
A uniform magnetic field B exists in the region between $x=0$ and $x = \dfrac{3R}{2}$ (region 2 in the figure) pointing normally into the plane of the paper. A particle with charge $+Q$ and momentum p directed along the x- axis enters region 2 from region 1 at point P1 $(y =-R)$. Which of the following option(s) is/are correct ?
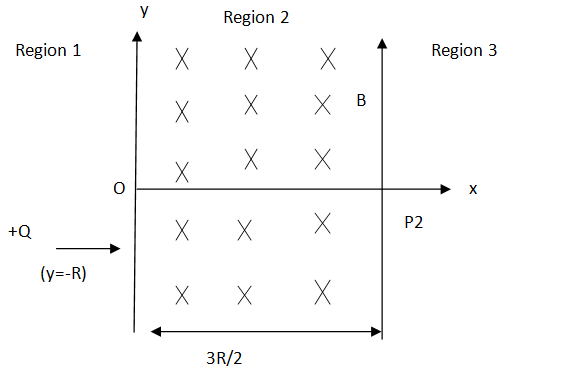
A) For $B = \dfrac{8}{{13}}\dfrac{P}{{QR}}$, the particle will enter region 3 through the point P2 on the x-axis.
B) For $B$ > $\dfrac{2}{3}\dfrac{P}{{QR}}$, the particle will re- enter region 1
C) For a fixed B, particles of same charge $Q$ and same velocity v, the distance between the point P1 and point of re-entry region 1 is inversely proportional to the mass of the particle.
D) When the particle re-enters region 1 through the longest possible path in region 2, the magnitude of the change in its linear momentum between point P1 and the farthest point from y- axis is $\dfrac{p}{{\sqrt 2 }}$.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The above question will counter the Centripetal force and electromagnetic force.
Centripetal force comes into play when the path taken by charge is circular and the electromagnetic force is seen when a charge moves in a magnetic field and the charge experiences the force.
Centripetal force is given by; $\dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r}$ (m is the mass of the charge, v is the velocity of the charge, r is the distance from the centre of the circle to the periphery of the circle)
Electromagnetic force is given as: $F = qv \times B$ (B is the magnetic field, q is the charge, v is the velocity, F is the electromagnetic force)
On equalizing the two forces we will solve the given problem.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us define centripetal force and Electromagnetic force in more detail first before doing the calculation.
A centripetal force is a net force that acts on an object to keep it moving along a circular path. As per Newton's first law of motion, an object keeps on moving along the same straight path unless an external force is applied on it, by external force we mean here the centripetal force. Centripetal force is not the fundamental force but a force that keeps the object intact while moving in a circular path.
Electromagnetic force: Electromagnetic force is a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. It acts between charged particles and is the combination of all magnetic and electrical forces. The electromagnetic force can be attractive or repulsive.
Now, we will come to the calculation part of the problem.
For the charge Q to return to region 1, the radius of the circular path taken by charge must be $\dfrac{3R}{2}$ which is the distance between region 1 and region 2.
Therefore, we will equate centripetal force and electromagnetic force.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{{(\dfrac{{3R}}{2})}} = QvB$
We will cancel the common terms from the above written equation and substitute $p =mv$;
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2p}}{{3R}} = QB$ .......................2
From equation 2 we can conclude that B should be greater than or equal to $\Rightarrow \dfrac{{2p}}{{3R}}$.
Option A is correct.
When $B = \dfrac{{8p}}{{13QR}}$ ...........................3
Again on equating centripetal force and electromagnetic force and substituting the value of B from equation 3
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r}} \right) = Qv(\dfrac{{8p}}{{13QR}})$
On cancelling the common terms we have;
$ \Rightarrow r = \dfrac{{13R}}{8}$
Thus, particles enter region 3 through point P2 on the x-axis as $r=\dfrac{13R}{8}$ is greater than $r = \dfrac{3R}{2}$.
Option B is correct.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r} = QvB$ (As per the equation r is directly proportional to m)
Thus, option C and D are incorrect.
Option A and B are correct.
Note: Electromagnetic force has many applications such as motion of the conductor in magnetic field when current is allowed to pass through the conductor (in alternators, dc motors). Similarly Centripetal force too has applications like the rotation and revolution of planets around the sun is possible all because of centripetal force.
Centripetal force comes into play when the path taken by charge is circular and the electromagnetic force is seen when a charge moves in a magnetic field and the charge experiences the force.
Centripetal force is given by; $\dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r}$ (m is the mass of the charge, v is the velocity of the charge, r is the distance from the centre of the circle to the periphery of the circle)
Electromagnetic force is given as: $F = qv \times B$ (B is the magnetic field, q is the charge, v is the velocity, F is the electromagnetic force)
On equalizing the two forces we will solve the given problem.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us define centripetal force and Electromagnetic force in more detail first before doing the calculation.
A centripetal force is a net force that acts on an object to keep it moving along a circular path. As per Newton's first law of motion, an object keeps on moving along the same straight path unless an external force is applied on it, by external force we mean here the centripetal force. Centripetal force is not the fundamental force but a force that keeps the object intact while moving in a circular path.
Electromagnetic force: Electromagnetic force is a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. It acts between charged particles and is the combination of all magnetic and electrical forces. The electromagnetic force can be attractive or repulsive.
Now, we will come to the calculation part of the problem.
For the charge Q to return to region 1, the radius of the circular path taken by charge must be $\dfrac{3R}{2}$ which is the distance between region 1 and region 2.
Therefore, we will equate centripetal force and electromagnetic force.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{{(\dfrac{{3R}}{2})}} = QvB$
We will cancel the common terms from the above written equation and substitute $p =mv$;
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2p}}{{3R}} = QB$ .......................2
From equation 2 we can conclude that B should be greater than or equal to $\Rightarrow \dfrac{{2p}}{{3R}}$.
Option A is correct.
When $B = \dfrac{{8p}}{{13QR}}$ ...........................3
Again on equating centripetal force and electromagnetic force and substituting the value of B from equation 3
$ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r}} \right) = Qv(\dfrac{{8p}}{{13QR}})$
On cancelling the common terms we have;
$ \Rightarrow r = \dfrac{{13R}}{8}$
Thus, particles enter region 3 through point P2 on the x-axis as $r=\dfrac{13R}{8}$ is greater than $r = \dfrac{3R}{2}$.
Option B is correct.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r} = QvB$ (As per the equation r is directly proportional to m)
Thus, option C and D are incorrect.
Option A and B are correct.
Note: Electromagnetic force has many applications such as motion of the conductor in magnetic field when current is allowed to pass through the conductor (in alternators, dc motors). Similarly Centripetal force too has applications like the rotation and revolution of planets around the sun is possible all because of centripetal force.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




