
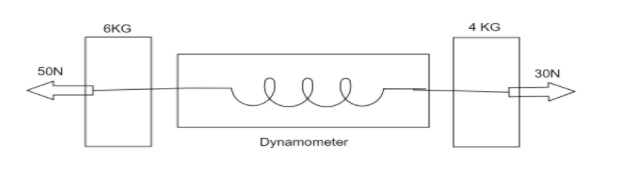
A dynamometer D is attached to two blocks of masses $6\,kg$ and $4\,kg$ as shown in the figure. The reading of the dynamometer is?
A. $18\,N$
B. $28\,N$
C. $38\,N$.
D. $48\,N$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint In the question, masses of the two blocks are given. By using the equation of the newton’s second law of motion and substituting the known parameters in that equation, we get the value of the force recorded by the dynamometer.
Formula used:
$F = ma$
Where,
$F$ be the force, $m$ be the mass and $a$ be the acceleration.
Complete step by step answer
Let x be the force recorded by the dynamometer
Given that the mass of the two blocks are $6\,kg\,{\text{and }}4kg$.
We know that, from the diagram both of the masses are applied in the same direction which means it is applied in one direction.
The largest force applied on the mass is $50\,N$ and the smallest force applied on the mass is $30\,N.$
So, the force is acting in the same direction. It lies between 50 and 30.
It can be written as,
$30 \ll x \ll 50$
The resultant force on the mass, we get
$\begin{gathered}
6\,kg\,{\text{mass}} = 50 - x \\
4\,kg\,{\text{mass}}\,\, = \,x - 30 \\
\end{gathered} $
${\text{Force}}\left( F \right) = {\text{mass}}\left( m \right) \times {\text{acceleration}}\left( a \right)$
Convert the equation of force in terms of the acceleration, we get
${\text{Acceleration}}\left( a \right) = \dfrac{{{\text{Force}}\left( F \right)}}{{{\text{mass}}\left( m \right)}}$
Comparing the two masses and substitute the known equation in the above equation, we get
$\dfrac{{\left( {50 - x} \right)}}{6} = \dfrac{{\left( {x - 30} \right)}}{4}$
Simplify the above equation, we get
$200 - x = 6x - 180$
$x = 38\,N.$
Therefore, the reading of the dynamometer is $38\,N.$
Hence from the above options, option C is correct.
Note In the question, two masses are given. The masses are acting in the same direction. So, the force is also acting on the same plane. So, we know the expression of mass and the force. By substituting the expression in the equation of motion, we get the result.
Formula used:
$F = ma$
Where,
$F$ be the force, $m$ be the mass and $a$ be the acceleration.
Complete step by step answer
Let x be the force recorded by the dynamometer
Given that the mass of the two blocks are $6\,kg\,{\text{and }}4kg$.
We know that, from the diagram both of the masses are applied in the same direction which means it is applied in one direction.
The largest force applied on the mass is $50\,N$ and the smallest force applied on the mass is $30\,N.$
So, the force is acting in the same direction. It lies between 50 and 30.
It can be written as,
$30 \ll x \ll 50$
The resultant force on the mass, we get
$\begin{gathered}
6\,kg\,{\text{mass}} = 50 - x \\
4\,kg\,{\text{mass}}\,\, = \,x - 30 \\
\end{gathered} $
${\text{Force}}\left( F \right) = {\text{mass}}\left( m \right) \times {\text{acceleration}}\left( a \right)$
Convert the equation of force in terms of the acceleration, we get
${\text{Acceleration}}\left( a \right) = \dfrac{{{\text{Force}}\left( F \right)}}{{{\text{mass}}\left( m \right)}}$
Comparing the two masses and substitute the known equation in the above equation, we get
$\dfrac{{\left( {50 - x} \right)}}{6} = \dfrac{{\left( {x - 30} \right)}}{4}$
Simplify the above equation, we get
$200 - x = 6x - 180$
$x = 38\,N.$
Therefore, the reading of the dynamometer is $38\,N.$
Hence from the above options, option C is correct.
Note In the question, two masses are given. The masses are acting in the same direction. So, the force is also acting on the same plane. So, we know the expression of mass and the force. By substituting the expression in the equation of motion, we get the result.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




