
In the above-shown figure, the direction of the magnetic force and magnetic field is given then find out the direction of the particle velocity v.
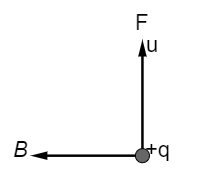
A) To the right.
B) Downward in the plane of the page
C) Upward in the plane of the page
D) Out of the plane of the page
E) Into the plane of the page.
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: For the motion of a charged particle in a magnetic field, the magnetic field vector $B$, the velocity of the particle vector $v$, and the magnetic force vector $F$ that exerted on the particle are all perpendicular to each other.
Complete answer:
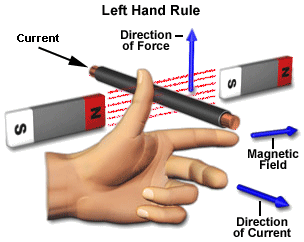
The right-hand rule of Fleming states that, to find the direction of the magnetic force on a positive charge, the thumb of the right-hand point in the direction of the velocity of the particle $v$, the fingers in the direction of the magnetic field ($B$), and the force ($F$) is directed perpendicular to the right-hand palm.
The magnetic force on a charged particle with positive charge $q$ moving in a magnetic field $B$ with a velocity $v$ (at angle $\theta $ to $B$) is –
\[\overrightarrow F = qvB\sin \theta \]
\[ \Rightarrow \overrightarrow F = q(\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow B )\]
Therefore we can say, force is the cross product of $B$ and $v$ and hence Force is in the perpendicular plane of velocity and magnetic field.
Hence In the figure,
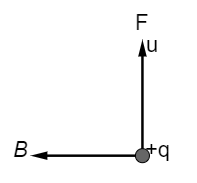
the direction of the magnetic field and force are given. Now if we apply Fleming right-hand rule the direction of the particle velocity will be into the plane of the page.
Hence, the option (E) is the correct answer.
Note: Fleming's rules are applied for determining the relation between the directions of magnetic field, electric current and velocity of a conductor.
There are two rules,
Fleming's left-hand rule for motors which applies for an electric current induces motion in the conductor in the presence of magnetic fields known as Lorentz force.
Fleming's right-hand rule for generators, which applies for a conductor moving through a magnetic field, has an electromotive force induced in it as a result known as Faraday's law of induction.
Complete answer:
The right-hand rule of Fleming states that, to find the direction of the magnetic force on a positive charge, the thumb of the right-hand point in the direction of the velocity of the particle $v$, the fingers in the direction of the magnetic field ($B$), and the force ($F$) is directed perpendicular to the right-hand palm.

The magnetic force on a charged particle with positive charge $q$ moving in a magnetic field $B$ with a velocity $v$ (at angle $\theta $ to $B$) is –
\[\overrightarrow F = qvB\sin \theta \]
\[ \Rightarrow \overrightarrow F = q(\overrightarrow v \times \overrightarrow B )\]
Therefore we can say, force is the cross product of $B$ and $v$ and hence Force is in the perpendicular plane of velocity and magnetic field.
Hence In the figure,

the direction of the magnetic field and force are given. Now if we apply Fleming right-hand rule the direction of the particle velocity will be into the plane of the page.
Hence, the option (E) is the correct answer.
Note: Fleming's rules are applied for determining the relation between the directions of magnetic field, electric current and velocity of a conductor.
There are two rules,
Fleming's left-hand rule for motors which applies for an electric current induces motion in the conductor in the presence of magnetic fields known as Lorentz force.
Fleming's right-hand rule for generators, which applies for a conductor moving through a magnetic field, has an electromotive force induced in it as a result known as Faraday's law of induction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Why does capacitor block DC and allow AC class 12 physics JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 2 (55/2/2) 2025 Question Paper & Solutions

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Units and Measurements Mock Test for JEE Main 2025-26 Preparation

Chemistry Question Papers for JEE Main, NEET & Boards (PDFs)




