
Formal charge on nitrogen and oxygen in $NO_3^ - $ ion are respectively:
(A) 0, $ - \dfrac{1}{3}$
(B) +1, $ - \dfrac{1}{3}$
(C) +1, $ - \dfrac{2}{3}$
(D) 0, $ - \dfrac{2}{3}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: To answer this question we must first recall the concept of a formal charge. We would also have to remember how it was calculated via formula and by instinct to some extent.
Complete step by step solution:
-Formal charge is actually the charge assigned to an atom, under the assumption that the electrons in a chemical bond are shared equally between the atoms and that they have almost no difference in their electronegativities.
-To calculate formal charges, we assign electrons in the molecule to individual atoms according to these rules:
(1)Non-bonding electrons are only assigned to the atom on which they are located.
(2)Bonding electrons are divided equally between the two bonded atoms, so one electron from each bond goes to each atom.
-On drawing the structure of nitrite ion, we can predict the number of electrons each element entails.
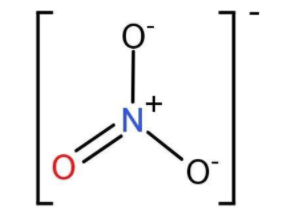
-The mathematical formula to calculate formal charge is:
$F.C. = V - N - \dfrac{B}{2}$
Where V = number of valence electrons;
N = number of nonbonding electrons;
B = Number of electrons in a covalent bond.
-For Nitrogen:
From the structure itself, we find a positive charge on Nitrogen, hence it carries a formal charge of +1. This is what we assign to every element of a compound. We are counting 4 electrons (4 bonding electrons, no nonbonding electrons). Since N is in Group 15, we have one less electron than N should have, and so it has a +1 charge.
-For oxygen,
From the structure, we see that, for the O with the double bond, we are counting 6 electrons for it (4 nonbonding electrons and 2 bonding electrons (one per band). Since O is in Group 16, that’s how many electrons it should have, so the charge for that O is zero. For either of the O atoms with a single bond, we can count 7 electrons (6 nonbonding electrons and one bonding electron). That’s one more than 6, so those O atoms have a charge of −1 each. Hence for 3 O atoms, we find the formal charge is $ - \dfrac{1}{3}$.
Hence the correct answer is Option (B) +1, $ - \dfrac{1}{3}$.
Additional information:
The structure with the most formal charges of zero on atoms is the most stable Lewis structure. In cases where there are positive or negative formal charges on various atoms, the most stable structures generally have negative formal charges on the more electronegative atoms and positive formal charges on the less electronegative atoms.
Note: The single bound oxygen atoms have nine electrons linked with them moreover they have a negative charge overall. This means the nitrate ion has an overall charge of -1.
Complete step by step solution:
-Formal charge is actually the charge assigned to an atom, under the assumption that the electrons in a chemical bond are shared equally between the atoms and that they have almost no difference in their electronegativities.
-To calculate formal charges, we assign electrons in the molecule to individual atoms according to these rules:
(1)Non-bonding electrons are only assigned to the atom on which they are located.
(2)Bonding electrons are divided equally between the two bonded atoms, so one electron from each bond goes to each atom.
-On drawing the structure of nitrite ion, we can predict the number of electrons each element entails.

-The mathematical formula to calculate formal charge is:
$F.C. = V - N - \dfrac{B}{2}$
Where V = number of valence electrons;
N = number of nonbonding electrons;
B = Number of electrons in a covalent bond.
-For Nitrogen:
From the structure itself, we find a positive charge on Nitrogen, hence it carries a formal charge of +1. This is what we assign to every element of a compound. We are counting 4 electrons (4 bonding electrons, no nonbonding electrons). Since N is in Group 15, we have one less electron than N should have, and so it has a +1 charge.
-For oxygen,
From the structure, we see that, for the O with the double bond, we are counting 6 electrons for it (4 nonbonding electrons and 2 bonding electrons (one per band). Since O is in Group 16, that’s how many electrons it should have, so the charge for that O is zero. For either of the O atoms with a single bond, we can count 7 electrons (6 nonbonding electrons and one bonding electron). That’s one more than 6, so those O atoms have a charge of −1 each. Hence for 3 O atoms, we find the formal charge is $ - \dfrac{1}{3}$.
Hence the correct answer is Option (B) +1, $ - \dfrac{1}{3}$.
Additional information:
The structure with the most formal charges of zero on atoms is the most stable Lewis structure. In cases where there are positive or negative formal charges on various atoms, the most stable structures generally have negative formal charges on the more electronegative atoms and positive formal charges on the less electronegative atoms.
Note: The single bound oxygen atoms have nine electrons linked with them moreover they have a negative charge overall. This means the nitrate ion has an overall charge of -1.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




