
Define relative velocity of an object with respect to another. Draw position-time graphs of two objects moving along a straight line, when their relative velocity is zero and non-zero.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: When two objects move along a straight line with zero relative velocity this means that they are travelling with the same and constant velocity. And when the relative velocity is non-zero then their velocity is different but at constant velocity.
Complete step by step answer:
Relative velocity is defined as the velocity of a body with respect to another moving body with some velocity. The total velocity between both the bodies changes. The relative velocity either increases or decreases on the basis of direction of both the moving bodies. If the bodies move in the same direction then the overall relative velocity decreases. And when the bodies travel in opposite directions then overall relative velocity increases. The expression for the relative velocity is given by:
When bodies are in same direction ${V_{ab}} = {V_a} - {V_b}$ and,
When bodies travel in opposite direction ${V_{ab}} = {V_a} + {V_b}$
The position-time graph which represents the motion of two bodies when teir relative velocity is zero and non-zero are given below:
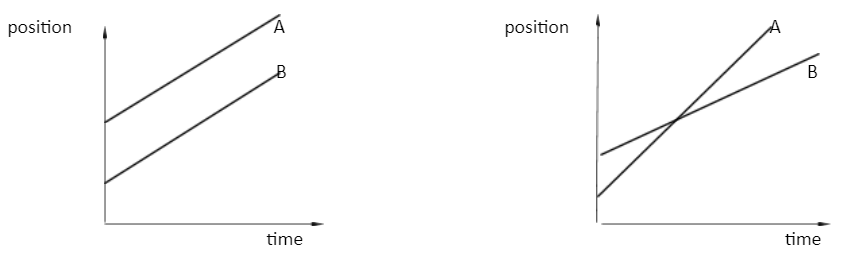
In the first graph both bodies have constant velocity to maintain zero or constant relative velocity. And in the second graph both bodies have different speeds. Due to which both have different positions at different times. Both the bodies may cross each other due to different velocities.
Note: Different velocities have non-zero relative velocity. To have zero relative velocity both bodies should have constant velocity. Also the relative velocity depends upon the direction of both the moving bodies.
Complete step by step answer:
Relative velocity is defined as the velocity of a body with respect to another moving body with some velocity. The total velocity between both the bodies changes. The relative velocity either increases or decreases on the basis of direction of both the moving bodies. If the bodies move in the same direction then the overall relative velocity decreases. And when the bodies travel in opposite directions then overall relative velocity increases. The expression for the relative velocity is given by:
When bodies are in same direction ${V_{ab}} = {V_a} - {V_b}$ and,
When bodies travel in opposite direction ${V_{ab}} = {V_a} + {V_b}$
The position-time graph which represents the motion of two bodies when teir relative velocity is zero and non-zero are given below:

In the first graph both bodies have constant velocity to maintain zero or constant relative velocity. And in the second graph both bodies have different speeds. Due to which both have different positions at different times. Both the bodies may cross each other due to different velocities.
Note: Different velocities have non-zero relative velocity. To have zero relative velocity both bodies should have constant velocity. Also the relative velocity depends upon the direction of both the moving bodies.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Derive an expression for maximum speed of a car on class 11 physics JEE_Main

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Fluids (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Law of Motion (2025-26)

Class 11 JEE Main Physics Mock Test 2025

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




