
A beam of light composed of red and green rays is incident obliquely at a point on the face of a rectangular glass slab. When coming out on the opposite parallel face, the red and green ray emerge from
A) Two points propagating in two different parallel directions
B) One point propagating in two different directions through slab
C) One point propagating in the same direction through the slab
D) Two points propagating in two different non-parallel directions
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: A beam of light composed of red and green ray when incidents on the glass slab forms an angle with the normal called incidence angle. Then, while passing through the rectangular glass slab gets separated into two rays. Both the rays move at different angles with the normal and thus have different angles of refraction.
Complete answer:
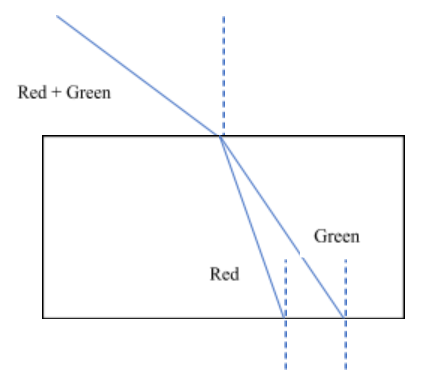
Different colors have different velocities. Thus, the velocity of red is different from the velocity of green. Due to different velocities, in a given medium, red and green refract at different angles of refraction. Thus, due to different angles of refraction they appear on opposite faces at two different points after emerging from the glass slab and move in two different parallel directions.
Hence, the correct answer is option A i.e. two points propagating in two different parallel directions.
Note: The velocity of different colours is the same in vacuum or air. When a light ray travels from one medium to another with different densities or refractive indices, then the ray refracts. However, if the light tray travels in the same medium throughout the journey then instead of refraction the ray gets reflected. There are certain laws related accompanied with reflection. The angle of incidence has to be always equal to the angle of reflection.
Complete answer:

Different colors have different velocities. Thus, the velocity of red is different from the velocity of green. Due to different velocities, in a given medium, red and green refract at different angles of refraction. Thus, due to different angles of refraction they appear on opposite faces at two different points after emerging from the glass slab and move in two different parallel directions.
Hence, the correct answer is option A i.e. two points propagating in two different parallel directions.
Note: The velocity of different colours is the same in vacuum or air. When a light ray travels from one medium to another with different densities or refractive indices, then the ray refracts. However, if the light tray travels in the same medium throughout the journey then instead of refraction the ray gets reflected. There are certain laws related accompanied with reflection. The angle of incidence has to be always equal to the angle of reflection.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




