
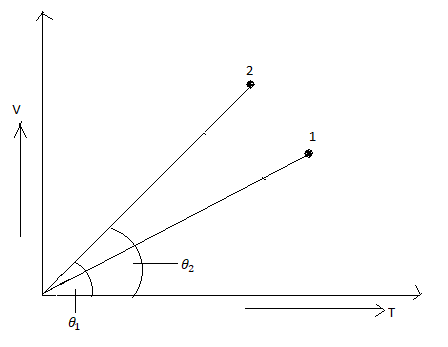
In the following V-T diagram what is the relation between \[{P_1}\] and \[{P_2}\]:
A) ${{\text{P}}_2} = {{\text{P}}_1}$
B) ${{\text{P}}_2} > {{\text{P}}_1}$
C) ${{\text{P}}_2} < {{\text{P}}_1}$
D) Cannot be predicted
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:
i)Ideal gas equation: It is the relationship between Boyle’s law, Charles law, and Avogadro’s law.
ii) Boyle’s law: This describes how the pressure of a gas tends to change as the volume of the container.
iii) Charles law: This describes how gas tends to expand when heated.
iv) Avogadro’s law: This describes the relationship between the volumes of gas to the amount of substance of gas present.
Formula used:
Ideal gas equation,${\text{PV = RT}}$,
Here\[\;P = \] pressure of the gas,
\[V = \] volume of the gas,
\[T = \] temperature,
\[R = \] universal gas constant
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that \[{P_1}\]and \[{P_2}\] is the pressure from the graph.
Therefore, the ideal gas equation can be re-written as, $\dfrac{{\text{V}}}{{\text{T}}} = \dfrac{{\text{R}}}{{\text{P}}}$
From the given graph we see that the slope of \[2\,\] is greater than the slope of\[1\].
Therefore, we can write that, $\dfrac{{{{\text{V}}_2}}}{{{{\text{T}}_2}}} > \dfrac{{{{\text{V}}_1}}}{{{{\text{T}}_1}}}$
From the ideal gas equation, $\dfrac{1}{{{{\text{P}}_2}}} > \dfrac{1}{{{{\text{P}}_1}}}$
So we can write it as,
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{P}}_2} < {{\text{P}}_1}$
Hence the correct option is (C).
Note:
i) By using the ideal gas equation, we can measure the temperature accurately irrespective of their masses and other physical quantities.
ii) Boyle’s law in thermodynamics explains the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure exerted by a gas at a constant temperature.
iii) Charles law in thermodynamics defines where the volume of a fixed mass of a dry gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
iv) Avogadro’s law in thermodynamics where number of atoms/ molecules of a gas is directly proportional to the volume occupied by the gas at a constant temperature.
v) Calorimeter is a device used to measure the heat energy added to the system
i)Ideal gas equation: It is the relationship between Boyle’s law, Charles law, and Avogadro’s law.
ii) Boyle’s law: This describes how the pressure of a gas tends to change as the volume of the container.
iii) Charles law: This describes how gas tends to expand when heated.
iv) Avogadro’s law: This describes the relationship between the volumes of gas to the amount of substance of gas present.
Formula used:
Ideal gas equation,${\text{PV = RT}}$,
Here\[\;P = \] pressure of the gas,
\[V = \] volume of the gas,
\[T = \] temperature,
\[R = \] universal gas constant
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that \[{P_1}\]and \[{P_2}\] is the pressure from the graph.
Therefore, the ideal gas equation can be re-written as, $\dfrac{{\text{V}}}{{\text{T}}} = \dfrac{{\text{R}}}{{\text{P}}}$
From the given graph we see that the slope of \[2\,\] is greater than the slope of\[1\].
Therefore, we can write that, $\dfrac{{{{\text{V}}_2}}}{{{{\text{T}}_2}}} > \dfrac{{{{\text{V}}_1}}}{{{{\text{T}}_1}}}$
From the ideal gas equation, $\dfrac{1}{{{{\text{P}}_2}}} > \dfrac{1}{{{{\text{P}}_1}}}$
So we can write it as,
$ \Rightarrow {{\text{P}}_2} < {{\text{P}}_1}$
Hence the correct option is (C).
Note:
i) By using the ideal gas equation, we can measure the temperature accurately irrespective of their masses and other physical quantities.
ii) Boyle’s law in thermodynamics explains the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure exerted by a gas at a constant temperature.
iii) Charles law in thermodynamics defines where the volume of a fixed mass of a dry gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
iv) Avogadro’s law in thermodynamics where number of atoms/ molecules of a gas is directly proportional to the volume occupied by the gas at a constant temperature.
v) Calorimeter is a device used to measure the heat energy added to the system
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




