
An object A is placed at a distance d in front of a plane mirror. If one stand s directly behind the object at distance S from the mirror, then the distance of the image of A from the individual is:
A) $2S$
B) $2d$
C) $S + d$
D) $S + 2d$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: A plane mirror is theoretically a part of a lens on infinite radius or we can say that the radius of curvature of a plane mirror is infinite.
The image formed in a pain mirror is of the same height as the object and is at the equal distance from the mirror as the object is.
a pain mirror just act as the midpoint about which on the other side we see a flipped image of the object
Complete step by step solution:
As plain mirror has an infinite radius of curvature so the image formed by it will not be enlarged or diminished as in the case of other mirror but here in this case the image will be of same height the and will be at the same distance from the mirror as the object
Refer to the ray diagram:
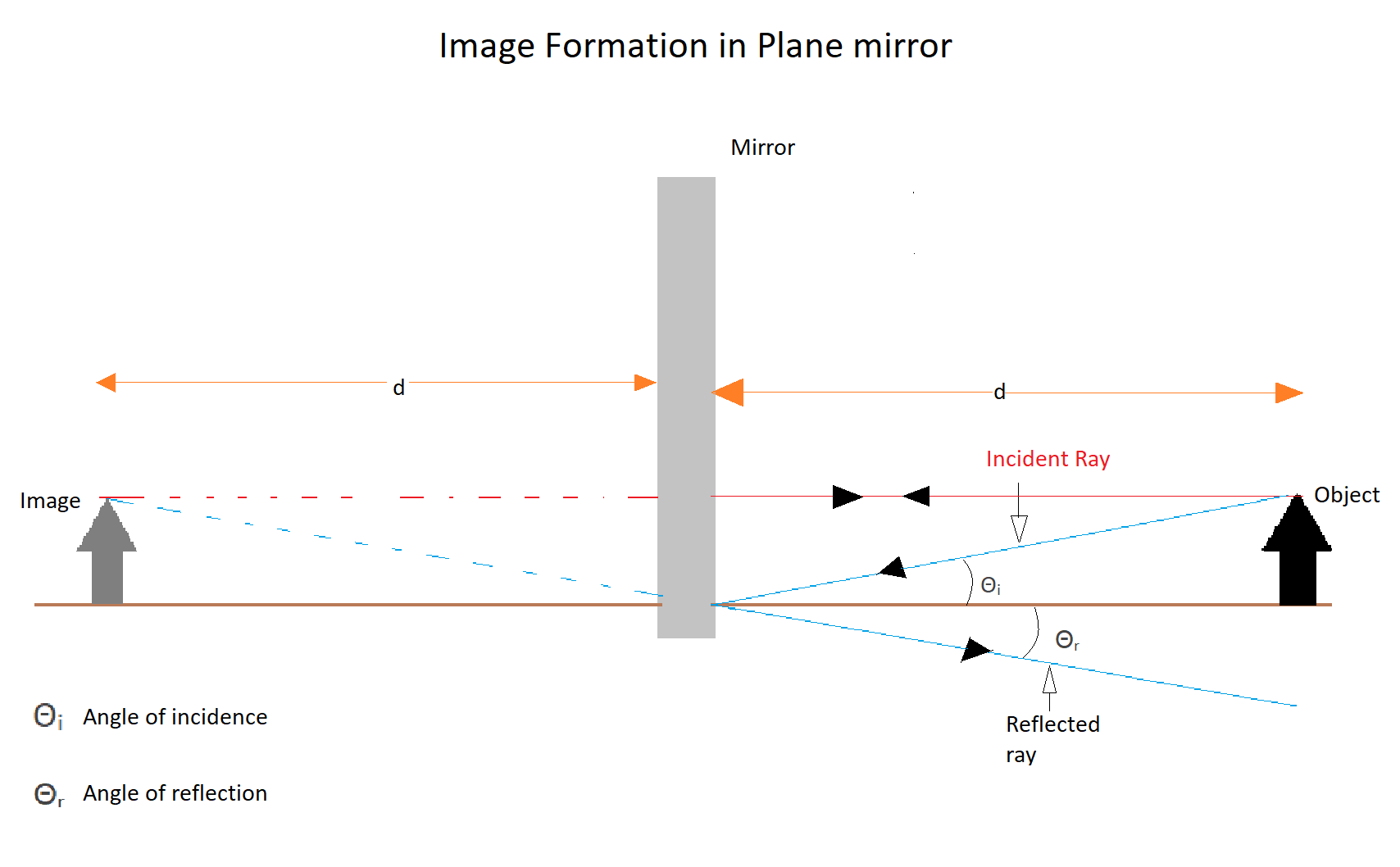 Here black arrow is the object and the grey arrow is the image now as we can see that
Here black arrow is the object and the grey arrow is the image now as we can see that
The incident and the reflected ray both lie in the same Plane and the angle between them is also equal so we can say that laws of reflection are satisfied.
Here it should be noted that every ray diagram need so satisfy laws of reflection
Now coming to the diagram we can say that the incident ray from the top of the object falls directly on the mirror at the right angle and gets reflected by the same angle another incident ray (blue) falls on the mirror at an angle $\theta $ is also reflected by the same angle the brown line is the reference line.
Now if we extend these rays inside the mirror we can see that the red ray and the blue ray meets at a particular point which is at a distance equal to the distance between the mirror and the object.
The point where the two rays intersect each other is the point where the image is formed Now in our question it is given that, object A is placed at a distance d in front of a plane mirror and the person stands right behind the object and the total distance between the person and the mirror is $S$. This is inclusive of the distance of the object from the mirror. Refer image
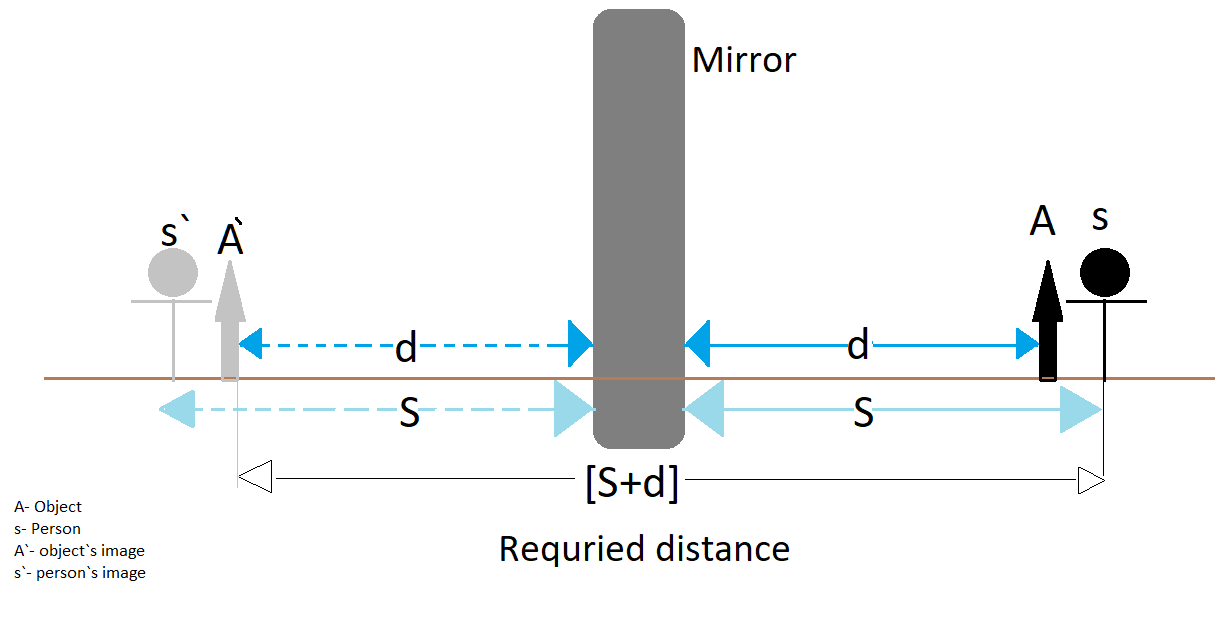
We need to find the distance between the person and the image of the object.
As we know as the distance between the object and the mirror is d so the distance between the mirror and its image will also be $d$
Now, as the distance between the mirror and person is $S$
So the required distance between the image of object A and the real person will be $S + d$.
Therefore, the distance of the image from the individual to the image that is formed at a distance d on the other side is given as $S + d$.
Note: 1. The ray diagram always needs to satisfy the laws of reflections.
2. When a ray of light strikes a plane mirror, the light ray gets reflected off the mirror. Reflection involves a change in direction of the ray.
3.The angle of incidence should be equal to the angle of reflection.
The image formed in a pain mirror is of the same height as the object and is at the equal distance from the mirror as the object is.
a pain mirror just act as the midpoint about which on the other side we see a flipped image of the object
Complete step by step solution:
As plain mirror has an infinite radius of curvature so the image formed by it will not be enlarged or diminished as in the case of other mirror but here in this case the image will be of same height the and will be at the same distance from the mirror as the object
Refer to the ray diagram:
 Here black arrow is the object and the grey arrow is the image now as we can see that
Here black arrow is the object and the grey arrow is the image now as we can see that The incident and the reflected ray both lie in the same Plane and the angle between them is also equal so we can say that laws of reflection are satisfied.
Here it should be noted that every ray diagram need so satisfy laws of reflection
Now coming to the diagram we can say that the incident ray from the top of the object falls directly on the mirror at the right angle and gets reflected by the same angle another incident ray (blue) falls on the mirror at an angle $\theta $ is also reflected by the same angle the brown line is the reference line.
Now if we extend these rays inside the mirror we can see that the red ray and the blue ray meets at a particular point which is at a distance equal to the distance between the mirror and the object.
The point where the two rays intersect each other is the point where the image is formed Now in our question it is given that, object A is placed at a distance d in front of a plane mirror and the person stands right behind the object and the total distance between the person and the mirror is $S$. This is inclusive of the distance of the object from the mirror. Refer image

We need to find the distance between the person and the image of the object.
As we know as the distance between the object and the mirror is d so the distance between the mirror and its image will also be $d$
Now, as the distance between the mirror and person is $S$
So the required distance between the image of object A and the real person will be $S + d$.
Therefore, the distance of the image from the individual to the image that is formed at a distance d on the other side is given as $S + d$.
Note: 1. The ray diagram always needs to satisfy the laws of reflections.
2. When a ray of light strikes a plane mirror, the light ray gets reflected off the mirror. Reflection involves a change in direction of the ray.
3.The angle of incidence should be equal to the angle of reflection.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




