
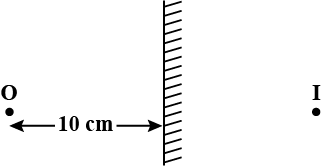
A plane mirror forms image I of an object O kept 10 cm from the mirror. It is found that when a Plano concave thin lens is placed in front of and in contact with the mirror (plane surface of the lens in contact with mirror), the position of the image formed by the plane mirror does not change. Then the refractive index of lens and radius of curvature of its curved surface are respectively'
A) $1.5,$ $10 cm$
B) $2.5,$ $10 cm$
C) $\sqrt 2 $, $10 cm$
D) $\text{All of these are possible}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: An image is defined as the collection of focus points of light rays coming from the object. The Refractive Index is defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to its speed in a specific medium. The concave lenses are best for light projection and beam expansion.
Complete step by step solution:
When the object is placed at the center of the curvature, we know that from the laws of refraction, the image will be formed at the same distance as that of the object from the optical center. Thus we can conclude that the objects must be placed at the center of the curvature of the concave lens and the refractive index of the lens is not considered.
Hence the correct option is D.
Note: 1) If the refractive index increases, the thickness of the lens decreases thus resulting in less weight. The Refractive index is independent of the angle of incidence. Optical polymers that have a high refractive index will allow the light rays to bend more within the material.
2) The radius of curvature of the lens is defined as the radius of the hollow sphere of the glass of which the lens is a part. Each lens will have two radii of curvature. And also the focal length of the lens is inversely proportional to the refractive index of the material of medium.
3) The radius of curvature is positive, when the vertex lies to the left of the center of curvature and the radius of curvature is negative, when the vertex lies to the right of the center of curvature.
Complete step by step solution:
When the object is placed at the center of the curvature, we know that from the laws of refraction, the image will be formed at the same distance as that of the object from the optical center. Thus we can conclude that the objects must be placed at the center of the curvature of the concave lens and the refractive index of the lens is not considered.
Hence the correct option is D.
Note: 1) If the refractive index increases, the thickness of the lens decreases thus resulting in less weight. The Refractive index is independent of the angle of incidence. Optical polymers that have a high refractive index will allow the light rays to bend more within the material.
2) The radius of curvature of the lens is defined as the radius of the hollow sphere of the glass of which the lens is a part. Each lens will have two radii of curvature. And also the focal length of the lens is inversely proportional to the refractive index of the material of medium.
3) The radius of curvature is positive, when the vertex lies to the left of the center of curvature and the radius of curvature is negative, when the vertex lies to the right of the center of curvature.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




