
Draw the pattern of magnetic field lines through and around a current carrying loop of wire. How does the strength of magnetic field due to current in a loop be affected if
$\left( A \right)$ Strength of the current passing through it is doubled
$\left( B \right)$ The radius of the loop is reduced to half the original value
$\left( C \right)$ The radius of the loop is doubled its original value and at the same time current passing through is doubled.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: All magnetic fields are due to currents and due to intrinsic magnetic moments of particles. The relation between current and magnetic field produced by the current is given by the Biot Savart law. Know the relation between the magnetic field, current and radius by using Biot Savart law. Apply the logic to answer the three parts of the question.
Complete step to step answer:
The magnetic field produced due to a current carrying segment is given by Biot Savart law. It is a vector quantity. In order to know the magnetic field produced at a point due to this small element, one can use Biot-Savart’s Law.
According to Biot Savart law, the magnetic field depends on
Is directly proportional to the current
Is directly proportional to the length
Is inversely proportional to the square of the distance of the point from the element.
$\left( A \right)$ Magnetic field is doubled when the current passing through is doubled since the magnetic field is directly proportional to current.
$\left( B \right)$ Magnetic field is doubled when the radius of the loop is reduced to half the original value since the magnetic field is inversely proportional to the square of the distance of the point from the element.
$\left( C \right)$ Magnetic field is doubled when the radius of the loop is doubled and the current passing through is doubled. Since magnetic field is directly proportional to the current and Is inversely proportional to the square of the distance of the point from the element.
Pattern of magnetic field lines through and around the current is given below:
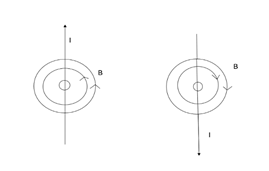
Note: Biot-Savart’s Law for the magnetic field has certain similarities as well as differences with Coulomb's law. In Biot-Savart’s Law the magnetic field is directly proportional to the sine of the angle. The magnetic field produced due to a current carrying segment is given by Biot Savart law. Biot-Savart’s Law is a vector quantity .
Complete step to step answer:
The magnetic field produced due to a current carrying segment is given by Biot Savart law. It is a vector quantity. In order to know the magnetic field produced at a point due to this small element, one can use Biot-Savart’s Law.
According to Biot Savart law, the magnetic field depends on
Is directly proportional to the current
Is directly proportional to the length
Is inversely proportional to the square of the distance of the point from the element.
$\left( A \right)$ Magnetic field is doubled when the current passing through is doubled since the magnetic field is directly proportional to current.
$\left( B \right)$ Magnetic field is doubled when the radius of the loop is reduced to half the original value since the magnetic field is inversely proportional to the square of the distance of the point from the element.
$\left( C \right)$ Magnetic field is doubled when the radius of the loop is doubled and the current passing through is doubled. Since magnetic field is directly proportional to the current and Is inversely proportional to the square of the distance of the point from the element.
Pattern of magnetic field lines through and around the current is given below:

Note: Biot-Savart’s Law for the magnetic field has certain similarities as well as differences with Coulomb's law. In Biot-Savart’s Law the magnetic field is directly proportional to the sine of the angle. The magnetic field produced due to a current carrying segment is given by Biot Savart law. Biot-Savart’s Law is a vector quantity .
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




