
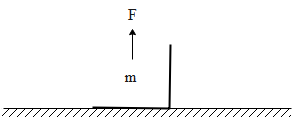
A block of mass $\mathrm{m}=2 \mathrm{kg}$ is pulled by a force $\mathrm{F}=40 \mathrm{N}$ upwards through a height
$h=2 \mathrm{m}$. Find the work done on the block by the applied force $\mathrm{F}$ and its weight $\mathrm{mg}$.
$\left(\mathrm{g}=10 \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\right)$
A ${{\text{W}}_{F}}=80\text{J};{{\text{W}}_{\text{mg}}}=-40\text{J}$
B ${{\text{W}}_{\text{F}}}=80\text{J};{{\text{W}}_{\text{mg}}}=40\text{J}$
C ${{\text{W}}_{\text{F}}}=-80\text{J};{{\text{W}}_{\text{mg}}}=-40\text{J}$
D ${{\text{W}}_{F}}=-80\text{J};{{\text{W}}_{\text{mg}}}=40\text{J}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: We know that a force is any interaction that, when unopposed, will change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (which includes to begin moving from a state of rest), that is to accelerate. Force can also be described intuitively as a push or a pull. A force has both magnitude and direction, making it a vector quantity. It is measured in the SI unit of newtons and represented by the symbol F. Force is the push or pull applied on an object. It can move a stationary object or stop a moving object. Force can also change the speed and direction of a moving object. When force is applied on an object, resulting in the movement of that object, work is said to be done. Based on this concept we have to solve this question.
Complete step by step answer
From the data of the given question, we can assume that,
Weight, $\mathrm{mg}=(2)(10)=20 \mathrm{N}$
Work done by the applied force, $\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{F}}=\mathrm{Fh} \cos 0^{\circ}$
As the angle between force and displacement is $0^{\circ}$
or $\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{F}}=(40)(2)(1)=80 \mathrm{J}$
Similarly, work done by its weight is
Therefore, we can derive the work done as
$\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{mg}}=(\mathrm{mg})(\mathrm{h}) \cos 180^{\circ}$
or $\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{mg}}=(20)(2)(-1)=-40 \mathrm{J}$
Therefore, the correct answer is Option A.
Note: We should know that tension is nothing but the drawing force acting on the body when it is hung from objects like chain, cable, string etc. It is represented by T. Tension is the force exerted by a rope, string, cable, or similar object on one or more objects. Anything pulled, hung, supported, or swung from a rope, string, cable, etc. is subject to the force of tension. Like all forces, tension can accelerate objects or cause them to deform.
It should be known to us that tension in the part of the rope that is more vertical must be greater. If the ruler has uniform mass(mass acts in the centre), and the rope is light and inextensible, then yes, the tension is equal throughout.
Complete step by step answer
From the data of the given question, we can assume that,
Weight, $\mathrm{mg}=(2)(10)=20 \mathrm{N}$
Work done by the applied force, $\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{F}}=\mathrm{Fh} \cos 0^{\circ}$
As the angle between force and displacement is $0^{\circ}$
or $\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{F}}=(40)(2)(1)=80 \mathrm{J}$
Similarly, work done by its weight is
Therefore, we can derive the work done as
$\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{mg}}=(\mathrm{mg})(\mathrm{h}) \cos 180^{\circ}$
or $\mathrm{W}_{\mathrm{mg}}=(20)(2)(-1)=-40 \mathrm{J}$
Therefore, the correct answer is Option A.
Note: We should know that tension is nothing but the drawing force acting on the body when it is hung from objects like chain, cable, string etc. It is represented by T. Tension is the force exerted by a rope, string, cable, or similar object on one or more objects. Anything pulled, hung, supported, or swung from a rope, string, cable, etc. is subject to the force of tension. Like all forces, tension can accelerate objects or cause them to deform.
It should be known to us that tension in the part of the rope that is more vertical must be greater. If the ruler has uniform mass(mass acts in the centre), and the rope is light and inextensible, then yes, the tension is equal throughout.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




