
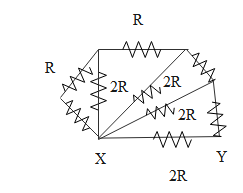
For the circuit, the equivalent resistance between X and Y is:
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint It should be known to us that the equivalent resistance of a network is given as the single resistor which can replace the entire network present within the system. The replacement should be made in such a way that a certain amount of voltage V can be applied so as to get the same amount of current, suppose I that we were getting from the network.
Complete step by step answer:
The 4 resistors which are of the value R are given as R each pair, as the equivalent resistance since they are in series with each other. Since there are 2 pairs so the resistance for the 4 R resistors will be 2R.
From the diagram, we can draw the equivalent circuit as, especially for the ones which are in the branches are given below:
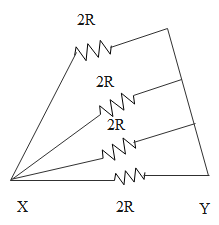
From the above diagram we can find the equivalent resistance as:
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{2R}} + \dfrac{1}{{2R}} = \dfrac{1}{R}$
(1 / 2R from the 4 series resistors and 1 / 2R from the resistors which are in the branches)
So, the value of ${R_{eq}}$or the equivalent resistance is given as R.
Hence, we can say that the equivalent resistance between the terminals X and Y is given as R ohm.
Note It should be known to us that the components in a series network are connected along a single conductive path. This is done because the same current is to be flown through every component but the voltage is dropped or we can say it is lost across each of the resistances.
On the other hand, in case of parallel connection there are multiple paths so that the current can split up through all the paths. The same voltage is received by all the components.
Complete step by step answer:
The 4 resistors which are of the value R are given as R each pair, as the equivalent resistance since they are in series with each other. Since there are 2 pairs so the resistance for the 4 R resistors will be 2R.
From the diagram, we can draw the equivalent circuit as, especially for the ones which are in the branches are given below:

From the above diagram we can find the equivalent resistance as:
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{2R}} + \dfrac{1}{{2R}} = \dfrac{1}{R}$
(1 / 2R from the 4 series resistors and 1 / 2R from the resistors which are in the branches)
So, the value of ${R_{eq}}$or the equivalent resistance is given as R.
Hence, we can say that the equivalent resistance between the terminals X and Y is given as R ohm.
Note It should be known to us that the components in a series network are connected along a single conductive path. This is done because the same current is to be flown through every component but the voltage is dropped or we can say it is lost across each of the resistances.
On the other hand, in case of parallel connection there are multiple paths so that the current can split up through all the paths. The same voltage is received by all the components.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




