
Given figure shows two cases. In the first case a spring (spring constant $K$) is pulled by two equal and opposite forces $F$ at both ends and in the second case, spring is pulled by a force $F$ at one end, then the extension $\left( x \right)$ in the springs is
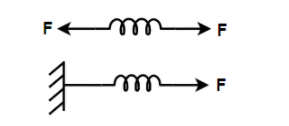
(A) In both cases $x = \dfrac{{2F}}{K}$
(B) In both cases $x = \dfrac{F}{K}$
(C) In first case $x = \dfrac{{2F}}{K}$ , In second case $x = \dfrac{F}{K}$
(D) In first case $x = \dfrac{F}{K}$ , In second case $x = \dfrac{{2F}}{K}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: - Here, write the value of restoring force in terms of spring constant and extension in each case from the given figure using Hooke’s law.
Formula Used: Here we will be using the formula for spring force given by Hooke’s law is ${F_{{\text{spring}}}} = - Kx$, where $K$ is the spring constant, $x$ is the extension in the string and ${F_{{\text{spring}}}}$ will be the spring force.
Complete step by step solution: -
The expression given by Hooke’s law for spring force is,
$ \Rightarrow {F_{{\text{spring}}}} = - Kx$
Here, negative sign indicates that the force exerted in an opposite direction by the spring to the spring displacement.
Consider the given two figures.
In the first figure, spring is pulled from both ends on either side by a force $F$.
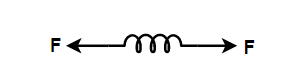
The two forces exerted on the spring are in the opposite direction to each other. So the net force will be equal to the sum of both the forces acting on the spring. Thus, the net forces stretched force applied on the spring is,
$ \Rightarrow F = {F_{{\text{spring}}}} + {F_{{\text{spring}}}}$
And on adding it
$ \Rightarrow 2{F_{{\text{spring}}}}$
Here, the stretched force of spring from either end is $F$.
Now, substitute $Kx$ for spring force.
$ \Rightarrow F = 2Kx$
Rearrange the equation for extension of spring.
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{2F}}{K}$
But in this case, the displacement or extension produced from each end is reduced to half as both applied equal force to stretch the spring. So, displacement produced in this case is,
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{x}{2}$
Now, the extension of spring is,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{2} = \dfrac{{2F}}{K}$
And on solving for the value of $x$ , we get
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{F}{K}$
In the second figure, a spring is tied to a wall and a force $F$is exerted to pull the spring.
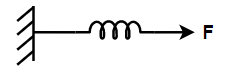
Calculate the stretched distance of spring from the above figure.
$ \Rightarrow F = {F_{{\text{spring}}}}$
Here, the stretched force applied opposite to the wall is $F$ .
Now, substitute $Kx$ for spring force.
$ \Rightarrow F = Kx$
Rearrange the equation for extension of spring.
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{F}{K}$
So, option $\left( 2 \right)$ is correct answer
Additional information: Hooke’s law states that the strain or force applied on a material to stretch or compress is directly proportional to the displacement of the object and the constant of proportionality is termed as spring constant and denoted as $K$. It is expressed with a negative value to determine whether it is stretched or compressed.
Note: The negative sign is to indicate that the force exerted in an opposite direction by the spring to the spring displacement. So, a sign is to be considered while doing calculation depending on the situations given. Always keep in mind the direction of force given in the figure or question.
Formula Used: Here we will be using the formula for spring force given by Hooke’s law is ${F_{{\text{spring}}}} = - Kx$, where $K$ is the spring constant, $x$ is the extension in the string and ${F_{{\text{spring}}}}$ will be the spring force.
Complete step by step solution: -
The expression given by Hooke’s law for spring force is,
$ \Rightarrow {F_{{\text{spring}}}} = - Kx$
Here, negative sign indicates that the force exerted in an opposite direction by the spring to the spring displacement.
Consider the given two figures.
In the first figure, spring is pulled from both ends on either side by a force $F$.

The two forces exerted on the spring are in the opposite direction to each other. So the net force will be equal to the sum of both the forces acting on the spring. Thus, the net forces stretched force applied on the spring is,
$ \Rightarrow F = {F_{{\text{spring}}}} + {F_{{\text{spring}}}}$
And on adding it
$ \Rightarrow 2{F_{{\text{spring}}}}$
Here, the stretched force of spring from either end is $F$.
Now, substitute $Kx$ for spring force.
$ \Rightarrow F = 2Kx$
Rearrange the equation for extension of spring.
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{2F}}{K}$
But in this case, the displacement or extension produced from each end is reduced to half as both applied equal force to stretch the spring. So, displacement produced in this case is,
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{x}{2}$
Now, the extension of spring is,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{2} = \dfrac{{2F}}{K}$
And on solving for the value of $x$ , we get
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{F}{K}$
In the second figure, a spring is tied to a wall and a force $F$is exerted to pull the spring.

Calculate the stretched distance of spring from the above figure.
$ \Rightarrow F = {F_{{\text{spring}}}}$
Here, the stretched force applied opposite to the wall is $F$ .
Now, substitute $Kx$ for spring force.
$ \Rightarrow F = Kx$
Rearrange the equation for extension of spring.
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{F}{K}$
So, option $\left( 2 \right)$ is correct answer
Additional information: Hooke’s law states that the strain or force applied on a material to stretch or compress is directly proportional to the displacement of the object and the constant of proportionality is termed as spring constant and denoted as $K$. It is expressed with a negative value to determine whether it is stretched or compressed.
Note: The negative sign is to indicate that the force exerted in an opposite direction by the spring to the spring displacement. So, a sign is to be considered while doing calculation depending on the situations given. Always keep in mind the direction of force given in the figure or question.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




