
Aromatization of n-hexane gives:
(A) Benzene
(B) Toluene
(C) Methane
(D) A mixture of octanes
Answer
528.9k+ views
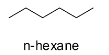
Hint: n-hexane is normal hexane or hexane and is a straight chain alkane having six carbon atoms. It has the molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{14}}}}$ . The structure of n-hexane is shown below.
Aromatization is a chemical reaction which involves the formation of an aromatic compound from a single non – aromatic precursor. It is usually achieved by dehydrogenation.
Complete step by step answer:
In the process of aromatization of n-hexane, the n-hexane at first is treated with vanadium oxide or chromium (III) oxide. This treatment gives a cyclic hexane or cyclohexane. This cyclohexane formed in the first step then undergoes dehydrogenation and aromatization to give benzene as the final product. The reaction of aromatization of n – hexane to give benzene is shown below:
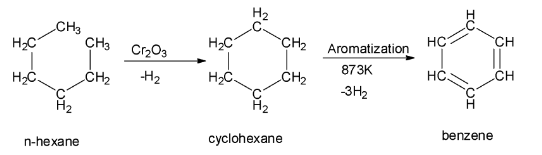
So, the option A is correct.
Toluene can be obtained from benzene through Friedel - Craft’s alkylation process. But it cannot be directly obtained from n – hexane through the aromatization of n – hexane as aromatization of n – hexane gives benzene as the product. So, the option B is not correct.
The third option is methane which is not an aromatic compound. Since aromatization means the formation of ‘aromatic’ compounds from non – aromatic compounds, therefore methane is not acceptable. So, the option C is also not correct.
The last option is a mixture of octanes which are again not aromatic compounds. Therefore, the option D is also not correct.
So, the option A is correct.
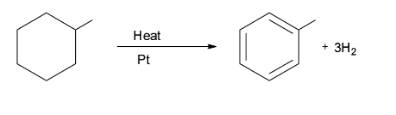
Note: The aromatization reaction has a huge application in the oil refining process. For example, it is observed in the conversion of naphthene into aromatics which is catalyzed by platinum. This is illustrated in the conversion of methylcyclohexane into toluene. This reaction is used in the production of gasoline from petroleum.

Aromatization is a chemical reaction which involves the formation of an aromatic compound from a single non – aromatic precursor. It is usually achieved by dehydrogenation.
Complete step by step answer:
In the process of aromatization of n-hexane, the n-hexane at first is treated with vanadium oxide or chromium (III) oxide. This treatment gives a cyclic hexane or cyclohexane. This cyclohexane formed in the first step then undergoes dehydrogenation and aromatization to give benzene as the final product. The reaction of aromatization of n – hexane to give benzene is shown below:

So, the option A is correct.
Toluene can be obtained from benzene through Friedel - Craft’s alkylation process. But it cannot be directly obtained from n – hexane through the aromatization of n – hexane as aromatization of n – hexane gives benzene as the product. So, the option B is not correct.
The third option is methane which is not an aromatic compound. Since aromatization means the formation of ‘aromatic’ compounds from non – aromatic compounds, therefore methane is not acceptable. So, the option C is also not correct.
The last option is a mixture of octanes which are again not aromatic compounds. Therefore, the option D is also not correct.
So, the option A is correct.
Note: The aromatization reaction has a huge application in the oil refining process. For example, it is observed in the conversion of naphthene into aromatics which is catalyzed by platinum. This is illustrated in the conversion of methylcyclohexane into toluene. This reaction is used in the production of gasoline from petroleum.

Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




