
A cubical block of wood of edge 3cm floats in water. The lower surface of the cube just touches the free end of a vertical spring fixed at the bottom of the pot. Find the maximum weight that can be put on the block without wetting it. Density of wood=800kg/m3 and spring constant of the spring =50N/m. Take g=10m/s2.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:
1. Use the law of floatation which states that the weight of an object submerged in liquid is the weight of liquid displaced.
2. When the system is in rest, the forces cancel out to give net force 0.
Formula Used:
Law of floatation:
Weight of block= weight of water displaced ……(1)
Spring force F:
$F = - Kx$ ……(2)
where,
K is a force constant of spring.
x is compression of spring.
Complete step by step answer:
Diagram:
Given:
1. Side of wooden block a=3cm
2. Density of wooden block $\rho $=800kg/m3
3. Force constant of spring K=50N/m
To find: The weight put over the block without wetting it.
Step1:
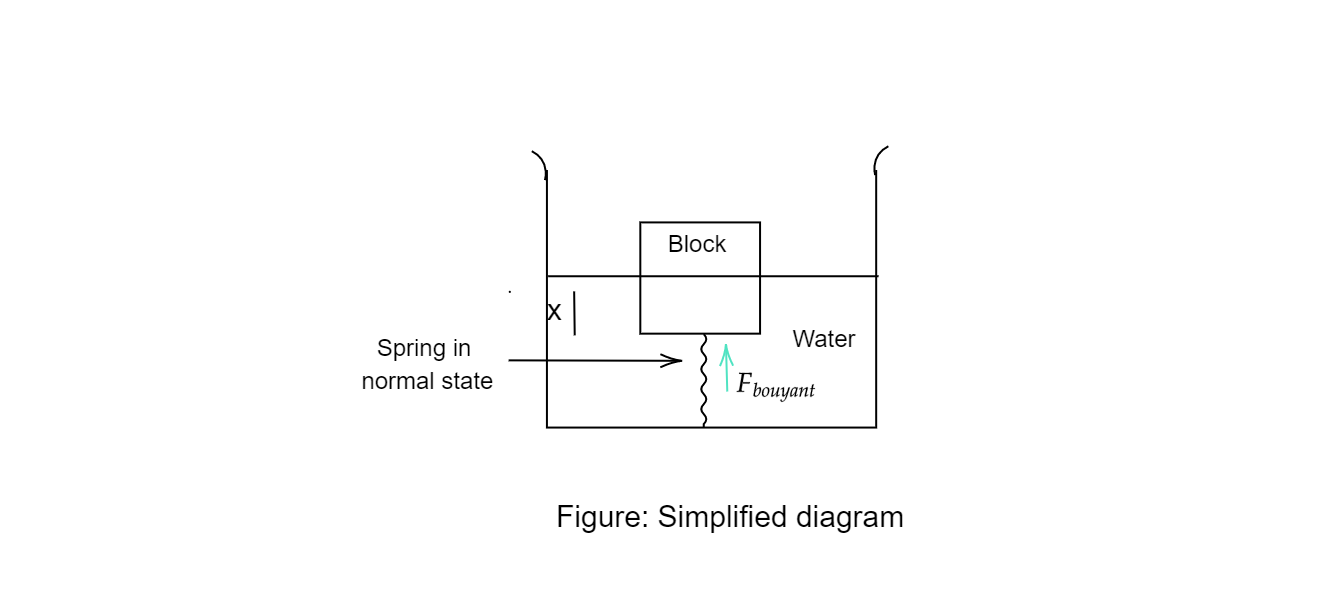
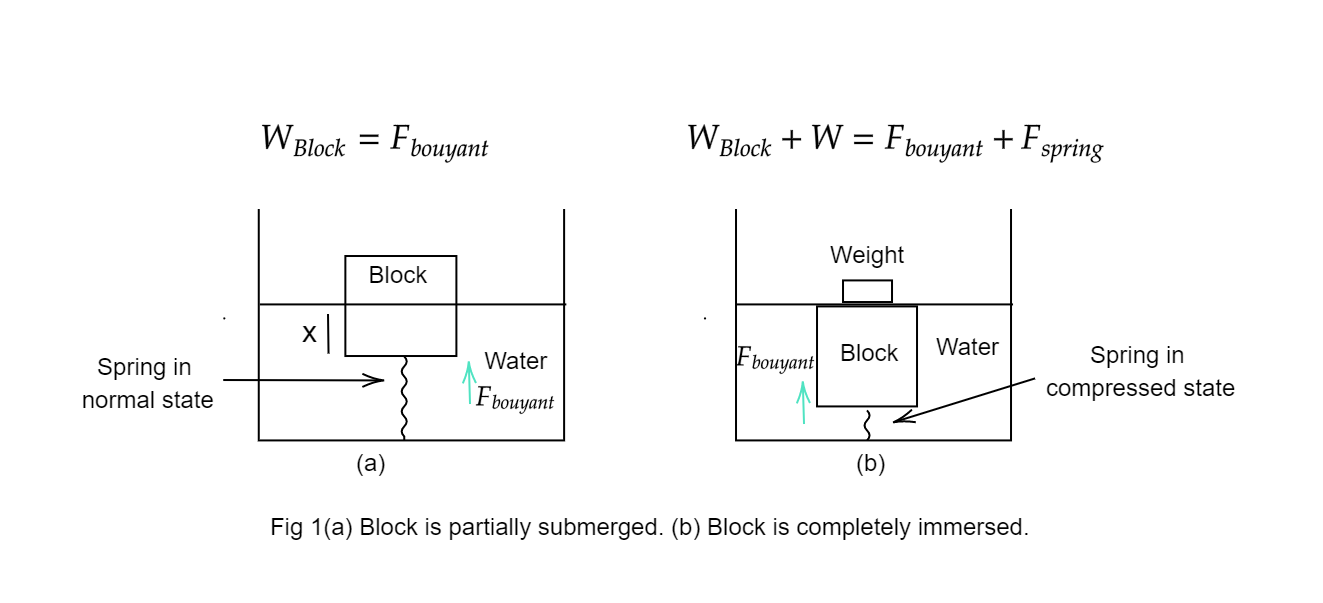
Initially in case (a), the spring is in a natural state as the block just touches it.
Let the length of the cube submerged in water be $x$. Weight of the cube is:
$ \Rightarrow {a^3}{\rho _{cube}}g = 27{(cm)^3} \times 800\left( {\dfrac{{kg}}{{{m^3}}}} \right) \times 10\left( {\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}} \right) = 21.6N$
Density of water ${\rho _w}$is 1gm/cm3. Weight of water displaced is:
$ \Rightarrow x \times {a^2} \times {\rho _w} \times g = 9000x$
Find $x$ using eq (1):
$
\Rightarrow 21.6 = 9000x \\
\Rightarrow x = 2.4cm \\
$
Step 2:
When the weight is just outside (case (b)), the spring is compressed by:
$ \Rightarrow a - x = 3 - 2.4 = 0.6cm$.
As the system is at rest, the net force in vertical direction is 0.
Buoyant force on block, $ \Rightarrow {a^3}{\rho _w}g = 27{(cm)^3} \times \dfrac{1}{{1000}}\left( {\dfrac{{kg}}{{{{(cm)}^3}}}} \right) \times 10\left( {\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}} \right) = 0.27N$
Force due to spring \[ \Rightarrow K(a - x) = 50\left( {\dfrac{N}{m}} \right) \times \dfrac{{0.6}}{{100}}\left( m \right) = 0.3N\]
Net force in downward direction = net force in upward direction
(Force due to gravity from block) + (Force due to gravity from extra weight)
= (Buoyant force on block) + (Force due to spring)
$
\Rightarrow 21.6 \times \dfrac{{10}}{{1000}} + W = 0.27 + 0.3 \\
\Rightarrow W = 0.354N \\
$
Note: Focus on the different forces acting in the vertical direction. Remember that when a spring is in its relaxed state, it exerts no force on the block. Then the force exerted by the spring in the second case will be proportional to the length by which the body has displaced.
1. Use the law of floatation which states that the weight of an object submerged in liquid is the weight of liquid displaced.
2. When the system is in rest, the forces cancel out to give net force 0.
Formula Used:
Law of floatation:
Weight of block= weight of water displaced ……(1)
Spring force F:
$F = - Kx$ ……(2)
where,
K is a force constant of spring.
x is compression of spring.
Complete step by step answer:
Diagram:

Given:
1. Side of wooden block a=3cm
2. Density of wooden block $\rho $=800kg/m3
3. Force constant of spring K=50N/m
To find: The weight put over the block without wetting it.
Step1:
Initially in case (a), the spring is in a natural state as the block just touches it.
Let the length of the cube submerged in water be $x$. Weight of the cube is:
$ \Rightarrow {a^3}{\rho _{cube}}g = 27{(cm)^3} \times 800\left( {\dfrac{{kg}}{{{m^3}}}} \right) \times 10\left( {\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}} \right) = 21.6N$
Density of water ${\rho _w}$is 1gm/cm3. Weight of water displaced is:
$ \Rightarrow x \times {a^2} \times {\rho _w} \times g = 9000x$
Find $x$ using eq (1):
$
\Rightarrow 21.6 = 9000x \\
\Rightarrow x = 2.4cm \\
$
Step 2:
When the weight is just outside (case (b)), the spring is compressed by:
$ \Rightarrow a - x = 3 - 2.4 = 0.6cm$.
As the system is at rest, the net force in vertical direction is 0.
Buoyant force on block, $ \Rightarrow {a^3}{\rho _w}g = 27{(cm)^3} \times \dfrac{1}{{1000}}\left( {\dfrac{{kg}}{{{{(cm)}^3}}}} \right) \times 10\left( {\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}} \right) = 0.27N$
Force due to spring \[ \Rightarrow K(a - x) = 50\left( {\dfrac{N}{m}} \right) \times \dfrac{{0.6}}{{100}}\left( m \right) = 0.3N\]
Net force in downward direction = net force in upward direction
(Force due to gravity from block) + (Force due to gravity from extra weight)
= (Buoyant force on block) + (Force due to spring)
$
\Rightarrow 21.6 \times \dfrac{{10}}{{1000}} + W = 0.27 + 0.3 \\
\Rightarrow W = 0.354N \\
$
Note: Focus on the different forces acting in the vertical direction. Remember that when a spring is in its relaxed state, it exerts no force on the block. Then the force exerted by the spring in the second case will be proportional to the length by which the body has displaced.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




