
A sphere of radius r is kept on a concave mirror of radius of curvature R. The arrangement's horizontal table (the surface of the concave mirror is frictionless and sliding not rolling displaced from its equilibrium position and left, then it executes S.H.M. The period of oscillation will be:
(A) $2 \pi \sqrt{\left[\dfrac{(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{r}) 1.4}{\mathrm{g}}\right]}$
(B) $2 \pi \sqrt{\left[\dfrac{(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{r})}{\mathrm{g}}\right]}$
(C) $2 \pi \sqrt{\left[\dfrac{\mathrm{Rr}}{\mathrm{g}}\right]}$
(D) $2 \pi \sqrt{\left[\dfrac{\mathrm{R}}{\mathrm{gr}}\right]}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: We know that angular acceleration is the change in angular velocity divided by time, while tangential acceleration is the change in linear velocity divided by time. People sometimes forget that angular acceleration does not change with radius, but tangential acceleration does. Acceleration is a change in velocity, either in its magnitude that is speed or in its direction, or both. In uniform circular motion, the direction of the velocity changes constantly, so there is always an associated acceleration, even though the speed might be constant.
Complete step by step answer
The diagram for the given question is given as:
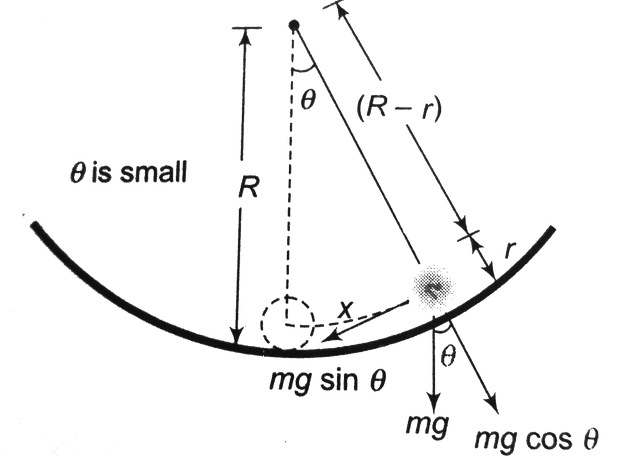
We know that the concept of tangential acceleration is used to measure the change in the tangential velocity of a point with a specific radius with the change in time. Tangential acceleration is defined as the rate of change of tangential velocity of the matter in the circular path.
We know that tangential acceleration, $a_{1}=-g \sin \theta=-g \theta$
$-\quad a_{1}=-g^{\prime} \dfrac{x}{(R-r)}$
Motion is SHM is with time period $T=2 \pi \sqrt{\dfrac{\text { displacement }}{\text { acceleration }}}=2 \pi \sqrt{\dfrac{x}{\dfrac{g x}{(R-r)}}}=2 \pi \sqrt{\dfrac{R-r}{g}}$
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note: We can say that in physics, circular motion is a movement of an object along the circumference of a circle or rotation along a circular path. Since the object's velocity vector is constantly changing direction, the moving object is undergoing acceleration by a centripetal force in the direction of the center of rotation. Any time the speed of an object is changing, it has an acceleration. Angular acceleration is defined as the rate at which the angular velocity is changing. If the Ferris wheel speeds up at a constant rate, then we would say that the angular acceleration is constant.
Complete step by step answer
The diagram for the given question is given as:

We know that the concept of tangential acceleration is used to measure the change in the tangential velocity of a point with a specific radius with the change in time. Tangential acceleration is defined as the rate of change of tangential velocity of the matter in the circular path.
We know that tangential acceleration, $a_{1}=-g \sin \theta=-g \theta$
$-\quad a_{1}=-g^{\prime} \dfrac{x}{(R-r)}$
Motion is SHM is with time period $T=2 \pi \sqrt{\dfrac{\text { displacement }}{\text { acceleration }}}=2 \pi \sqrt{\dfrac{x}{\dfrac{g x}{(R-r)}}}=2 \pi \sqrt{\dfrac{R-r}{g}}$
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note: We can say that in physics, circular motion is a movement of an object along the circumference of a circle or rotation along a circular path. Since the object's velocity vector is constantly changing direction, the moving object is undergoing acceleration by a centripetal force in the direction of the center of rotation. Any time the speed of an object is changing, it has an acceleration. Angular acceleration is defined as the rate at which the angular velocity is changing. If the Ferris wheel speeds up at a constant rate, then we would say that the angular acceleration is constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Important Concepts and Tips for JEE

How to find Oxidation Number - Important Concepts for JEE

How Electromagnetic Waves Are Formed Explained Simply

Household Electricity: Basics, Usage & Safety Explained

Hinge Force Explained: Formula, Examples & Applications

Half Life of Zero Order Reaction for JEE

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




