
(a) What is shunt?
(b) State Ampere’s circuital law. Using the law, obtain an expression for the magnetic field well aside the solenoid of finite length
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Shunt can be an electrical device that is used to protect valuable electrical equipment from electrical surges by providing a low resistance path. Ampere’s current law deals with the magnetic field due to a current loop. It gives us a relation between the two quantities.
Complete step-by-step answer:
(a) A stunt is an electrical circuit which provides an alternate low resistance path to pass around a point in the circuit. Hence, we can say that a shunt connection is a parallel low resistance path with respect to another element in the circuit. Now, the word ‘shunt’ is used to denote parallel connection as well. However, it should be a low resistance path.
One of the uses of shunt is as a protective device. If there is a surge of current in the circuit, it will flow through the low resistance path and the other device will be protected.
(b) Ampere’s circuital law is one of the most important laws in the domain of electromagnetism. It states that,
“The line integral of the magnetic field around some closed loop is equal to the net current enclosed by this path’
So, the mathematical expression of the Ampere’s circuital law is,
$\oint{B.dl={{\mu }_{0}}I}$
Where, I is the total current passing through the loop
B is the magnetic field due to the wire.
Now, let’s use this law to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid of finite length.
Let’s look at the following diagram to understand the application of Ampere’s law.
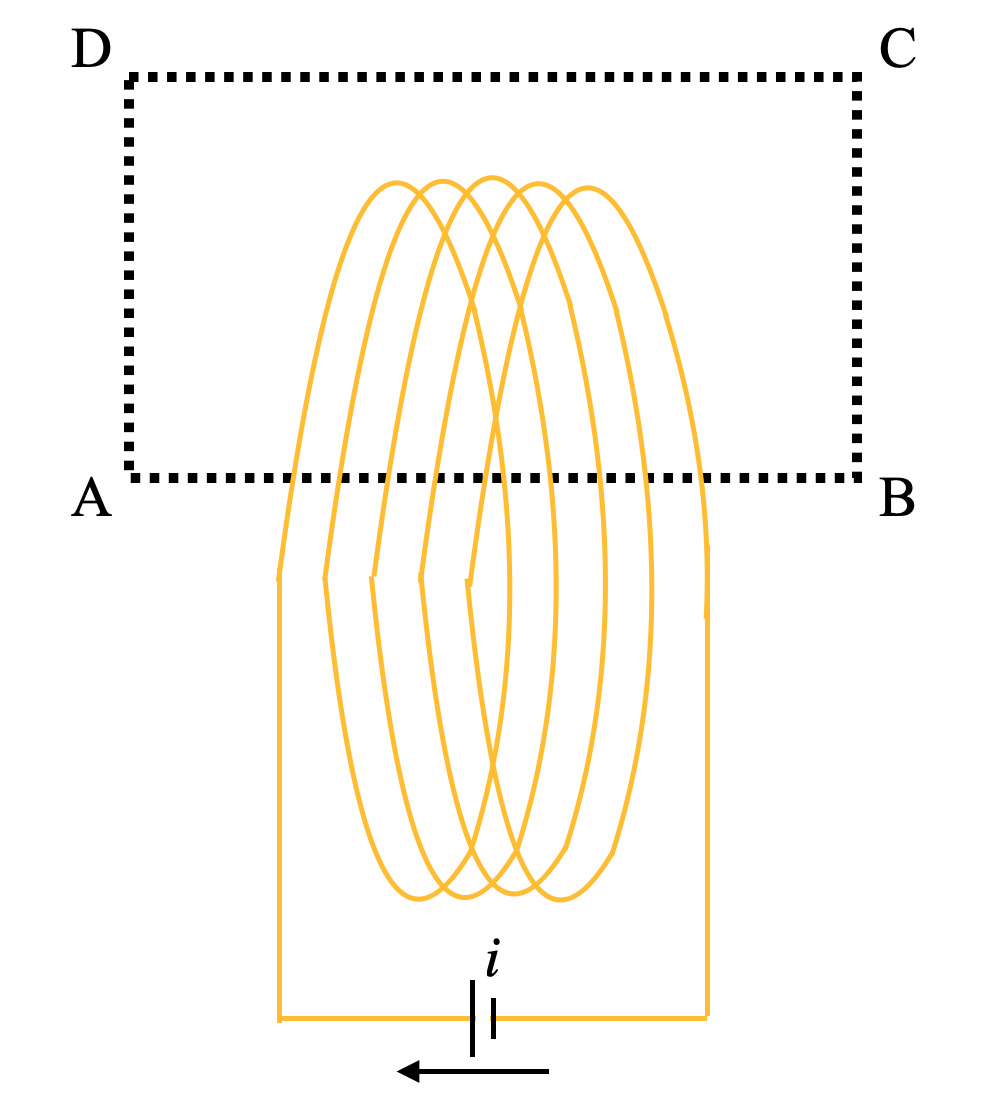
Let the length of the solenoid be ‘l’
And the number of turns is ‘I’.
Let the square ABCD be the enclosed path in which AB passes through the coaxial loops of the solenoid.
We will assume that the solenoid only has a magnetic field inside the solenoid. However, there is no magnetic field outside and there is no fringing effect as well at the end of the solenoid.
So, we can write ampere’s law for the loop ABCD,
$\oint\limits_{ABCD}{B.dl={{\mu }_{0}}I}$
We can divide the term $\oint\limits_{ABCD}{B.dl}$ in four segments, which are as follows-
$\oint\limits_{ABCD}{B.dl}=\oint\limits_{AB}{B.dl}+\oint\limits_{BC}{B.dl}+\oint\limits_{CD}{B.dl}+\oint\limits_{DA}{B.dl}$
$\Rightarrow \oint\limits_{ABCD}{B.dl}=\oint\limits_{AB}{B.dl}$
$\Rightarrow \oint\limits_{ABCD}{B.dl}=B.l$
Total current passing through the loop =
Current × Number of turns
$=NI$
Hence, we can write,
$Bl={{\mu }_{0}}NI$
$\Rightarrow B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}NI}{l}$
So, the magnetic field inside the solenoid =
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}NI}{l}$
Note:
We need to define the loop such that it is simple to perform the line integral. You can divide the line integral into various segments so that the calculation is easy. Generally, we express the term in turns per unit length, because that is a significant quantity while deriving the magnetic flux or self-inductance.
Complete step-by-step answer:
(a) A stunt is an electrical circuit which provides an alternate low resistance path to pass around a point in the circuit. Hence, we can say that a shunt connection is a parallel low resistance path with respect to another element in the circuit. Now, the word ‘shunt’ is used to denote parallel connection as well. However, it should be a low resistance path.
One of the uses of shunt is as a protective device. If there is a surge of current in the circuit, it will flow through the low resistance path and the other device will be protected.
(b) Ampere’s circuital law is one of the most important laws in the domain of electromagnetism. It states that,
“The line integral of the magnetic field around some closed loop is equal to the net current enclosed by this path’
So, the mathematical expression of the Ampere’s circuital law is,
$\oint{B.dl={{\mu }_{0}}I}$
Where, I is the total current passing through the loop
B is the magnetic field due to the wire.
Now, let’s use this law to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid of finite length.
Let’s look at the following diagram to understand the application of Ampere’s law.

Let the length of the solenoid be ‘l’
And the number of turns is ‘I’.
Let the square ABCD be the enclosed path in which AB passes through the coaxial loops of the solenoid.
We will assume that the solenoid only has a magnetic field inside the solenoid. However, there is no magnetic field outside and there is no fringing effect as well at the end of the solenoid.
So, we can write ampere’s law for the loop ABCD,
$\oint\limits_{ABCD}{B.dl={{\mu }_{0}}I}$
We can divide the term $\oint\limits_{ABCD}{B.dl}$ in four segments, which are as follows-
$\oint\limits_{ABCD}{B.dl}=\oint\limits_{AB}{B.dl}+\oint\limits_{BC}{B.dl}+\oint\limits_{CD}{B.dl}+\oint\limits_{DA}{B.dl}$
$\Rightarrow \oint\limits_{ABCD}{B.dl}=\oint\limits_{AB}{B.dl}$
$\Rightarrow \oint\limits_{ABCD}{B.dl}=B.l$
Total current passing through the loop =
Current × Number of turns
$=NI$
Hence, we can write,
$Bl={{\mu }_{0}}NI$
$\Rightarrow B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}NI}{l}$
So, the magnetic field inside the solenoid =
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}NI}{l}$
Note:
We need to define the loop such that it is simple to perform the line integral. You can divide the line integral into various segments so that the calculation is easy. Generally, we express the term in turns per unit length, because that is a significant quantity while deriving the magnetic flux or self-inductance.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




