
A reaction that occurs only when heat is added is best described as:
A. Exothermic
B. Endothermic
C. An equilibrium process
D. Spontaneous
E. Non-spontaneous
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: Chemical reaction is a process in which one or more substances are converted to more different substances. Substances may be either chemical elements or compounds. Some reactions may involve energy changes, like absorption of heat energy etc.
Complete step by step answer:
An endothermic reaction is a chemical reaction in which more energy is needed to break bonds in the reactants than the energy released when new bonds are formed in the form of products. These are basically the reactions in which the reactants absorb heat energy from the surroundings to form products. This reaction occurs only when the heat is added.
Moreover, these reactions lower the temperature of their surrounding area, thereby creating a cooling effect.
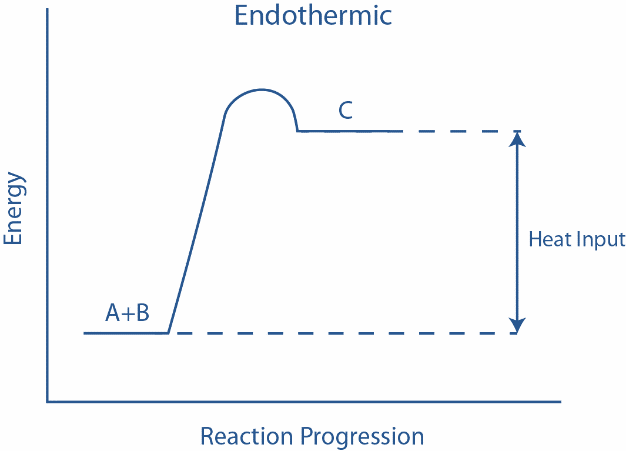
Now, in the given picture, the energy tied up in the molecular bonds is greater in the products than in the reactants. However, there is a need for the activation energy to commence the reaction but, once that hurdle is overcome, the reaction proceeds resulting in the formation of product C and the resulting product has more bond energy than the reactants. Some examples of endothermic reactions are melting of ice to form water, sublimation of solid $C{O_2}$ , baking of bread, evaporation of liquid water to form water vapor etc.
Hence, option B is correct.
Note: For exothermic reactions, the potential energy of the product is generally lower than that of the reactants. On the other hand, the potential energy of the product in an endothermic reaction is higher than that of the reactants.
Complete step by step answer:
An endothermic reaction is a chemical reaction in which more energy is needed to break bonds in the reactants than the energy released when new bonds are formed in the form of products. These are basically the reactions in which the reactants absorb heat energy from the surroundings to form products. This reaction occurs only when the heat is added.
Moreover, these reactions lower the temperature of their surrounding area, thereby creating a cooling effect.

Now, in the given picture, the energy tied up in the molecular bonds is greater in the products than in the reactants. However, there is a need for the activation energy to commence the reaction but, once that hurdle is overcome, the reaction proceeds resulting in the formation of product C and the resulting product has more bond energy than the reactants. Some examples of endothermic reactions are melting of ice to form water, sublimation of solid $C{O_2}$ , baking of bread, evaporation of liquid water to form water vapor etc.
Hence, option B is correct.
Note: For exothermic reactions, the potential energy of the product is generally lower than that of the reactants. On the other hand, the potential energy of the product in an endothermic reaction is higher than that of the reactants.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




