
Electric field due to uniformly charged sphere.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: This is the case of solid non-conducting spheres. We will have three cases associated with it . They are : electric fields inside the sphere, on the surface, outside the sphere .
Apply the gauss theorem to find the electric field at the three different places.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider a charged solid sphere of radius $R$ and charge $q$ which is uniformly distributed over the sphere. We will use Gauss Theorem to calculate electric fields. If $\phi $ be the electric flux and $Q$ be the charge then :
${\varepsilon _0}\phi = {Q_{enclosed}}$
Also , electric flux=electric field X area of the enclosed surface : $\phi = EA$
Case I- Inside the sphere $(r < R)$
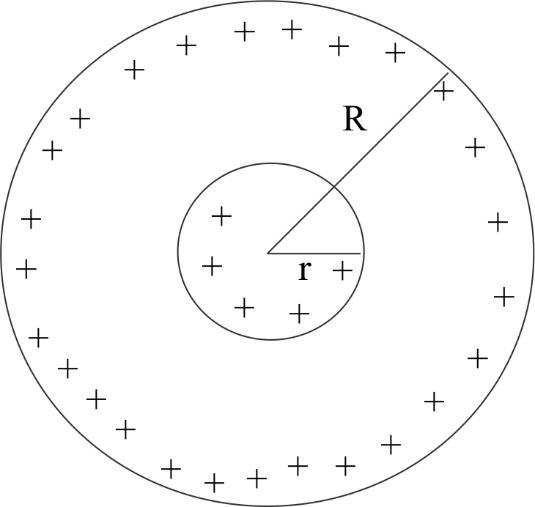
The charge distribution is uniform . Volume density will be the same. Let the charge enclosed by a circle of radius $r$ be $q'$ . Since volume density is same then-
$
\dfrac{{q'}}{{\dfrac{4}{3}\pi {r^3}}} = \dfrac{q}{{\dfrac{4}{3}\pi {R^3}}} \\
q' = q\dfrac{{{r^3}}}{{{R^3}}} \\
$
Applying Gauss Theorem here-
$
\phi = E4\pi {r^2} \\
\dfrac{{{Q_{enclosed}}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} = E4\pi {r^2} \\
\dfrac{{q'}}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} = E4\pi {r^2} \\
\dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{{r^3}}}{{{R^3}}} = E4\pi {r^2} \\
E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{qr}}{{{R^3}}} \\
$
This is the electric field inside the charged sphere .
Case II: On the surface $(r = R)$
In the above case we have calculated the electric field inside the sphere. In that formula we will put $(r = R)$ , so evaluate the electric field on the surface of the sphere .
$
E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{qr}}{{{R^3}}} \\
E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{qR}}{{{R^3}}} \\
E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{q}{{{R^2}}} \\
$
This is the electric field on the surface.
Case III: Outside the sphere $(r > R)$
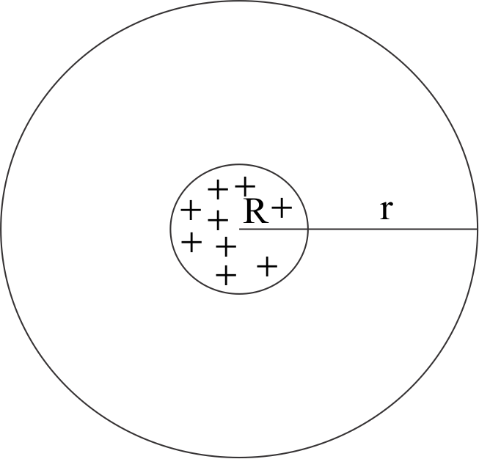
We will apply Gauss theorem in this too.
$
\phi = EA \\
\dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} = E4\pi {r^2} \\
E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{q}{{{r^2}}} \\
$
This is the electric field outside the sphere.
If we plot these variations on a graph we will get the following graph:
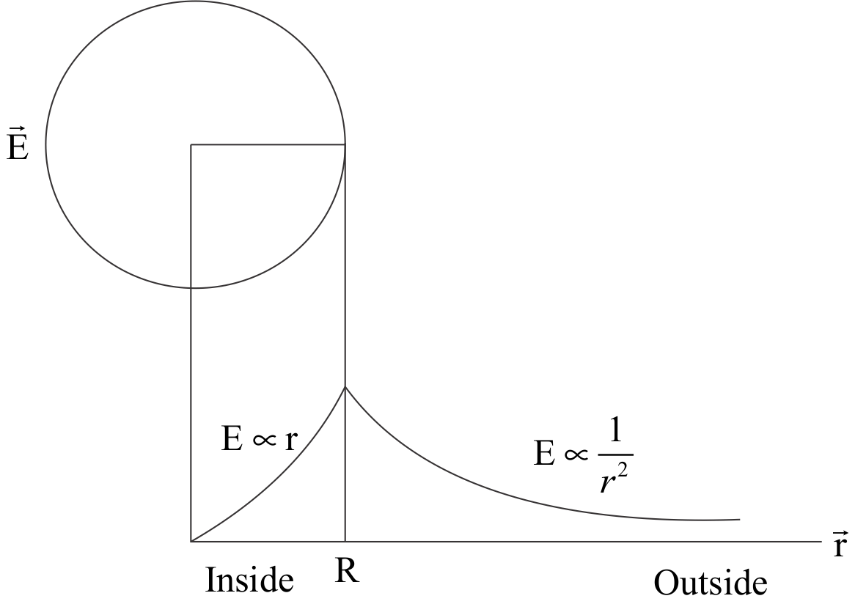
Note: Since this is a solid sphere , it has charge inside it as well and that is why the electric field is non zero. In case of a hollow spherical shell, the electric field inside the shell is zero .
Apply the gauss theorem to find the electric field at the three different places.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider a charged solid sphere of radius $R$ and charge $q$ which is uniformly distributed over the sphere. We will use Gauss Theorem to calculate electric fields. If $\phi $ be the electric flux and $Q$ be the charge then :
${\varepsilon _0}\phi = {Q_{enclosed}}$
Also , electric flux=electric field X area of the enclosed surface : $\phi = EA$
Case I- Inside the sphere $(r < R)$

The charge distribution is uniform . Volume density will be the same. Let the charge enclosed by a circle of radius $r$ be $q'$ . Since volume density is same then-
$
\dfrac{{q'}}{{\dfrac{4}{3}\pi {r^3}}} = \dfrac{q}{{\dfrac{4}{3}\pi {R^3}}} \\
q' = q\dfrac{{{r^3}}}{{{R^3}}} \\
$
Applying Gauss Theorem here-
$
\phi = E4\pi {r^2} \\
\dfrac{{{Q_{enclosed}}}}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} = E4\pi {r^2} \\
\dfrac{{q'}}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} = E4\pi {r^2} \\
\dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{{r^3}}}{{{R^3}}} = E4\pi {r^2} \\
E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{qr}}{{{R^3}}} \\
$
This is the electric field inside the charged sphere .
Case II: On the surface $(r = R)$
In the above case we have calculated the electric field inside the sphere. In that formula we will put $(r = R)$ , so evaluate the electric field on the surface of the sphere .
$
E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{qr}}{{{R^3}}} \\
E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{{qR}}{{{R^3}}} \\
E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{q}{{{R^2}}} \\
$
This is the electric field on the surface.
Case III: Outside the sphere $(r > R)$

We will apply Gauss theorem in this too.
$
\phi = EA \\
\dfrac{q}{{{\varepsilon _0}}} = E4\pi {r^2} \\
E = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi {\varepsilon _0}}} \times \dfrac{q}{{{r^2}}} \\
$
This is the electric field outside the sphere.
If we plot these variations on a graph we will get the following graph:

Note: Since this is a solid sphere , it has charge inside it as well and that is why the electric field is non zero. In case of a hollow spherical shell, the electric field inside the shell is zero .
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




