for the diverging effect of convex.
Formation of Images with Spherical Mirrors
Concave and convex mirrors differ not just in geometry but in how they form images. Concave mirrors can produce real (inverted) or virtual (upright) images, depending on object placement. Convex mirrors always yield upright, diminished, virtual images, which is vital for safety and clarity in road mirrors.
For JEE Main, you may need to draw or interpret ray diagrams. Master three principal rays:
- A ray parallel to the axis passes through the focus (concave) or appears from it (convex).
- A ray through the center of curvature reflects back on itself.
- A ray hitting the pole reflects at an angle equal to incidence.
Tests often ask about sign conventions for the mirror formula. Distances measured in the direction of incident light are negative; opposite direction, positive. For concave mirrors, focal length is negative; for convex, it is positive.
Why Spherical Mirrors Matter for JEE Main
Whether it’s a matching-type, assertion-reason, or numericals, Uses of Spherical Mirrors is a high-probability topic, combining theory and practical relevance. Understanding application logic aids quick elimination in MCQs. Numerical questions may give object and image distances for you to calculate focal length or magnification, so it’s crucial to remember formulae and sign rules.
Compare spherical mirrors with lenses to solidify conceptual differences. For more on that, you can read this comparative guide.
Vedantu provides detailed, exam-aligned explanations that align with NCERT and JEE Main trends. Always draw neat diagrams where required and highlight which mirror type fits which use-case.
Summary Table: Spherical Mirrors at a Glance
| Mirror Type | Image Features | Main Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Concave | Real/virtual, larger, smaller, inverted or upright | Headlights, telescopes, shaving mirrors |
| Convex | Always virtual, upright, diminished | Rear-view, security mirrors, ATMs |
With a clear grasp of spherical mirror applications and mirror formulae, you’ll approach JEE Main optics questions efficiently and confidently. Practise drawing ray diagrams by referring to NCERT examples to reinforce your skills.
See what a typical spherical mirror looks like in physics:
By focusing on the conceptual roots and use-cases as shown, you’ll outperform rote learners and handle application-based questions smoothly in your exam. Trust Vedantu for more JEE-centric physics insights and exam tips.
FAQs on Practical Applications of Spherical Mirrors Explained
1. What are the main uses of spherical mirrors?
Spherical mirrors have various practical applications based on whether they are concave or convex mirrors. Their uses include:
- Concave mirrors: Used in shaving mirrors, makeup mirrors, dental mirrors, and solar concentrators due to their ability to form magnified images.
- Convex mirrors: Employed as rear-view mirrors in vehicles and security mirrors in stores to provide a wide field of view.
These uses depend on image formation properties described in Physics Class 10 and 12 syllabus and frequently appear in board exam questions.
2. What are the uses of concave mirrors in daily life?
Concave mirrors are widely used for their ability to form real or magnified images:
- In shaving and makeup mirrors for enlarged, upright reflections
- By dentists to examine teeth by creating a magnified image
- In solar furnaces and torches to concentrate light at a focal point
- In headlights of vehicles to project a parallel beam of light
These uses align with daily life applications described in the Physics syllabus and practical learning outcomes.
3. What are the uses of convex mirrors?
Convex mirrors are mostly used for safety and monitoring purposes due to their wide-angle reflection:
- As rear-view mirrors in cars, bikes, and other vehicles
- For security mirrors in stores and parking lots
- In ATMs and offices for surveillance
Their ability to form virtual, diminished, and wider field images makes convex mirrors highly useful, as highlighted in most Physics exams.
4. What is the function of a shaving mirror and which type of spherical mirror is used?
A shaving mirror uses a concave mirror as it produces a magnified and upright image when the face is placed between its pole and focus. This helps in getting a clear and enlarged view of the face for precise shaving.
5. Why are concave mirrors used in headlights of vehicles?
Concave mirrors are used in headlights because they reflect and concentrate light from the bulb placed near the focus, projecting a strong, parallel beam forward. This improves road visibility and safety at night, as required by CBSE Physics curriculum examples.
6. Why are convex mirrors preferred as rear-view mirrors in vehicles?
Convex mirrors give a wider field of view and always form virtual, diminished, and upright images of traffic behind, allowing drivers to see more area and drive safely. This is a standard question in Class 10 and 12 Physics exams.
7. What are the advantages of using convex mirrors in security applications?
The main advantages of convex mirrors in security are:
- Provide a large field of view to monitor wide areas easily
- Form smaller, upright images for overall surveillance
- Help prevent theft and accidents in stores, corridors, and parking lots
These points are often covered under practical applications in board exam questions.
8. In which medical instruments are spherical mirrors used?
Concave mirrors are commonly used in medical instruments such as:
- Dental mirrors for magnified view of teeth
- Ophthalmoscopes to examine eyes
- Reflecting mirrors in laryngoscopes for viewing the throat
These uses help doctors observe and treat areas clearly by producing enlarged images.
9. How do spherical mirrors help in solar energy applications?
In solar furnaces and solar cookers, concave mirrors focus sunlight onto a single point, generating intense heat for cooking or power generation. This practical use of spherical mirrors is emphasized in CBSE's renewable energy syllabus sections.
10. List four uses each of concave and convex mirrors.
Concave mirror uses:
- Shaving and makeup mirrors
- Vehicle headlights and torches
- Solar cookers and solar heaters
- Dental and medical examination tools
Convex mirror uses:
- Vehicle rear-view mirrors
- Security and surveillance mirrors in stores, schools, and roads
- Blind spot mirrors
- ATM monitoring and corridor safety mirrors
11. Name the type of spherical mirror used by dentists and explain why.
Dentists use concave mirrors to obtain a magnified and upright image of teeth. This helps in examining small cavities and other details more clearly, making dental check-ups more accurate.
12. Why do we not use concave mirrors as rear view mirrors in vehicles?
Concave mirrors are not used as rear-view mirrors because they can produce either magnified or inverted images depending on the position of the object. This can be confusing and dangerous when driving, so convex mirrors are preferred for consistent, reduced-size, and upright images.
























