
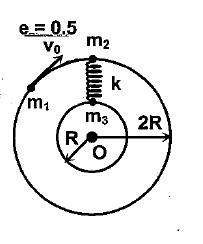
Find the maximum extension in the spring.
A) $\dfrac{{{v_o}}}{4}\sqrt {\dfrac{m}{{5k}}} $
B) $\dfrac{{3{v_o}}}{4}\sqrt {\dfrac{m}{{5k}}} $
C) $\dfrac{{{v_o}}}{3}\sqrt {\dfrac{m}{{5k}}} $
D) $\dfrac{{{v_o}}}{8}\sqrt {\dfrac{m}{{5k}}} $
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The maximum extension of the spring is defined as the elastic limit of the spring which can achieve due to the proportion of physical dimensions. A collision takes place when particles move towards each other and come near to interact and then exert a mutual influence.
Complete step by step solution:
By conservation of linear momentum between $m_1$ and $m_2$ and also by using the coefficient of restitution,
The velocity of $m_2$ just after collision $ = \dfrac{{3{v_o}}}{4}$ $\left( {\because {V_f} = \dfrac{{{m_1}v}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}} \right)$
Similarly, after the collision, the maximum extension in the spring occurs when the angular velocity of $m_2$ and m3 about the point O becomes the same.
By conservation of angular momentum about O and by energy conservation,
Velocity of $m_2$ $ = r\omega = 2r\omega = \dfrac{3}{5}{v_o}$ $\left( {\because v = r\omega } \right)$
Similarly velocity of $m_3$ $ = r\omega = r\omega = \dfrac{3}{{10}}{v_o}$ $\left( {\because v = r\omega } \right)$
Thus maximum extension in the spring $ = \dfrac{{3{v_o}}}{4}\sqrt {\dfrac{m}{{5k}}} $ ${\because}$ k = Spring constant
Hence the correct option is B.
Note: 1) A coefficient of restitution equal to zero indicates a perfectly inelastic collision. Also, the coefficient of restitution indicates how elastic or inelastic the collision is.
2) The spring constant is defined as the ratio of the force affecting the spring to the displacement caused by it. It is denoted by k. When stretching a material, the limit of proportionality refers to the point beyond which Hooke’s law is no longer.
3) According to the principle of conservation of momentum, the total momentum of the system is unchanged in the collision process. Collisions are classified as elastic or inelastic based on whether mechanical energy or kinetic energy is conserved or not conserved.
4) The spring is said to be stiff if the spring constant is large and is said to be soft if the spring constant is small.
Complete step by step solution:
By conservation of linear momentum between $m_1$ and $m_2$ and also by using the coefficient of restitution,
The velocity of $m_2$ just after collision $ = \dfrac{{3{v_o}}}{4}$ $\left( {\because {V_f} = \dfrac{{{m_1}v}}{{{m_1} + {m_2}}}} \right)$
Similarly, after the collision, the maximum extension in the spring occurs when the angular velocity of $m_2$ and m3 about the point O becomes the same.
By conservation of angular momentum about O and by energy conservation,
Velocity of $m_2$ $ = r\omega = 2r\omega = \dfrac{3}{5}{v_o}$ $\left( {\because v = r\omega } \right)$
Similarly velocity of $m_3$ $ = r\omega = r\omega = \dfrac{3}{{10}}{v_o}$ $\left( {\because v = r\omega } \right)$
Thus maximum extension in the spring $ = \dfrac{{3{v_o}}}{4}\sqrt {\dfrac{m}{{5k}}} $ ${\because}$ k = Spring constant
Hence the correct option is B.
Note: 1) A coefficient of restitution equal to zero indicates a perfectly inelastic collision. Also, the coefficient of restitution indicates how elastic or inelastic the collision is.
2) The spring constant is defined as the ratio of the force affecting the spring to the displacement caused by it. It is denoted by k. When stretching a material, the limit of proportionality refers to the point beyond which Hooke’s law is no longer.
3) According to the principle of conservation of momentum, the total momentum of the system is unchanged in the collision process. Collisions are classified as elastic or inelastic based on whether mechanical energy or kinetic energy is conserved or not conserved.
4) The spring is said to be stiff if the spring constant is large and is said to be soft if the spring constant is small.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




