
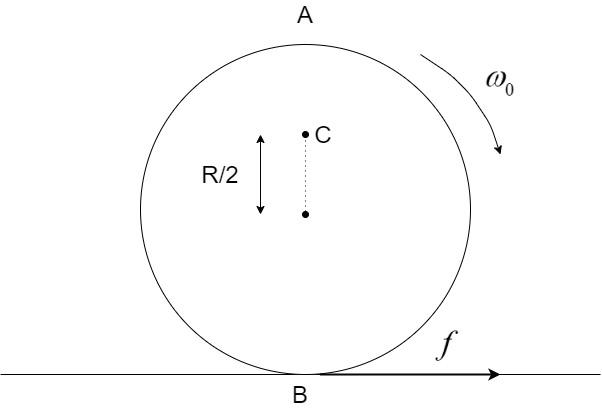
Explain why friction is necessary to make the disc in figure roll in the direction indicated.
(A) Give the direction of frictional force at B, and the sense of frictional torque, before perfect rolling begins.
(B) What is the force of friction after perfect rolling begins?

Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: From Newton’s law we know that without any external force a rest body will always remain at rest. Using this law, we can identify the force of friction acting on the disc during its rolling motion. The direction has to be computed by the fact that, at B, there shall be no relative velocity with respect to the ground.
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
1. Angular velocity of the disc is $\omega$whose direction is clockwise.
2. Radius of the disc is R.
To find:
1. Explanation regarding the necessity of friction for the disc’s movement.
2. Direction of friction force f at B and sense of frictional torque before perfect rolling begins.
3. Frictional force after perfect rolling begins.
(A) Explanation:
As the angular velocity of the disc is in clockwise direction so it will try to create a velocity from right to left direction at B. Now, if there is no friction in the surface then no external force will act upon the disc and it will just spin at a constant angular velocity $\omega$. Now, the direction of the friction force is always opposite to the direction of the velocity at the contact point. So, here it will act from left to right direction as shown in the figure. This frictional force will act as the external force on the disc which will provide the necessary acceleration to it to go forward. Hence, to create the motion of the disc friction of the surface is necessary.
Here, the frictional torque at point B is given by:
${\vec \tau _f} = \vec R \times \vec f$
Where,
${\vec \tau _f}$ denotes the frictional torque,
$\vec R$ is the radius of the disc,
$\vec f$ is the frictional force.
Now, from this vector(cross) product use the right-hand thumb rule to determine the direction of this torque, which is out of the plane.
(B) Explanation:
For perfect rolling the disc will satisfy the following condition:
$\left| {{{\vec v}_{CM}}} \right| = \left| {{{\vec v}_B}} \right|$
Where,
${\vec v_{CM}}$ is the velocity of the center of mass (CM) of the disc,
${\vec v_B}$ is the velocity of the disc at point B w.r.t the CM.
Now at the time of perfect rolling direction of ${\vec v_{CM}}$ is from left to right and direction of ${\vec v_B}$ is from right to left. Since, their magnitude is the same so w.r.t. the ground net velocity of the disc at point B will be ${\vec v_{CM}} + {\vec v_B} = 0$. Hence, the point B of the disc will be at rest w.r.t the ground and there will be no frictional force acting on the disc.
Final answer:
(A) Frictional force will act from left to right and frictional torque direction will be out of the plane before perfect rolling begins.
(B) Force of friction will be 0 after perfect rolling begins.
Note: A common conceptual mistake many students suffer from is they think both the direction of motion of the body at contact point and the direction of the frictional force is the same. But always remember that the actual case is just opposite. Friction always acts opposite in the direction of motion and tries to stop it. But eventually that opposite directional force makes the whole body move forward.
Complete step by step answer:
Given:
1. Angular velocity of the disc is $\omega$whose direction is clockwise.
2. Radius of the disc is R.
To find:
1. Explanation regarding the necessity of friction for the disc’s movement.
2. Direction of friction force f at B and sense of frictional torque before perfect rolling begins.
3. Frictional force after perfect rolling begins.
(A) Explanation:
As the angular velocity of the disc is in clockwise direction so it will try to create a velocity from right to left direction at B. Now, if there is no friction in the surface then no external force will act upon the disc and it will just spin at a constant angular velocity $\omega$. Now, the direction of the friction force is always opposite to the direction of the velocity at the contact point. So, here it will act from left to right direction as shown in the figure. This frictional force will act as the external force on the disc which will provide the necessary acceleration to it to go forward. Hence, to create the motion of the disc friction of the surface is necessary.
Here, the frictional torque at point B is given by:
${\vec \tau _f} = \vec R \times \vec f$
Where,
${\vec \tau _f}$ denotes the frictional torque,
$\vec R$ is the radius of the disc,
$\vec f$ is the frictional force.
Now, from this vector(cross) product use the right-hand thumb rule to determine the direction of this torque, which is out of the plane.
(B) Explanation:
For perfect rolling the disc will satisfy the following condition:
$\left| {{{\vec v}_{CM}}} \right| = \left| {{{\vec v}_B}} \right|$
Where,
${\vec v_{CM}}$ is the velocity of the center of mass (CM) of the disc,
${\vec v_B}$ is the velocity of the disc at point B w.r.t the CM.
Now at the time of perfect rolling direction of ${\vec v_{CM}}$ is from left to right and direction of ${\vec v_B}$ is from right to left. Since, their magnitude is the same so w.r.t. the ground net velocity of the disc at point B will be ${\vec v_{CM}} + {\vec v_B} = 0$. Hence, the point B of the disc will be at rest w.r.t the ground and there will be no frictional force acting on the disc.
Final answer:
(A) Frictional force will act from left to right and frictional torque direction will be out of the plane before perfect rolling begins.
(B) Force of friction will be 0 after perfect rolling begins.
Note: A common conceptual mistake many students suffer from is they think both the direction of motion of the body at contact point and the direction of the frictional force is the same. But always remember that the actual case is just opposite. Friction always acts opposite in the direction of motion and tries to stop it. But eventually that opposite directional force makes the whole body move forward.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




