
Distillation of phenol with zinc-dust gives:
(A) Benzene
(B) Diphenyl - zinc
(C) Diphenyl Ether
(D) none of the above
Answer
519.6k+ views
The product was discovered by Kekule. It has the molecular formula \[{{C}_{6}}{{H}_{6}}\].
It is an aromatic compound as it obeys Huckel’s rule of \[(4n+2)\pi \]electrons. It is a very stable compound due to resonance.
Complete step by step answer:
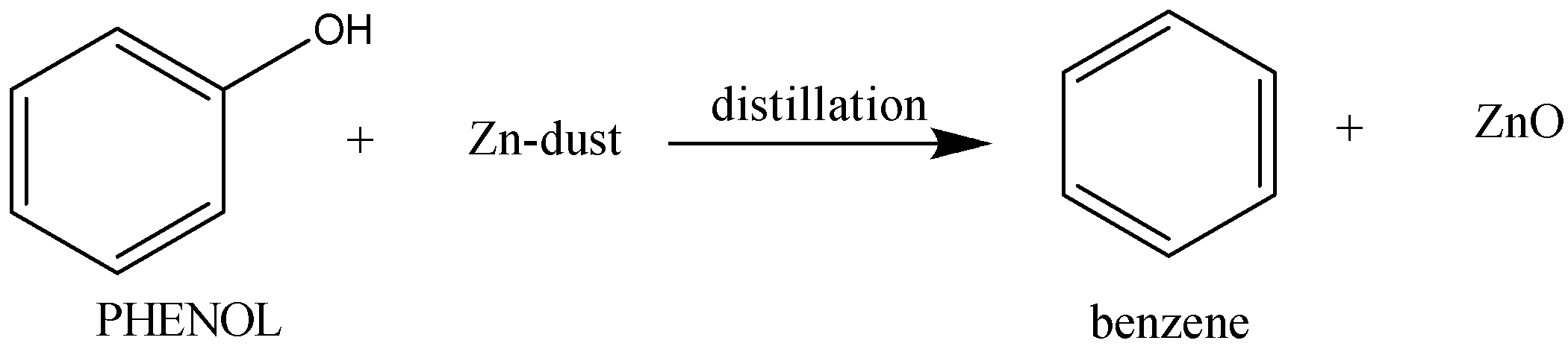
Distillation of phenol with zinc-dust gives benzene and ZnO as a side-product.
The reaction proceeds as follows:
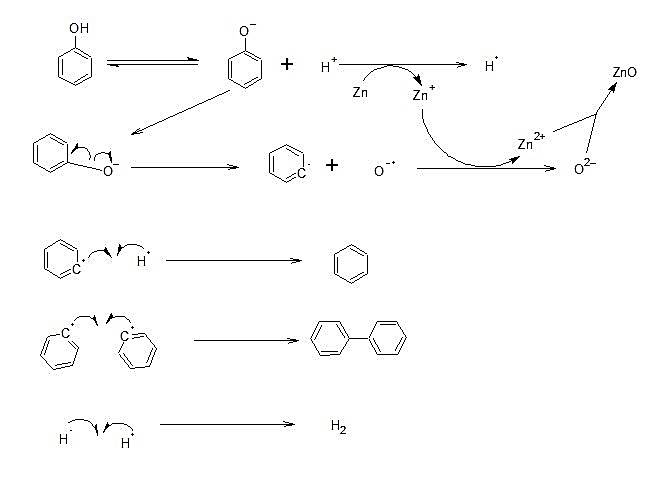
 Detailed Mechanism:
Detailed Mechanism:
- Zn is in the +2 oxidation state.
- The phenol gets converted into phenoxide ion and the released proton accepts an electron from Zn forming hydrogen radical. Due to the heating, there is homolytic fission of C of the phenyl ring and\[{{O}^{-}}\].
- Then\[{{O}^{-}}\]forms an electron from Zn and forms an oxide ion. In this way, zinc forms zinc oxide, and the phenyl radical produced forms a bond with hydrogen radical to form Benzene and bi-phenyl.
So, the correct option is A.
Note: The yield of this reaction used for benzene formation is lower.
Homolytic fission is the equal splitting of a pair of electrons between two separated atoms.
It is a reduction reaction of phenol to benzene by zinc dust. So, zinc is a reducing agent.
Benzene formed is volatile in nature. It is separated by fractional distillation.
It is an aromatic compound as it obeys Huckel’s rule of \[(4n+2)\pi \]electrons. It is a very stable compound due to resonance.
Complete step by step answer:
Distillation of phenol with zinc-dust gives benzene and ZnO as a side-product.
The reaction proceeds as follows:
 Detailed Mechanism:
Detailed Mechanism:- Zn is in the +2 oxidation state.
- The phenol gets converted into phenoxide ion and the released proton accepts an electron from Zn forming hydrogen radical. Due to the heating, there is homolytic fission of C of the phenyl ring and\[{{O}^{-}}\].
- Then\[{{O}^{-}}\]forms an electron from Zn and forms an oxide ion. In this way, zinc forms zinc oxide, and the phenyl radical produced forms a bond with hydrogen radical to form Benzene and bi-phenyl.

So, the correct option is A.
Note: The yield of this reaction used for benzene formation is lower.
Homolytic fission is the equal splitting of a pair of electrons between two separated atoms.
It is a reduction reaction of phenol to benzene by zinc dust. So, zinc is a reducing agent.
Benzene formed is volatile in nature. It is separated by fractional distillation.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




