
A body is thrown vertically upward in air and air resistance is taken into account. The time of ascent is ${t_1}$ and time of descent is ${t_2}$, then which of the following is true
(A) ${t_1} = {t_2}$
(B) ${t_1} > {t_2}$
(C) ${t_1} < {t_2}$
(D) Cannot be predicted
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:In order to solve this question, we should know that air resistance force always acts in a direction opposite to that of direction of motion of the body, so here we will find effective acceleration of body in both cases and then using newton’s equation of motion to find relation between time of ascent and time of descent.
Formula used:
$v = u + at$
${v^2} - {u^2} = 2aS$
$S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
where,
v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity of the body
S is the distance covered, a is the acceleration of the body and t denotes time taken by the body.
Complete answer:
Let us assume the acceleration due to air resistance force is ‘a’ and acceleration due to gravity is ‘g’ and total height reached by the body is H, during ascent and descent of the particle the net acceleration acting on the particle is shown in the diagram as
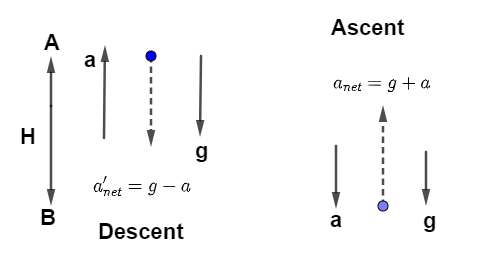
Now, During ascent time taken by the body to rise with initial velocity u and net acceleration ${a_{net}} = g + a$ is
using equation $v = u + at$ as final velocity during ascent is zero and net acceleration will be taken as negative so ${t_1} = \dfrac{u}{{g + a}}$ and height H reached by the body can be calculated using ${v^2} - {u^2} = 2aS$ we get
$
{u^2} = 2(g + a)H \\
\Rightarrow H = \dfrac{{{u^2}}}{{2(g + a)}} \to (i) \\
$
Now, during the descent the distance covered by the body will be H with acceleration $a{'_{net}} = g - a$ with time ${t_2}$ so using newton’s equation of motion as
$S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$ and since initial velocity is zero during descent so we get,
$H = \dfrac{1}{2}(g - a){t_2}^2$ using the value of H from equation (i) we get,
$
\dfrac{{{u^2}}}{{2(g + a)}} = \dfrac{1}{2}(g - a){t_2}^2 \\
{t_2} = \dfrac{u}{{g + a}}\sqrt {\dfrac{{g + a}}{{g - a}}} \\
$
using the value ${t_1} = \dfrac{u}{{g + a}}$ we get,
${t_2} = {t_1}\sqrt {\dfrac{{g + a}}{{g - a}}} $
now since, we know that $\dfrac{{g + a}}{{g - a}} > 1$ so,
${t_2} > {t_1}$ or ${t_1} < {t_2}$
So, the time of descent will be larger than the time of ascent.
Hence, the correct answer is ${t_1} > {t_2}$
Hence, the correct option is Option (B).
Note:Always pay attention while calculating the acceleration values during ascent and descent. Also consider the effect of gravity on the motion of the body during ascent and descent.
Formula used:
$v = u + at$
${v^2} - {u^2} = 2aS$
$S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
where,
v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity of the body
S is the distance covered, a is the acceleration of the body and t denotes time taken by the body.
Complete answer:
Let us assume the acceleration due to air resistance force is ‘a’ and acceleration due to gravity is ‘g’ and total height reached by the body is H, during ascent and descent of the particle the net acceleration acting on the particle is shown in the diagram as

Now, During ascent time taken by the body to rise with initial velocity u and net acceleration ${a_{net}} = g + a$ is
using equation $v = u + at$ as final velocity during ascent is zero and net acceleration will be taken as negative so ${t_1} = \dfrac{u}{{g + a}}$ and height H reached by the body can be calculated using ${v^2} - {u^2} = 2aS$ we get
$
{u^2} = 2(g + a)H \\
\Rightarrow H = \dfrac{{{u^2}}}{{2(g + a)}} \to (i) \\
$
Now, during the descent the distance covered by the body will be H with acceleration $a{'_{net}} = g - a$ with time ${t_2}$ so using newton’s equation of motion as
$S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$ and since initial velocity is zero during descent so we get,
$H = \dfrac{1}{2}(g - a){t_2}^2$ using the value of H from equation (i) we get,
$
\dfrac{{{u^2}}}{{2(g + a)}} = \dfrac{1}{2}(g - a){t_2}^2 \\
{t_2} = \dfrac{u}{{g + a}}\sqrt {\dfrac{{g + a}}{{g - a}}} \\
$
using the value ${t_1} = \dfrac{u}{{g + a}}$ we get,
${t_2} = {t_1}\sqrt {\dfrac{{g + a}}{{g - a}}} $
now since, we know that $\dfrac{{g + a}}{{g - a}} > 1$ so,
${t_2} > {t_1}$ or ${t_1} < {t_2}$
So, the time of descent will be larger than the time of ascent.
Hence, the correct answer is ${t_1} > {t_2}$
Hence, the correct option is Option (B).
Note:Always pay attention while calculating the acceleration values during ascent and descent. Also consider the effect of gravity on the motion of the body during ascent and descent.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




