
A ball rolls down an inclined plane and acquires a velocity${v_r}$when it is reaching the bottom of the plane. If the same ball slides without friction and acquires rolling from the same height down an equally inclined smooth plane and acquires a velocity ${v_s}$, then which of the following statements are not correct?
A. ${v_r} < {v_s}$, because a work done by the rolling ball against the frictional force.
B. ${v_r} > {v_s}$, because the angular velocity acquired makes the rolling ball travel faster.
C. ${v_r} = {v_s}$, because the kinetic energy of the two balls is the same at the bottom of the planes.
D. ${v_r} < {v_s}$, because the rolling ball acquires rotational as well as translational kinetic energy.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: When a ball rolls down a rough plane in comparison to a smooth plane, there is an additional factor of friction acting against the downward acceleration of the rolling ball in case of a rough plane. So as a consequence the velocities will have a difference between them. Their exact relation can be concluded using Newtonian physics. And comparing it with the given options provides the right answer.
Formula Used:
Newton’s third law of motion:
$\eqalign{
& {v^2} - {u^2} = 2as \cr
& {\text{where }}v{\text{ is the final velocity of the object,}} \cr
& u{\text{ is the initial velocity of the object,}} \cr
& a{\text{ is the acceleration of the object,}} \cr
& s{\text{ is the displacement of the object}}{\text{.}} \cr} $
Complete step by step answer:
When the ball moves down a rough plane, there are a total of four components of forces acting in it as shown in the figure below. The horizontal components cancel each other out as there is no horizontal displacement clearly. Similarly, for a ball rolling down a smooth plane there are three components of forces acting as shown below:
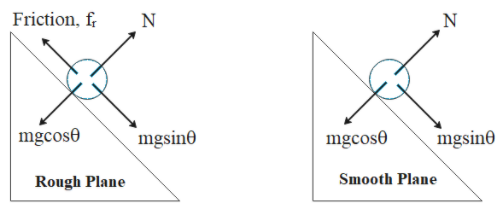
In case of the rough plane:
Let ${f_r}$ be the force of friction, and ${a_r}$ the acceleration of the ball downwards.
So we have: $mg\sin \theta - {f_r} = m{a_r} \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 1 \right)$
In case of the smooth plane:
Let ${a_s}$the acceleration of the ball downwards.
So we have: $mg\sin \theta = m{a_s} \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 2 \right)$
From equation (1) and (2), it is clear that:
${a_r} < {a_s}$
Using Newton’s third law of motion we have:
${v^2} = {u^2} + 2as$
But we know that initially in both the cases the ball was at rest, so initial velocity is zero and at the endpoint the displacement is same so, we get:
${v_r} < {v_s}$
So, it is true that${v_r} < {v_s}$.
Clearly option C is incorrect and option B is incorrect.
The work done by the rolling ball will be zero as its instantaneous displacement is zero when it rolls down the rough plane. So option A is also incorrect.
When the ball rolls down a rough surface it acquires translational as well as rotational energy. Thus the kinetic energy of the ball rolling down will be greater than the kinetic energy of the other ball moving down on a smooth plane. Hence option D. is correct.
Therefore, the incorrect statements are A, B, and C.
Note: When a sphere or ball is rolled on a horizontal surface it slows down and eventually stops because the normal force does not pass through its center, rather it gets shifted towards the right. This in turn results in an anticlockwise torque, so the net torque causes an angular deceleration.
Formula Used:
Newton’s third law of motion:
$\eqalign{
& {v^2} - {u^2} = 2as \cr
& {\text{where }}v{\text{ is the final velocity of the object,}} \cr
& u{\text{ is the initial velocity of the object,}} \cr
& a{\text{ is the acceleration of the object,}} \cr
& s{\text{ is the displacement of the object}}{\text{.}} \cr} $
Complete step by step answer:
When the ball moves down a rough plane, there are a total of four components of forces acting in it as shown in the figure below. The horizontal components cancel each other out as there is no horizontal displacement clearly. Similarly, for a ball rolling down a smooth plane there are three components of forces acting as shown below:

In case of the rough plane:
Let ${f_r}$ be the force of friction, and ${a_r}$ the acceleration of the ball downwards.
So we have: $mg\sin \theta - {f_r} = m{a_r} \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 1 \right)$
In case of the smooth plane:
Let ${a_s}$the acceleration of the ball downwards.
So we have: $mg\sin \theta = m{a_s} \cdots \cdots \cdots \left( 2 \right)$
From equation (1) and (2), it is clear that:
${a_r} < {a_s}$
Using Newton’s third law of motion we have:
${v^2} = {u^2} + 2as$
But we know that initially in both the cases the ball was at rest, so initial velocity is zero and at the endpoint the displacement is same so, we get:
${v_r} < {v_s}$
So, it is true that${v_r} < {v_s}$.
Clearly option C is incorrect and option B is incorrect.
The work done by the rolling ball will be zero as its instantaneous displacement is zero when it rolls down the rough plane. So option A is also incorrect.
When the ball rolls down a rough surface it acquires translational as well as rotational energy. Thus the kinetic energy of the ball rolling down will be greater than the kinetic energy of the other ball moving down on a smooth plane. Hence option D. is correct.
Therefore, the incorrect statements are A, B, and C.
Note: When a sphere or ball is rolled on a horizontal surface it slows down and eventually stops because the normal force does not pass through its center, rather it gets shifted towards the right. This in turn results in an anticlockwise torque, so the net torque causes an angular deceleration.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




