
A 5m long pole of 3kg mass is placed against a smooth vertical wall as shown in the picture. Under equilibrium condition, if the pole makes an angle of \[{37^0}\] with the horizontal, the frictional force between the pole and horizontal surface is
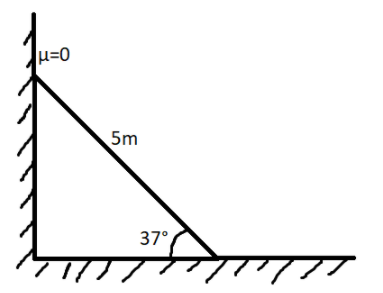
(A) $20N$
(B) $30N$
(C) ${20\mu N}$
(D) ${30\mu N}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: This could be simply solved by breaking the diagrams into simple free body diagrams of both the blocks. Then we need to apply Newton’s law of motion.
Formula used: Here, we will use the basic formula NLM-2:
${{\text{F}}_{fr}}{{ = }}\mu {\text{N}}$
Here, ${{\text{F}}_{fr}}$ is the friction force acting on the body
$\mu $ is the coefficient of friction
$N$ is normal force
Complete step by step answer:
We already know that there are frictional forces acting on the horizontal wall.
And also, we have weight acting downwards.
Frictional force in this case is opposite and equal to the horizontal component of weight.
Balancing the components:
${{mgcos\theta = \mu N}}$
For the body:
${F_{fr}} = 3 \times 10 \times \cos {37^0} = 20N$
Then we need to match the correct option.
The correct option is A.
Additional Information: Whenever a body tends to slide over another’s surface, an opposing force, called force of friction comes into play. The force acts tangentially to the interface of two bodies is known as friction. Static friction is the force of friction between two surfaces so long as there is no relative motion between them. It is always equal to the applied force whereas, kinetic friction is the force of friction which comes into play between two surfaces when there is some relative motion between them. The magnitude of force of kinetic friction (kinetic frictional force) is proportional to the normal force. The angle made by the resultant reaction force with the vertical (normal reaction) is known as the angle of the friction.
Note: It should be always kept in mind that we should always draw the FBD of the body before solving any force questions. Friction acts as a resisting force which is generated, when two solid surfaces slide against one another. Some examples are friction between our shoes and the floor stops us from slipping. Friction between tyres and the road stop cars from skidding. Friction between the brakes and wheel helps bikes and cars to slow down.
Formula used: Here, we will use the basic formula NLM-2:
${{\text{F}}_{fr}}{{ = }}\mu {\text{N}}$
Here, ${{\text{F}}_{fr}}$ is the friction force acting on the body
$\mu $ is the coefficient of friction
$N$ is normal force
Complete step by step answer:
We already know that there are frictional forces acting on the horizontal wall.
And also, we have weight acting downwards.
Frictional force in this case is opposite and equal to the horizontal component of weight.
Balancing the components:
${{mgcos\theta = \mu N}}$
For the body:
${F_{fr}} = 3 \times 10 \times \cos {37^0} = 20N$
Then we need to match the correct option.
The correct option is A.
Additional Information: Whenever a body tends to slide over another’s surface, an opposing force, called force of friction comes into play. The force acts tangentially to the interface of two bodies is known as friction. Static friction is the force of friction between two surfaces so long as there is no relative motion between them. It is always equal to the applied force whereas, kinetic friction is the force of friction which comes into play between two surfaces when there is some relative motion between them. The magnitude of force of kinetic friction (kinetic frictional force) is proportional to the normal force. The angle made by the resultant reaction force with the vertical (normal reaction) is known as the angle of the friction.
Note: It should be always kept in mind that we should always draw the FBD of the body before solving any force questions. Friction acts as a resisting force which is generated, when two solid surfaces slide against one another. Some examples are friction between our shoes and the floor stops us from slipping. Friction between tyres and the road stop cars from skidding. Friction between the brakes and wheel helps bikes and cars to slow down.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




