
Consider the following two reactions:
i. Propene +${{H}_{2}}$→ Propane, $\Delta {{H}_{1}}$
ii. Cyclo-propane +${{H}_{2}}$→ Propane: $\Delta {{H}_{2}}$
Then, ΔH2−ΔH1 will be:
(A) 0
(B) $2{{(B.E)}_{C-C}}-{{(B.E)}_{C=C}}$
(C) ${{(B.E)}_{C=C}}$
(D) $2{{(B.E)}_{C=C}}-{{(B.E)}_{C-C}}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: First write down the reactions and their enthalpies in terms of bond energy. The energy for each type of bond is different, like B.E. for C-C, B.E. for C-H and B.E. for C=C will be different from each other but all C-H bonds will have the same bond energies. So, for each compound count the number of bonds for each type and write their enthalpies. Now subtract the enthalpies of both the reactions.
Complete step by step solution:
So, first of all, we have to write a reaction. And from that, we will find the number of bonds of different bond energy. The reaction of hydrogenation of propene and hydrogen is as follows.

The above reaction is the hydrogenation of propene into propane. Now we will write enthalpy in terms of bond energy.
\[\begin{align}
& \Delta {{H}_{1}}=\sum{(B.E}{{)}_{reac\tan ts}}-\sum{(B.E}{{)}_{products}} \\
& \Delta {{H}_{1}}=6{{(B.E)}_{C-H}}+{{(B.E)}_{C-C}}+{{(B.E)}_{C=C}}+{{(B.E)}_{H-H}} \\
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,-8{{(B.E)}_{C-H}}-2{{(B.E)}_{C-C}} \\
\end{align}\]
From the above equation we can say that, 6 denotes the number of hydrogen single bonds, whereas, in propene there is one single C-C bond and one carbon double bond. Whereas, on the product side, we have eight carbon hydrogen single bonds and two carbon-carbon single bonds. Now, we will further simplify the above equation.
\[\,\,\Delta {{H}_{1}}\,\,\,={{(B.E)}_{C=C}}+{{(B.E)}_{H-H}}-{{(B.E)}_{C-H}}-{{(B.E)}_{C-C}}\]
So, the above equation represents the enthalpy of reaction in terms of bond energy.
Now, in the same way, we will write the equation of cyclo-propane.
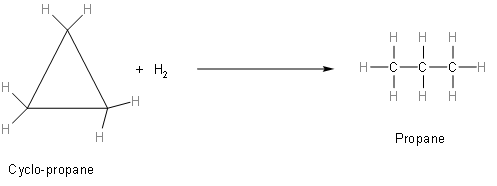
The above figure represents the hydrogenation of cyclopropane into propane.
\[\begin{align}
& \Delta {{H}_{2}}=\sum{(B.E}{{)}_{reac\tan ts}}-\sum{(B.E}{{)}_{products}} \\
& \Delta {{H}_{2}}={{(B.E)}_{C-C}}-{{(B.E)}_{C-H}}+{{(B.E)}_{H-H}} \\
\end{align}\]
This above equation represents hydrogenation of cyclopropane.
Now, we should calculate the difference in enthalpy in terms of bond energy.
\[\Delta {{H}_{2}}-\,\Delta {{H}_{1}}\,={{(B.E)}_{C-C}}-{{(B.E)}_{C-H}}+{{(B.E)}_{H-H}}-{{(B.E)}_{C=C}}+{{(B.E)}_{H-H}}-{{(B.E)}_{C-H}}-(B.E)\]
\[\Delta {{H}_{2}}-\,\Delta {{H}_{1}}=2{{(B.E)}_{C-C}}-{{(B.E)}_{C=C}}\]
Now, we can say that option B is the correct answer.
Note: We should now know about bond energy. We should know that bond energy (E) is defined as the amount of energy, which is required to break apart a mole of molecules into its component atoms. It is a measure of the strength of a chemical bond. Bond energy is also known as bond enthalpy (H) or simply as bond strength.
Complete step by step solution:
So, first of all, we have to write a reaction. And from that, we will find the number of bonds of different bond energy. The reaction of hydrogenation of propene and hydrogen is as follows.

The above reaction is the hydrogenation of propene into propane. Now we will write enthalpy in terms of bond energy.
\[\begin{align}
& \Delta {{H}_{1}}=\sum{(B.E}{{)}_{reac\tan ts}}-\sum{(B.E}{{)}_{products}} \\
& \Delta {{H}_{1}}=6{{(B.E)}_{C-H}}+{{(B.E)}_{C-C}}+{{(B.E)}_{C=C}}+{{(B.E)}_{H-H}} \\
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,-8{{(B.E)}_{C-H}}-2{{(B.E)}_{C-C}} \\
\end{align}\]
From the above equation we can say that, 6 denotes the number of hydrogen single bonds, whereas, in propene there is one single C-C bond and one carbon double bond. Whereas, on the product side, we have eight carbon hydrogen single bonds and two carbon-carbon single bonds. Now, we will further simplify the above equation.
\[\,\,\Delta {{H}_{1}}\,\,\,={{(B.E)}_{C=C}}+{{(B.E)}_{H-H}}-{{(B.E)}_{C-H}}-{{(B.E)}_{C-C}}\]
So, the above equation represents the enthalpy of reaction in terms of bond energy.
Now, in the same way, we will write the equation of cyclo-propane.

The above figure represents the hydrogenation of cyclopropane into propane.
\[\begin{align}
& \Delta {{H}_{2}}=\sum{(B.E}{{)}_{reac\tan ts}}-\sum{(B.E}{{)}_{products}} \\
& \Delta {{H}_{2}}={{(B.E)}_{C-C}}-{{(B.E)}_{C-H}}+{{(B.E)}_{H-H}} \\
\end{align}\]
This above equation represents hydrogenation of cyclopropane.
Now, we should calculate the difference in enthalpy in terms of bond energy.
\[\Delta {{H}_{2}}-\,\Delta {{H}_{1}}\,={{(B.E)}_{C-C}}-{{(B.E)}_{C-H}}+{{(B.E)}_{H-H}}-{{(B.E)}_{C=C}}+{{(B.E)}_{H-H}}-{{(B.E)}_{C-H}}-(B.E)\]
\[\Delta {{H}_{2}}-\,\Delta {{H}_{1}}=2{{(B.E)}_{C-C}}-{{(B.E)}_{C=C}}\]
Now, we can say that option B is the correct answer.
Note: We should now know about bond energy. We should know that bond energy (E) is defined as the amount of energy, which is required to break apart a mole of molecules into its component atoms. It is a measure of the strength of a chemical bond. Bond energy is also known as bond enthalpy (H) or simply as bond strength.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




