
If we have a function as $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{3}}-6{{x}^{2}}-36x+2$ which is decreasing function, then x belongs to
A. \[\left( 6,\infty \right)\]
B. \[\left( -\infty ,-2 \right)\]
C. \[\left( -2,6 \right)\]
D. None of the above
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: We will be using the concept of polynomial specifically cubic equations to solve the problem. We will be using the concept of differential calculus to further simplify the solution.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Now, we have been given that $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{3}}-6{{x}^{2}}-36x+2$.
We have to find the domain for which the function is a decreasing function.
We know that the derivative of a function can be used to determine whether the function is decreasing or decreasing.
For a function to be decreasing we know $f'\left( x \right)<0$ for each point in an interval I.
For finding the interval in which the function is decreasing we have to first the critical points by $f'\left( x \right)=0$.
Now, we have $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{3}}-6{{x}^{2}}-36x+2$.
$\begin{align}
\Rightarrow & f'\left( x \right)=3{{x}^{2}}-12x-36 \\
\Rightarrow & 3{{x}^{2}}-12x-36=0 \\
\Rightarrow & 3\left( {{x}^{2}}-4x-12 \right)=0 \\
\Rightarrow & {{x}^{2}}-6x+2x-12=0 \\
\Rightarrow & x\left( x-6 \right)+2\left( x-6 \right)=0 \\
\Rightarrow & \left( x+2 \right)\left( x-6 \right)=0 \\
\end{align}$
So, critical points are – 2, 6.
Now, we have to find for which range $f'\left( x \right)<0$. So, we will use the number line to show the critical points and find in which range $f'\left( x \right)<0$.
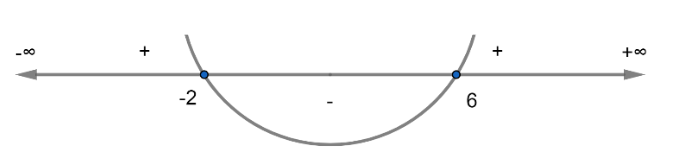
Now, for $x<-2\ and\ x>6$
$f'\left( x \right)>0$
Now, for $-2 < x < 6$
$f'\left( x \right)<0$
So, we have $f'\left( x \right)<0$ for $x\in \left( -2,6 \right)$.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note: To solve these types of questions it is important to know the concepts of inequality as we have used inequality to find the final answer, also it has to be noted that the function is decreasing if $f'\left( x \right) < 0$.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Now, we have been given that $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{3}}-6{{x}^{2}}-36x+2$.
We have to find the domain for which the function is a decreasing function.
We know that the derivative of a function can be used to determine whether the function is decreasing or decreasing.
For a function to be decreasing we know $f'\left( x \right)<0$ for each point in an interval I.
For finding the interval in which the function is decreasing we have to first the critical points by $f'\left( x \right)=0$.
Now, we have $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{3}}-6{{x}^{2}}-36x+2$.
$\begin{align}
\Rightarrow & f'\left( x \right)=3{{x}^{2}}-12x-36 \\
\Rightarrow & 3{{x}^{2}}-12x-36=0 \\
\Rightarrow & 3\left( {{x}^{2}}-4x-12 \right)=0 \\
\Rightarrow & {{x}^{2}}-6x+2x-12=0 \\
\Rightarrow & x\left( x-6 \right)+2\left( x-6 \right)=0 \\
\Rightarrow & \left( x+2 \right)\left( x-6 \right)=0 \\
\end{align}$
So, critical points are – 2, 6.
Now, we have to find for which range $f'\left( x \right)<0$. So, we will use the number line to show the critical points and find in which range $f'\left( x \right)<0$.

Now, for $x<-2\ and\ x>6$
$f'\left( x \right)>0$
Now, for $-2 < x < 6$
$f'\left( x \right)<0$
So, we have $f'\left( x \right)<0$ for $x\in \left( -2,6 \right)$.
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note: To solve these types of questions it is important to know the concepts of inequality as we have used inequality to find the final answer, also it has to be noted that the function is decreasing if $f'\left( x \right) < 0$.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits




