
If equation of sound wave is $y = 0.0015\sin (62.4x + 316t)$ , then its wavelength will be
(A) 2 unit
(B) 0.3unit
(C) 0.1unit
(D) 0.2 unit
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The given equation takes the exact form of the progressive wave equation$y = A\sin (\omega t - kx)$. So, on comparing both the wave functions, find out the value of the propagation constant k. k is related to the wavelength by $k = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }$ . Now on substituting the values calculate the wavelength of the wave.
Complete step-by-step answer
A mathematical description of the disturbance created by a wave is called a wave function.
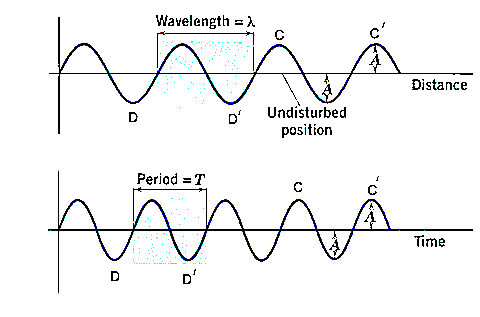
We know that, a progressive wave function is given by,
$y = A\sin (\omega t - kx)$
Where,
Y is the displacement; A is the amplitude; \[\omega \]is the angular frequency; x is the position; k is the propagation constant and t is the time.
$y = 0.0015\sin (62.4x + 316t)$
The given equation is similar to this wave function and therefore has corresponding values. On comparing with the progressive wave function we find out the value of the propagation constant also known as angular wave number.
$k = 62.8$
The number of wavelengths in the distance\[2\pi \]is called the wave number which is given by,
$k = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }$
Substitute the value of the angular wave number.
$\lambda = \dfrac{{2 \times 3.14}}{{62.8}}$
$\lambda = 0.1unit$
Hence, the wavelength of the wave is 0.1 units and the correct option is C.
Note: If during the propagation of a progressive wave, the particles of the medium perform SHM about their mean position then the wave is known as a harmonic progressive wave. Various forms of progressive wave function.
$y = A\sin 2\pi \left( {\dfrac{t}{T} - \dfrac{x}{\lambda }} \right)$
$y = A\sin \dfrac{{2\pi }}{T}\left( {t - \dfrac{{xT}}{\lambda }} \right)$
$y = A\sin \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }\left( {vt - x} \right)$
$y = A\sin \omega \left( {t - \dfrac{x}{v}} \right)$
We can also write it in exponential form
$y = A\dfrac{{{e^{i\omega \left( {t - \dfrac{x}{v}} \right)}} - {e^{ - i\omega \left( {t - \dfrac{x}{v}} \right)}}}}{{2i}}$
Complete step-by-step answer
A mathematical description of the disturbance created by a wave is called a wave function.

We know that, a progressive wave function is given by,
$y = A\sin (\omega t - kx)$
Where,
Y is the displacement; A is the amplitude; \[\omega \]is the angular frequency; x is the position; k is the propagation constant and t is the time.
$y = 0.0015\sin (62.4x + 316t)$
The given equation is similar to this wave function and therefore has corresponding values. On comparing with the progressive wave function we find out the value of the propagation constant also known as angular wave number.
$k = 62.8$
The number of wavelengths in the distance\[2\pi \]is called the wave number which is given by,
$k = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }$
Substitute the value of the angular wave number.
$\lambda = \dfrac{{2 \times 3.14}}{{62.8}}$
$\lambda = 0.1unit$
Hence, the wavelength of the wave is 0.1 units and the correct option is C.
Note: If during the propagation of a progressive wave, the particles of the medium perform SHM about their mean position then the wave is known as a harmonic progressive wave. Various forms of progressive wave function.
$y = A\sin 2\pi \left( {\dfrac{t}{T} - \dfrac{x}{\lambda }} \right)$
$y = A\sin \dfrac{{2\pi }}{T}\left( {t - \dfrac{{xT}}{\lambda }} \right)$
$y = A\sin \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\lambda }\left( {vt - x} \right)$
$y = A\sin \omega \left( {t - \dfrac{x}{v}} \right)$
We can also write it in exponential form
$y = A\dfrac{{{e^{i\omega \left( {t - \dfrac{x}{v}} \right)}} - {e^{ - i\omega \left( {t - \dfrac{x}{v}} \right)}}}}{{2i}}$
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




