
A uniform rod of 20 kg is hanging in a horizontal position with the help of two threads. It also supports a 40 kg mass as shown in the figure. Find the tensions developed in each thread.

Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: We will draw a free body diagram. We will calculate tension in string using translational equilibrium using $\Sigma F = 0$. Then using rotational equilibrium $\tau = 0$, we will calculate individual tensions at point C and D.
Complete step by step answer:
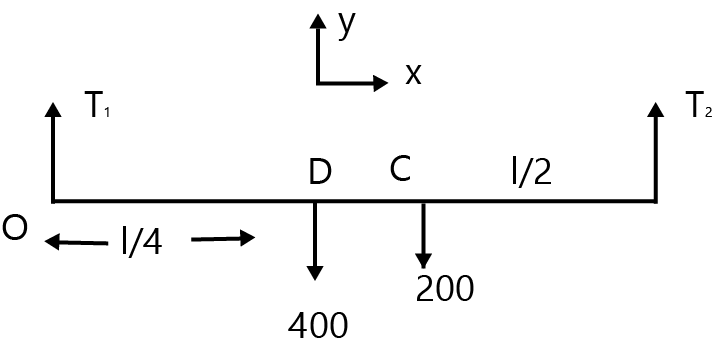
Free body diagram is shown in the figure.
Translational Equilibrium:
A body moving with constant velocity or no acceleration. Then it is said to possess translational equilibrium.
$\Sigma F = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \Sigma \,m\,a = 0$
$ \Rightarrow a = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}} = 0$
$v = const$
Rotational Equilibrium:
A body experiencing a constant rotational velocity or no angular acceleration.
$\Sigma \tau = 0$
$\Sigma \,r \times F = 0$
$F = 0$
In this case object shows a rotational motion in only one direction at a constant angular velocity
$\omega = 0$
According to translational equilibrium
$\Sigma {F_y} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow {T_1} + {T_2} = 0$
${T_1}$= tension in string where 40 kg mass is hanged at a distance of $\dfrac{l}{4}$
${T_2}$= tension in string lying at a distance of $\dfrac{l}{2}$ at point C as shown in figure.
$ = 40 \times 10 + 20 \times 10$
$ = 400 + 200N$
$ = 600N$
According to rotational equilibrium
Applying at A, we get
${\tau _A} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow - 400\,(l/4) - 200(l/2) + {T_2}l = 0$
${T_2} = 200N$
${T_1} = 100N$
Therefore, tension in string AB is 600 N and tensions at point D and C is 200 N and 100 N respectively.
Note:
If value of g is taken as $9.8\,\dfrac{m}{{{{\sec }^2}}}$instead of $10\dfrac{m}{{{{\sec }^2}}}$ then values would have been different. If the object would have been accelerating then there would be no equilibrium.
Since the direction in which force is acting at point C and D is opposite to point A and B do opposite signs will be used while doing calculation. Negative signs used while calculating torque indicates direction.
Complete step by step answer:

Free body diagram is shown in the figure.
Translational Equilibrium:
A body moving with constant velocity or no acceleration. Then it is said to possess translational equilibrium.
$\Sigma F = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \Sigma \,m\,a = 0$
$ \Rightarrow a = 0$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}} = 0$
$v = const$
Rotational Equilibrium:
A body experiencing a constant rotational velocity or no angular acceleration.
$\Sigma \tau = 0$
$\Sigma \,r \times F = 0$
$F = 0$
In this case object shows a rotational motion in only one direction at a constant angular velocity
$\omega = 0$
According to translational equilibrium
$\Sigma {F_y} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow {T_1} + {T_2} = 0$
${T_1}$= tension in string where 40 kg mass is hanged at a distance of $\dfrac{l}{4}$
${T_2}$= tension in string lying at a distance of $\dfrac{l}{2}$ at point C as shown in figure.
$ = 40 \times 10 + 20 \times 10$
$ = 400 + 200N$
$ = 600N$
According to rotational equilibrium
Applying at A, we get
${\tau _A} = 0$
$ \Rightarrow - 400\,(l/4) - 200(l/2) + {T_2}l = 0$
${T_2} = 200N$
${T_1} = 100N$
Therefore, tension in string AB is 600 N and tensions at point D and C is 200 N and 100 N respectively.
Note:
If value of g is taken as $9.8\,\dfrac{m}{{{{\sec }^2}}}$instead of $10\dfrac{m}{{{{\sec }^2}}}$ then values would have been different. If the object would have been accelerating then there would be no equilibrium.
Since the direction in which force is acting at point C and D is opposite to point A and B do opposite signs will be used while doing calculation. Negative signs used while calculating torque indicates direction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




