
Block A of weight $100{\text{N}}$ reset on a frictionless inclined plane of slope angle ${30^\circ }$ as shown in the figure. A flexible cord attached to $A$ passes over a frictionless pulley and is connected to a block $B$ of weight $W$. Find the weight $W$ of which the system is in equilibrium.
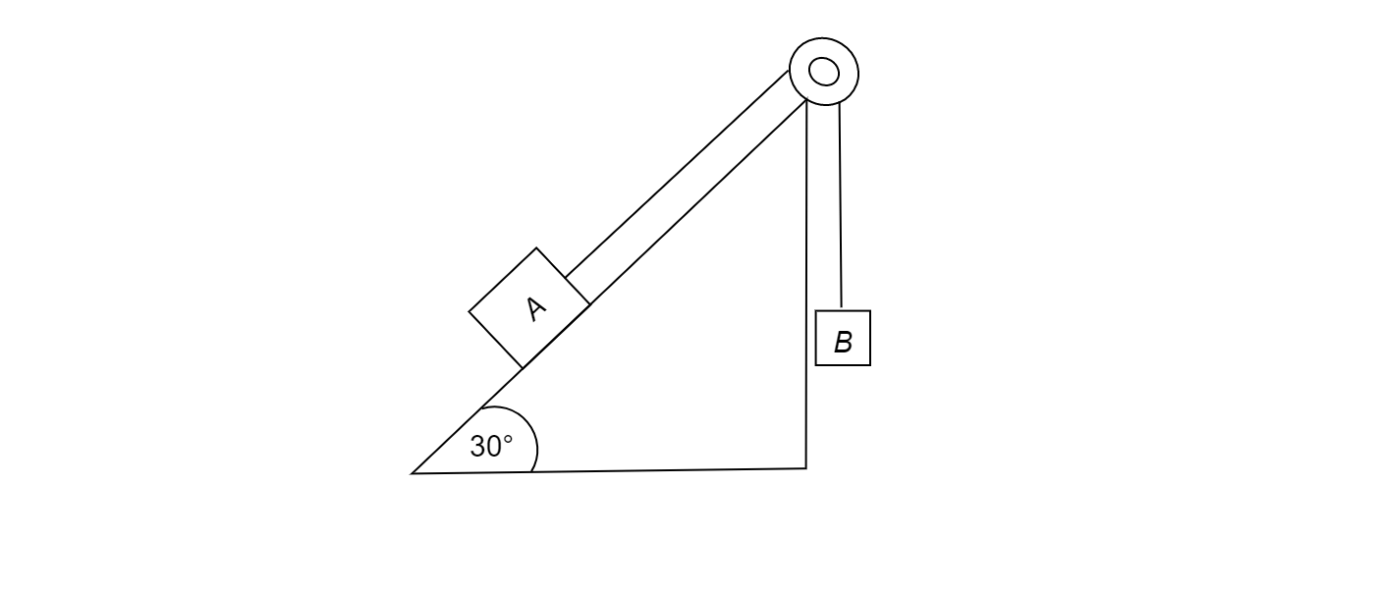
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: We have to know how all the forces are acting on this system at every point. We can then continue to break every force vector into its components, which will give us a better overview of this problem. After that, we will balance every force component and will try to find out our desired answer.
Complete step by step solution:
We will break every force vectors into its components and will add the tension on the string, and redraw our given figure as following-
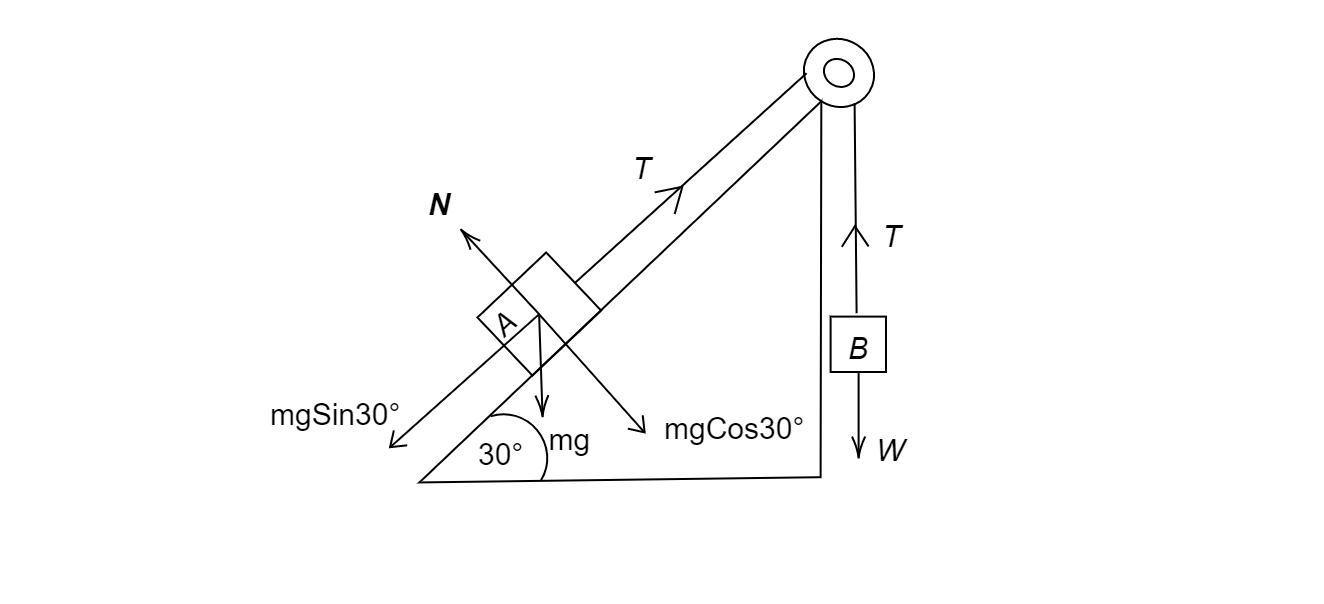
In the above figure, we have-
$T$ is the tension in the string
$W$ is the weight of the block ${\text{B}}$
$N$ is the normal force acting on the block ${\text{A}}$ by the surface
$mg$ is the weight of the block ${\text{A}}$
Given that the weight of the block $A$ is $100{\text{N}}$ i.e. $mg = 100{\text{N}}$
All the forces are acting in the same direction, as shown by arrows in the figure. We break $mg$ into its components, and we have $mg\cos {30^\circ }$ to balance the vector $N$ and $mg\sin 30^\circ $ to balance $T$. Also, the vector $W$ is balancing $T$ on the other side.
Hence in the equilibrium of the system, we have-
$T = W$ ………..$(1)$
$T = mg\sin {30^\circ }$……....$(2)$
By comparing equations $(1)$ and $(2)$, we get-
$W = mg\sin {30^\circ }$
We put $mg = 100{\text{N}}$ and $\sin {30^\circ } = \dfrac{1}{2}$-
$\therefore W = 100 \times \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{N}}$
$ \Rightarrow W = 50{\text{N}}$
Therefore, the weight of the block $B$ is $50{\text{N}}$.
Note: This problem is a special case of the most generic problem. The tension at the two parts of the string is identical because the pulley and the inclined surface are frictionless. Furthermore, the sting is taken to be as massless here. In the generic problem, one must take account of the other forces that are involved.
Complete step by step solution:
We will break every force vectors into its components and will add the tension on the string, and redraw our given figure as following-

In the above figure, we have-
$T$ is the tension in the string
$W$ is the weight of the block ${\text{B}}$
$N$ is the normal force acting on the block ${\text{A}}$ by the surface
$mg$ is the weight of the block ${\text{A}}$
Given that the weight of the block $A$ is $100{\text{N}}$ i.e. $mg = 100{\text{N}}$
All the forces are acting in the same direction, as shown by arrows in the figure. We break $mg$ into its components, and we have $mg\cos {30^\circ }$ to balance the vector $N$ and $mg\sin 30^\circ $ to balance $T$. Also, the vector $W$ is balancing $T$ on the other side.
Hence in the equilibrium of the system, we have-
$T = W$ ………..$(1)$
$T = mg\sin {30^\circ }$……....$(2)$
By comparing equations $(1)$ and $(2)$, we get-
$W = mg\sin {30^\circ }$
We put $mg = 100{\text{N}}$ and $\sin {30^\circ } = \dfrac{1}{2}$-
$\therefore W = 100 \times \dfrac{1}{2}{\text{N}}$
$ \Rightarrow W = 50{\text{N}}$
Therefore, the weight of the block $B$ is $50{\text{N}}$.
Note: This problem is a special case of the most generic problem. The tension at the two parts of the string is identical because the pulley and the inclined surface are frictionless. Furthermore, the sting is taken to be as massless here. In the generic problem, one must take account of the other forces that are involved.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




