
Assertion:In electrolytic refining of metal, impure metal is made cathode while a strip of pure metal is used as anode.
Reason: The pure metal gets deposited at anode as anode mud.
(A) Both assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(B) Both assertion and Reason are correct but reason is not the correct explanation for assertion.
(C) Assertion is correct but reason is incorrect.
(D) Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Electrolytic refining process is used for purification of metal. Metals obtained after smelting or other methods may contain impurities like unreacted oxides, other metals, non- metals and gases.
The purification of crude metals by removing metallic and non- metallic impurities is known as refining.
Complete step by step answer:
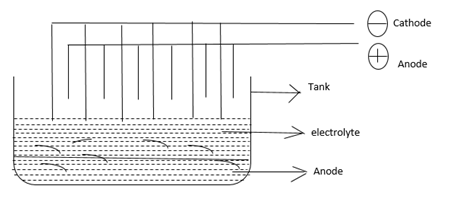
In electrolytic refining, anode [positively charged] and cathode [negatively charged] electrode is dipped into aqueous solution of their salt.
The rod of impure metal is used as anode and thin sheet of pure metal as cathode.
During electrolysis, metal from anode dissolve in the solution while the same amount of pure metal deposits on cathode.
The impurities like more reactive metals dissolve in the solution.
Less reactive metals are insoluble. They form anode mud at the bottom.
In this process $99.99\% $ pure metal is obtained.
Metals like $Ni,Al,Zn$ are refined by his method.
In the given question:
Assertion is – impure metal is made cathode while a strip of pure metal is used as anode.
But as we already discussed, impure metal is made anode and pure metal is used as cathode.
Reason is – The pure metal gets deposited at anode mud.
But pure metal gets deposited at cathode and impurities form anode mud.
Therefore, the above explanation, the correct option is [D] Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Note: Impure metal is made anode and pure metal strip is made cathode during electrolytic refining. During electrolysis pure metal from impure anode gets dissolved in the solution. As metal is always positively charged, it is migrated towards cathode and deposit. then cathodes become thick and replaced from time to time.
The purification of crude metals by removing metallic and non- metallic impurities is known as refining.
Complete step by step answer:
In electrolytic refining, anode [positively charged] and cathode [negatively charged] electrode is dipped into aqueous solution of their salt.
The rod of impure metal is used as anode and thin sheet of pure metal as cathode.
During electrolysis, metal from anode dissolve in the solution while the same amount of pure metal deposits on cathode.
The impurities like more reactive metals dissolve in the solution.
Less reactive metals are insoluble. They form anode mud at the bottom.
In this process $99.99\% $ pure metal is obtained.
Metals like $Ni,Al,Zn$ are refined by his method.

In the given question:
Assertion is – impure metal is made cathode while a strip of pure metal is used as anode.
But as we already discussed, impure metal is made anode and pure metal is used as cathode.
Reason is – The pure metal gets deposited at anode mud.
But pure metal gets deposited at cathode and impurities form anode mud.
Therefore, the above explanation, the correct option is [D] Both assertion and reason are incorrect.
Note: Impure metal is made anode and pure metal strip is made cathode during electrolytic refining. During electrolysis pure metal from impure anode gets dissolved in the solution. As metal is always positively charged, it is migrated towards cathode and deposit. then cathodes become thick and replaced from time to time.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




