
Identify ‘C’ in the following reaction:
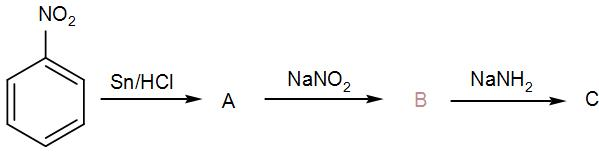
[A] Benzamide
[B] Benzoic acid
[C] Chlorobenzene
[D] Aniline
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: To solve this, proceed step wise and identify A, B and then arrive at C. Remember that tin with hydrochloric acid will reduce nitrobenzene and will give you an amine. Upon reaction with sodium nitride the amine will give you a salt. The salt will react with sodium amide and again arrive at phenyl amine.
Complete step by step solution:
To solve this, let’s see the reaction of nitrobenzene with the given reagents and then arrive at the final result.
In the first step, nitrobenzene reacts with tin and hydrochloric acid. It is a redox reaction and here the nitrobenzene is reduced to phenylamine. The reaction proceeds via formation of a phenyl ammonium cation by reduction of nitrobenzene. We can write the reaction as-
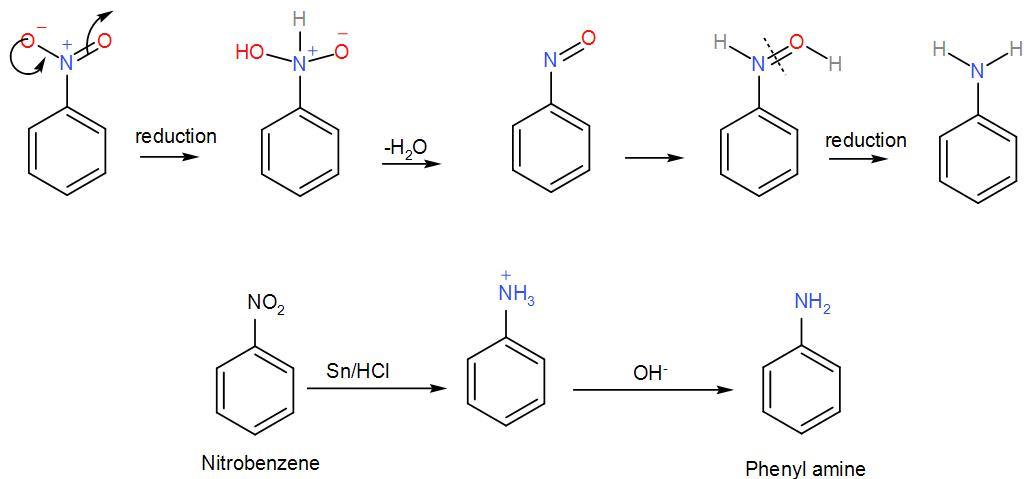
So, phenylamine is ‘A’. To this, sodium nitrite is added which will cause the amine to undergo diazotization. The hydrochloric acid in the reaction will react with it thus leading to the formation of a diazonium salt of benzene called benzene diazonium chloride. We can write the reaction as-
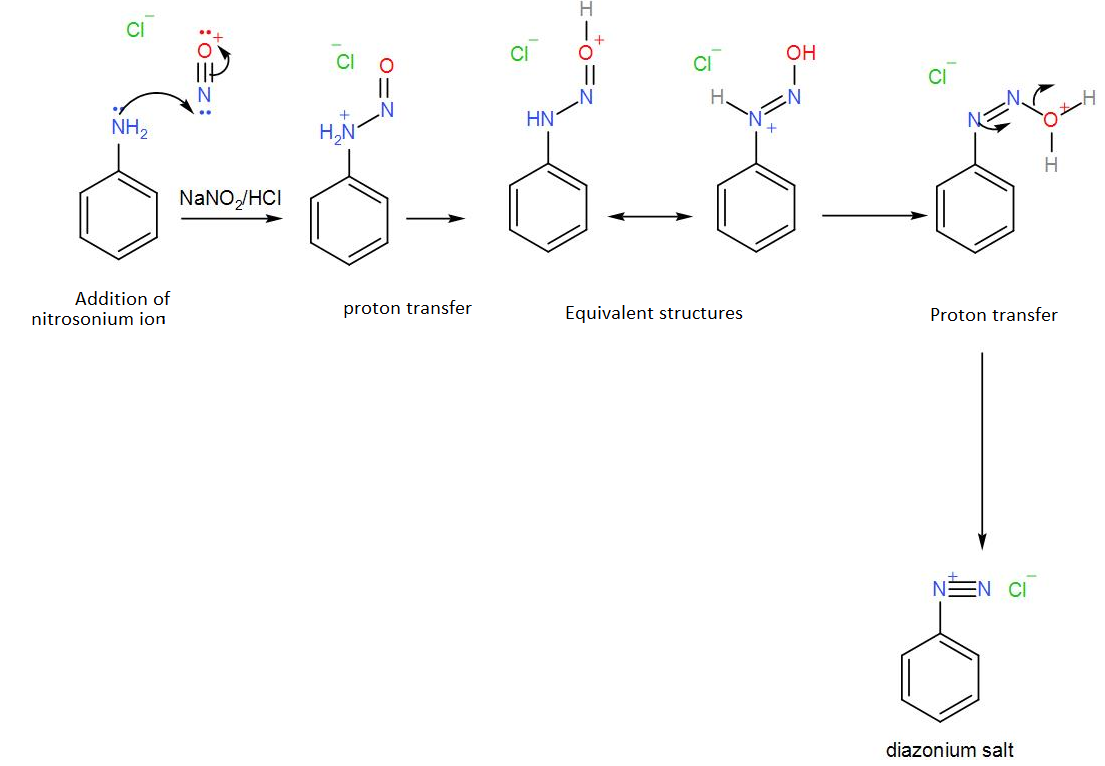
The diazonium salt thus obtained is our ‘B’.
To this diazonium salt when we add sodium amide we will again get the phenyl amine. We can write the reaction as-
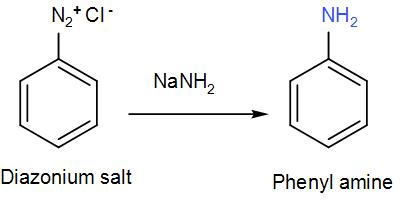
The phenyl amine is ‘C’. It is also known as aniline.
We can see from the above discussion that the ‘C’ in the reaction series is aniline.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [D] Aniline.
Note: Primary amines give us a diazonium salt which forms alcohols in addition to water but secondary amines have one hydrogen atom attached to them therefore, they cannot complete the diazotization reaction and give us a yellow oily nitrosamine product. Three degree amines have no hydrogen atoms attached to them thus they undergo simple acid- base reactions and give us soluble salts.
Complete step by step solution:
To solve this, let’s see the reaction of nitrobenzene with the given reagents and then arrive at the final result.
In the first step, nitrobenzene reacts with tin and hydrochloric acid. It is a redox reaction and here the nitrobenzene is reduced to phenylamine. The reaction proceeds via formation of a phenyl ammonium cation by reduction of nitrobenzene. We can write the reaction as-

So, phenylamine is ‘A’. To this, sodium nitrite is added which will cause the amine to undergo diazotization. The hydrochloric acid in the reaction will react with it thus leading to the formation of a diazonium salt of benzene called benzene diazonium chloride. We can write the reaction as-

The diazonium salt thus obtained is our ‘B’.
To this diazonium salt when we add sodium amide we will again get the phenyl amine. We can write the reaction as-

The phenyl amine is ‘C’. It is also known as aniline.
We can see from the above discussion that the ‘C’ in the reaction series is aniline.
Therefore, the correct answer is option [D] Aniline.
Note: Primary amines give us a diazonium salt which forms alcohols in addition to water but secondary amines have one hydrogen atom attached to them therefore, they cannot complete the diazotization reaction and give us a yellow oily nitrosamine product. Three degree amines have no hydrogen atoms attached to them thus they undergo simple acid- base reactions and give us soluble salts.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




