
A rod of length $L$ rotates about an axis passing through one of its ends and perpendicular to its plane. If the linear mass density of the rod varies as $\rho = \left( {A{r^3} + B} \right){\text{kg/m}}$ then find the moment of inertia of the rod about the given axis of rotation.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Linear mass density refers to the mass per unit length of an object. To find the moment of inertia of the rod view it as a collection of small particles/infinitesimals and find their mass(using the linear mass density) and position/distance from the axis to find their individual moment of inertia and then integrate under appropriate limits to find the moment of inertia of entire rod.
Formula Used:
The moment of inertia of a rod of length $L$ rotating about an axis is given by, $I = \int\limits_0^M {dm \cdot {r^2}} $ where $dm$ is the mass of a small element in the rod at a distance $r$from its end.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: Sketch a figure representing the rod and list the parameters given.
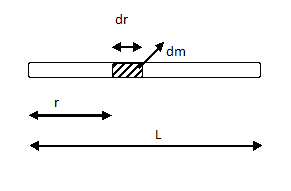
In the figure, we consider a small element of mass $dm$ and length $dr$ at a distance $r$from the end of the rod through which the rotating axis passes.
Given, the linear mass density of the rod is $\rho = \left( {A{r^3} + B} \right){\text{kg/m}}$ where $A$ and $B$ are constants and $L$ is the length of the rod.
Step 2: Express the relation for the moment of inertia of the rod about an axis passing through one end of the rod and find its moment of inertia about that axis.
The moment of inertia of a rod of length $L$ rotating about an axis passing through one end of the rod is given by, $I = \int\limits_0^M {dm \cdot {r^2}} $ ----------(1)
where $dm$ is the mass of a small element in the rod at a distance $r$from its end.
The mass of the element of the rod can be expressed in terms of its linear density as $dm = \rho dr = \left( {A{r^3} + B} \right)dr$ .
Substituting for $dm = \left( {A{r^3} + B} \right)dr$ in the equation (1) and changing the limits of the integral we get, $I = \int\limits_0^L {\left( {A{r^3} + B} \right){r^2}dr} $
Simplifying the above integral we get, $I = \int\limits_0^L {\left( {A{r^5} + B{r^2}} \right)dr} $
Splitting the integrals and calculating we get, $I = \left[ {\dfrac{{A{r^6}}}{6}} \right]_0^L + \left[ {\dfrac{{B{r^3}}}{3}} \right]_0^L$
Applying the limits in the above expression we get $I = \left[ {\dfrac{{A{L^6}}}{6}} \right] + \left[ {\dfrac{{B{L^3}}}{3}} \right]$
Simplifying we get, $I = \dfrac{{{L^3}}}{3}\left( {\dfrac{{A{L^3}}}{2} + B} \right)$
$\therefore $ the moment of inertia of the rod about the given axis is $I = \dfrac{{{L^3}}}{3}\left( {\dfrac{{A{L^3}}}{2} + B} \right)$ .
Note: It is always important to break down any solid continuous body into small finite elements known as infinitesimals on which the equation for a particle can be applied and then integrate under proper limits to find the moment of inertia of the entire system of particles/continuous body.
Formula Used:
The moment of inertia of a rod of length $L$ rotating about an axis is given by, $I = \int\limits_0^M {dm \cdot {r^2}} $ where $dm$ is the mass of a small element in the rod at a distance $r$from its end.
Complete step by step answer:
Step 1: Sketch a figure representing the rod and list the parameters given.

In the figure, we consider a small element of mass $dm$ and length $dr$ at a distance $r$from the end of the rod through which the rotating axis passes.
Given, the linear mass density of the rod is $\rho = \left( {A{r^3} + B} \right){\text{kg/m}}$ where $A$ and $B$ are constants and $L$ is the length of the rod.
Step 2: Express the relation for the moment of inertia of the rod about an axis passing through one end of the rod and find its moment of inertia about that axis.
The moment of inertia of a rod of length $L$ rotating about an axis passing through one end of the rod is given by, $I = \int\limits_0^M {dm \cdot {r^2}} $ ----------(1)
where $dm$ is the mass of a small element in the rod at a distance $r$from its end.
The mass of the element of the rod can be expressed in terms of its linear density as $dm = \rho dr = \left( {A{r^3} + B} \right)dr$ .
Substituting for $dm = \left( {A{r^3} + B} \right)dr$ in the equation (1) and changing the limits of the integral we get, $I = \int\limits_0^L {\left( {A{r^3} + B} \right){r^2}dr} $
Simplifying the above integral we get, $I = \int\limits_0^L {\left( {A{r^5} + B{r^2}} \right)dr} $
Splitting the integrals and calculating we get, $I = \left[ {\dfrac{{A{r^6}}}{6}} \right]_0^L + \left[ {\dfrac{{B{r^3}}}{3}} \right]_0^L$
Applying the limits in the above expression we get $I = \left[ {\dfrac{{A{L^6}}}{6}} \right] + \left[ {\dfrac{{B{L^3}}}{3}} \right]$
Simplifying we get, $I = \dfrac{{{L^3}}}{3}\left( {\dfrac{{A{L^3}}}{2} + B} \right)$
$\therefore $ the moment of inertia of the rod about the given axis is $I = \dfrac{{{L^3}}}{3}\left( {\dfrac{{A{L^3}}}{2} + B} \right)$ .
Note: It is always important to break down any solid continuous body into small finite elements known as infinitesimals on which the equation for a particle can be applied and then integrate under proper limits to find the moment of inertia of the entire system of particles/continuous body.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




