
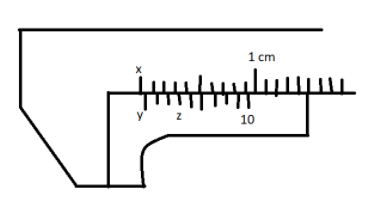
Find the zero error in the figure given.
A) $0.3mm$
B) $-0.3mm$
C) $-0.7mm$
D) $0.7mm$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Zero error is defined as the state under which a measurement tool reports a read where no reading is to occur. When vernier callipers do not balance a zero in the main scale with a zero in the vernier scale. There can be two forms of zero error: if the scale is more than zero it is positive; otherwise it is negative. Using the formulation: real read = main scale $ + $ vernier scale $ - $ (zero error). The way of using a vernier scale or calliper is to use the formula.
Complete step by step solution:
As the vernier scale zero is ahead of the main scale zero. Thus, the error is zero positive.
Least count of the vernier calliper \[L.C. = 0.1\; mm\]
Since the third division matches with the main scale division.
Zero error is \[n \times L.C. = 3 \times 0.1 = 0.3\; mm\].
Note: The vernier scale is a visual aid to compare accurately between two linear graduation marks by means of mechanical interpolation; this increases the resolution and the ambiguity of estimation by using vernier acuity to reduce the error of the human approximation.
The vernier is a secondary scale that replaces a single indicator and has ten divisions on the main scale, for instance, which are equal in distance to nine divisions. Interpolated readings can be achieved by looking at which vernier measures are coincidental with the main scale graduation, which is much easier to interpret than the two-point visual estimate. Such a solution can be achieved with a higher resolution, known as the vernier constant. In circular or straight scales, a vernier may be used if the linear system is appropriate.
Complete step by step solution:
As the vernier scale zero is ahead of the main scale zero. Thus, the error is zero positive.
Least count of the vernier calliper \[L.C. = 0.1\; mm\]
Since the third division matches with the main scale division.
Zero error is \[n \times L.C. = 3 \times 0.1 = 0.3\; mm\].
Note: The vernier scale is a visual aid to compare accurately between two linear graduation marks by means of mechanical interpolation; this increases the resolution and the ambiguity of estimation by using vernier acuity to reduce the error of the human approximation.
The vernier is a secondary scale that replaces a single indicator and has ten divisions on the main scale, for instance, which are equal in distance to nine divisions. Interpolated readings can be achieved by looking at which vernier measures are coincidental with the main scale graduation, which is much easier to interpret than the two-point visual estimate. Such a solution can be achieved with a higher resolution, known as the vernier constant. In circular or straight scales, a vernier may be used if the linear system is appropriate.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Derive an expression for maximum speed of a car on class 11 physics JEE_Main

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Fluids (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Law of Motion (2025-26)

Class 11 JEE Main Physics Mock Test 2025

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




