
An acyl halide is formed when \[PC{l_5}\] reacts with an:
A. Acid
B. Alcohol
C. Amide
D. Ester
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Let us first understand some basic concepts before we proceed with the solution for this question:
Acyl halides can be explained as the halogen substituted hydroxyl groups in organic compounds. Acyl halides are basically formed when the hydroxy or the -OH group of the hydroxyl or -COOH group gets replaced by a halogen. This is a basic substitution reaction.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
In order to solve this question, we must find the products formed by \[PC{l_5}\] with all the given options.
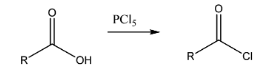
Reaction with acid: the reaction of \[PC{l_5}\] with a given acid would result in the formation of acid chlorides in the products. Acid chloride is the common name for acyl halide where chlorine is the halogen.
Reaction with alcohol: alcohols react in a rather violent manner with \[PC{l_5}\], resulting in the emissive release of hydrochloric acid.
\[R - OH + PC{l_5} \to R - Cl + POC{l_3} + HCl\]
Reaction with amide: when amides are reacted with \[PC{l_5}\], it results in the dehydration of the amide. The corresponding reaction can be given as:
\[R - CON{H_2} + PC{l_5} \to R - C{(Cl)_2}N{H_2} + PC{l_3}\]
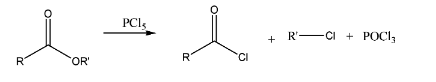
Reaction with esters: reaction between esters and \[PC{l_5}\] results in the formation of an alkyl halide, an acyl halide and also phosphorous oxychloride. Hence, only acyl halide cannot be obtained from esters.
Hence, Option A is the correct option.
Note: In the reaction of \[PC{l_5}\] with carboxylic acid, the reaction goes firstly by a cyclic transition state with the removal of HCl. Then via a nucleophilic addition of chloride where the carbonyl is simultaneously protonated.
Acyl halides can be explained as the halogen substituted hydroxyl groups in organic compounds. Acyl halides are basically formed when the hydroxy or the -OH group of the hydroxyl or -COOH group gets replaced by a halogen. This is a basic substitution reaction.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
In order to solve this question, we must find the products formed by \[PC{l_5}\] with all the given options.
Reaction with acid: the reaction of \[PC{l_5}\] with a given acid would result in the formation of acid chlorides in the products. Acid chloride is the common name for acyl halide where chlorine is the halogen.

Reaction with alcohol: alcohols react in a rather violent manner with \[PC{l_5}\], resulting in the emissive release of hydrochloric acid.
\[R - OH + PC{l_5} \to R - Cl + POC{l_3} + HCl\]
Reaction with amide: when amides are reacted with \[PC{l_5}\], it results in the dehydration of the amide. The corresponding reaction can be given as:
\[R - CON{H_2} + PC{l_5} \to R - C{(Cl)_2}N{H_2} + PC{l_3}\]
Reaction with esters: reaction between esters and \[PC{l_5}\] results in the formation of an alkyl halide, an acyl halide and also phosphorous oxychloride. Hence, only acyl halide cannot be obtained from esters.

Hence, Option A is the correct option.
Note: In the reaction of \[PC{l_5}\] with carboxylic acid, the reaction goes firstly by a cyclic transition state with the removal of HCl. Then via a nucleophilic addition of chloride where the carbonyl is simultaneously protonated.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




