
Find the current in wire AB
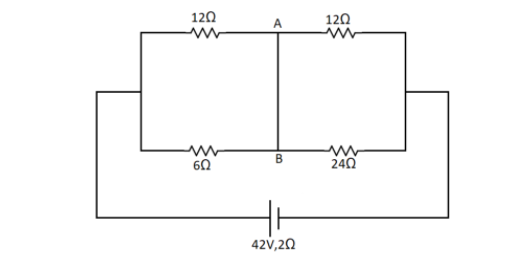
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The wire AB in between connects all the 4 resistances. So by drawing the circuit in a simpler way, we can find the equivalent resistance. Then we can calculate the current being drawn from the cell using the emf of the call. This will be the current in the wire AB.
Formula Used In this solution, we are going to use the following formula,
${R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3} + ....$ where ${R_{eq}}$ is the equivalent resistance when the resistances are placed in series.
And $\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}} + ....$ where ${R_{eq}}$ is the equivalent resistance when the resistances are placed in a parallel circuit.
$V = IR$ where $V$ is the emf of the cell, $I$ is the current in the wires and $R$ is the equivalent resistance.
Complete Step by Step Solution
To find the current in the wire AB we need to first redraw the circuit in a more simple way. Here the points A and B are the same point joined by a wire. So we can draw the circuit as,
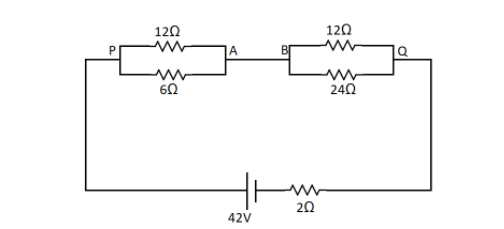
From this circuit we can see that there are 2 parallel circuits consisting of 2 resistances each.
Let us first find the equivalent resistance between the points P and Q. The formula for parallel combination is
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}} + ....$
Here we have ${R_1} = 12\Omega $ and ${R_2} = 6\Omega $
So substituting we get,
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq1}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{12}} + \dfrac{1}{6}$
Taking LCM as 12
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq1}}}} = \dfrac{{1 + 2}}{{12}}$
So by taking the reciprocal we get,
${R_{eq1}} = \dfrac{{12}}{3} = 4\Omega $
Similarly, between the points B and Q we have 2 resistances in parallel combination. So again here ${R_1} = 12\Omega $ and ${R_2} = 24\Omega $
Substituting we get,
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq2}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{12}} + \dfrac{1}{{24}}$
Taking LCM as 24,
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq2}}}} = \dfrac{{2 + 1}}{{24}}$
Taking the reciprocal we get,
${R_{eq2}} = \dfrac{{24}}{3} = 8\Omega $
Now the resistance ${R_{eq1}}$, ${R_{eq2}}$ and the internal resistance of the battery are in series in the circuit. So we use the formula for series combination given by,
${R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3} + ....$
Here ${R_1} = {R_{eq1}} = 4\Omega $, ${R_2} = {R_{eq2}} = 8\Omega $ and ${R_3} = 2\Omega $
So we get,
${R_{eq}} = 4 + 8 + 2$
Therefore, we get the equivalent resistance as,
${R_{eq}} = 14\Omega $
Now it is given that the battery has an emf of $V = 42V$
So from the Ohm’s law $V = IR$, we can get the current as,
$I = \dfrac{V}{{{\operatorname{R} _{eq}}}}$
Substituting we get,
$I = \dfrac{{42}}{{14}} = 3A$
This is the whole current that is in the flowing through the wire. Now since between the points A and B the current doesn’t get divided, so the current in the wire AB will be $3A$.
Note: In the given circuit, when the two resistances are in series condition then the current that flows in them both is the same whereas when the resistances are in parallel, the potential difference is the same across the resistances but the current varies. So the current in the 2 wires between P and A are different and depends on the magnitude of the resistance.
Formula Used In this solution, we are going to use the following formula,
${R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3} + ....$ where ${R_{eq}}$ is the equivalent resistance when the resistances are placed in series.
And $\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}} + ....$ where ${R_{eq}}$ is the equivalent resistance when the resistances are placed in a parallel circuit.
$V = IR$ where $V$ is the emf of the cell, $I$ is the current in the wires and $R$ is the equivalent resistance.
Complete Step by Step Solution
To find the current in the wire AB we need to first redraw the circuit in a more simple way. Here the points A and B are the same point joined by a wire. So we can draw the circuit as,

From this circuit we can see that there are 2 parallel circuits consisting of 2 resistances each.
Let us first find the equivalent resistance between the points P and Q. The formula for parallel combination is
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}}} + ....$
Here we have ${R_1} = 12\Omega $ and ${R_2} = 6\Omega $
So substituting we get,
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq1}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{12}} + \dfrac{1}{6}$
Taking LCM as 12
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq1}}}} = \dfrac{{1 + 2}}{{12}}$
So by taking the reciprocal we get,
${R_{eq1}} = \dfrac{{12}}{3} = 4\Omega $
Similarly, between the points B and Q we have 2 resistances in parallel combination. So again here ${R_1} = 12\Omega $ and ${R_2} = 24\Omega $
Substituting we get,
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq2}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{12}} + \dfrac{1}{{24}}$
Taking LCM as 24,
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq2}}}} = \dfrac{{2 + 1}}{{24}}$
Taking the reciprocal we get,
${R_{eq2}} = \dfrac{{24}}{3} = 8\Omega $
Now the resistance ${R_{eq1}}$, ${R_{eq2}}$ and the internal resistance of the battery are in series in the circuit. So we use the formula for series combination given by,
${R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3} + ....$
Here ${R_1} = {R_{eq1}} = 4\Omega $, ${R_2} = {R_{eq2}} = 8\Omega $ and ${R_3} = 2\Omega $
So we get,
${R_{eq}} = 4 + 8 + 2$
Therefore, we get the equivalent resistance as,
${R_{eq}} = 14\Omega $
Now it is given that the battery has an emf of $V = 42V$
So from the Ohm’s law $V = IR$, we can get the current as,
$I = \dfrac{V}{{{\operatorname{R} _{eq}}}}$
Substituting we get,
$I = \dfrac{{42}}{{14}} = 3A$
This is the whole current that is in the flowing through the wire. Now since between the points A and B the current doesn’t get divided, so the current in the wire AB will be $3A$.
Note: In the given circuit, when the two resistances are in series condition then the current that flows in them both is the same whereas when the resistances are in parallel, the potential difference is the same across the resistances but the current varies. So the current in the 2 wires between P and A are different and depends on the magnitude of the resistance.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




