
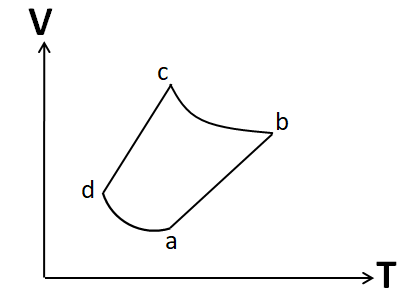
An ideal gas goes through a reversible cycle $a \to b \to c \to d$ has the V- T diagram shown below. Process $d \to a$ and $b \to c$ are adiabatic. The corresponding P- V diagram for the process is (all figures are schematic and not drawn to scale).
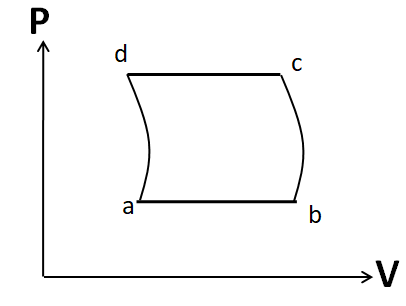
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)




Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we need to obtain the equation for each of the four processes given in the cycle. We also have to use the ideal equation for identifying each process.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Process a to b:
In the given V-T diagram, the process a-b is represented by a straight line. From the ideal gas equation we have
$PV = nRT$
$ \Rightarrow T = \dfrac{P}{{nR}}V$
Comparing with the equation of the straight line $y = mx$, we have the slope of the diagram for this process as
${m_{ab}} = \dfrac{P}{{nR}}$
Since the slope of a straight line is a constant, so we have
\[\dfrac{P}{{nR}} = constant\]
Since the number of moles is constant, we have a constant pressure. So this process is isobaric. Hence it must be represented by a horizontal line. So the P-V diagram for this process will look like
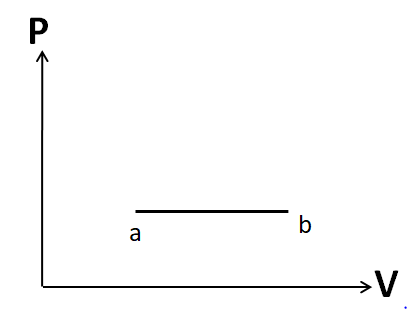
Process b to c:
According to the question, this process is adiabatic. We know that the adiabatic process is represented by the equation
$P{V^\gamma } = Constant$
So we can write
$P = \dfrac{k}{{{V^\gamma }}}$
So the P-V graph for this process will look like
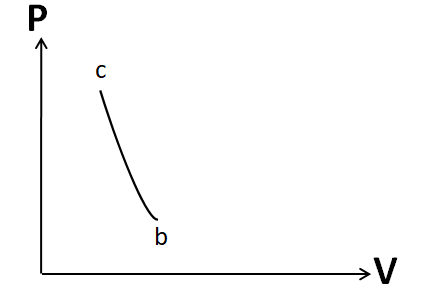
Similarly, we can show that the process c to d is also isobaric. So its P-V graph will be similar to the P-V graph of the process a to b.
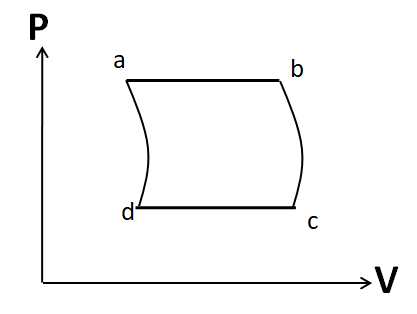
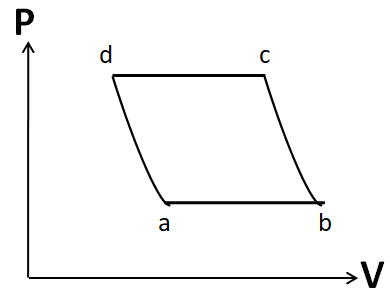
Also the process d to a is given to be adiabatic. So its P-V graph will be similar to that of the process b to c. Hence, the P-V graph for the cycle given in the question is
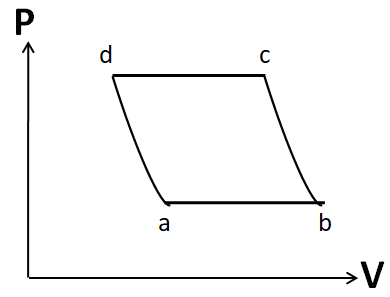
Hence, the correct answer is option D.
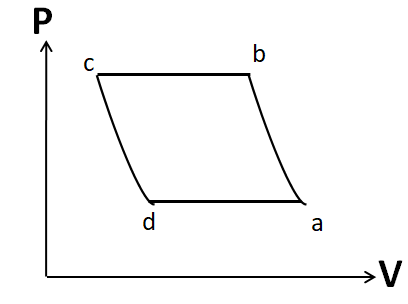
Note: It is important to draw the P-V plot in the same order as that given in the question. Otherwise you may get the same shape, but due to a different order you may tick the incorrect option. For example, the P-V diagram given in option A is similar to that in the correct option D. But it has different order.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Process a to b:
In the given V-T diagram, the process a-b is represented by a straight line. From the ideal gas equation we have
$PV = nRT$
$ \Rightarrow T = \dfrac{P}{{nR}}V$
Comparing with the equation of the straight line $y = mx$, we have the slope of the diagram for this process as
${m_{ab}} = \dfrac{P}{{nR}}$
Since the slope of a straight line is a constant, so we have
\[\dfrac{P}{{nR}} = constant\]
Since the number of moles is constant, we have a constant pressure. So this process is isobaric. Hence it must be represented by a horizontal line. So the P-V diagram for this process will look like
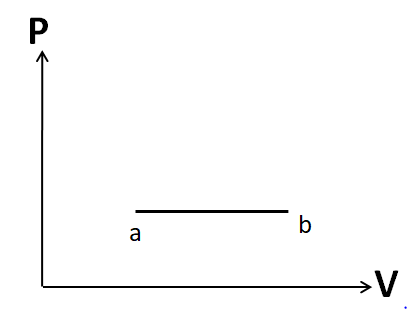
Process b to c:
According to the question, this process is adiabatic. We know that the adiabatic process is represented by the equation
$P{V^\gamma } = Constant$
So we can write
$P = \dfrac{k}{{{V^\gamma }}}$
So the P-V graph for this process will look like

Similarly, we can show that the process c to d is also isobaric. So its P-V graph will be similar to the P-V graph of the process a to b.
Also the process d to a is given to be adiabatic. So its P-V graph will be similar to that of the process b to c. Hence, the P-V graph for the cycle given in the question is

Hence, the correct answer is option D.
Note: It is important to draw the P-V plot in the same order as that given in the question. Otherwise you may get the same shape, but due to a different order you may tick the incorrect option. For example, the P-V diagram given in option A is similar to that in the correct option D. But it has different order.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




