
If ${w_1}$, ${w_2}$,${w_3}$,${w_4}$ are work done in isothermal, adiabatic, isobaric and isochoric reversible processes, then the correct sequence (for expansion) would be :
(A) ${w_1}$> ${w_2}$>${w_3}$>${w_4}$
(B) ${w_3}$> ${w_2}$>${w_1}$>${w_4}$
(C) ${w_3}$> ${w_2}$>${w_4}$>${w_1}$
(D) ${w_3}$>${w_1}$> ${w_2}$>${w_4}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The work done by any thermodynamic process can be given by the area enclosed by the P-V graph by that process. As in the case of isochoric, the volume remains constant. So, no change in volume and hence no work done. So, it will have the least value while in the case of isobaric, the value will be highest.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we will know about the different types of process. What is the difference between these and then we will be able to find out the answer to our question?
The first process is the isothermal process. This may be defined as the process in which thermal meaning temperature is constant. The word ‘iso’ means constant and the word thermal means ‘temperature’. In the isothermal process, the temperature of the system remains constant throughout.
The next process is the adiabatic process. In such a process, The heat and mass is not transformed between the thermodynamic system and its surroundings.
After this, the next process is the isobaric one. The term ‘baric’ is related to pressure. The isobaric process is the one in which the pressure remains constant throughout the process. There may be changes in volume or temperature but the pressure will remain constant.
The last process mentioned is the isochoric one. In this process, the volume of the system remains constant. The term choric stands for the volume.
In the question, it is mentioned that expansion is occurring.
Further, we have that ${w_1}$is the work done during an isothermal process
${w_2}$ is the work done during an adiabatic process
${w_3}$ is the work done during the isobaric process
${w_4}$ is the work done during an isochoric process.
We have the graph for the different processes as-
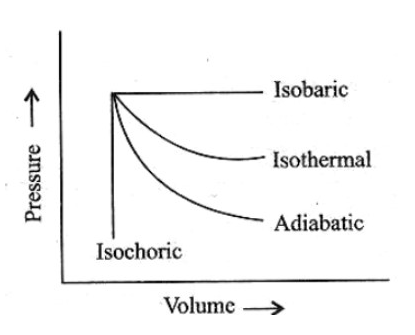
The area under this pressure-volume graph tells us about the work done in any system. If we observe this graph, we can see that
The area under isobaric expansion is the maximum. Thus, the highest work done will be by the isobaric expansion. So, the ${w_3}$will hold the greatest value.
After this, the next maximum area cover is by the isothermal process. So, after this, the ${w_1}$ will be there.
Then after this, comes the area enclosed by the adiabatic process and at last by the isochoric process.
So, the order of work done is as -
${w_3}$>${w_1}$> ${w_2}$>${w_4}$
Thus, the option (D) is the correct answer.
Note: It must be noted that the process is reversible. In any reversible process, the products may go back to the reactant side. The work done by a system is given by PdV. The Pressure-Volume graph is formed as a result of integrating the PdV equation which will give work done.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we will know about the different types of process. What is the difference between these and then we will be able to find out the answer to our question?
The first process is the isothermal process. This may be defined as the process in which thermal meaning temperature is constant. The word ‘iso’ means constant and the word thermal means ‘temperature’. In the isothermal process, the temperature of the system remains constant throughout.
The next process is the adiabatic process. In such a process, The heat and mass is not transformed between the thermodynamic system and its surroundings.
After this, the next process is the isobaric one. The term ‘baric’ is related to pressure. The isobaric process is the one in which the pressure remains constant throughout the process. There may be changes in volume or temperature but the pressure will remain constant.
The last process mentioned is the isochoric one. In this process, the volume of the system remains constant. The term choric stands for the volume.
In the question, it is mentioned that expansion is occurring.
Further, we have that ${w_1}$is the work done during an isothermal process
${w_2}$ is the work done during an adiabatic process
${w_3}$ is the work done during the isobaric process
${w_4}$ is the work done during an isochoric process.
We have the graph for the different processes as-

The area under this pressure-volume graph tells us about the work done in any system. If we observe this graph, we can see that
The area under isobaric expansion is the maximum. Thus, the highest work done will be by the isobaric expansion. So, the ${w_3}$will hold the greatest value.
After this, the next maximum area cover is by the isothermal process. So, after this, the ${w_1}$ will be there.
Then after this, comes the area enclosed by the adiabatic process and at last by the isochoric process.
So, the order of work done is as -
${w_3}$>${w_1}$> ${w_2}$>${w_4}$
Thus, the option (D) is the correct answer.
Note: It must be noted that the process is reversible. In any reversible process, the products may go back to the reactant side. The work done by a system is given by PdV. The Pressure-Volume graph is formed as a result of integrating the PdV equation which will give work done.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




