
In the Molisch reagent the substance used is:
A) β- naphthol in alcohol
B) α-naphthol in alcohol
C) Resorcinol in alcohol
D) Rosaniline in water
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Molisch test is a test to check for the presence of carbohydrates, whether they are in free or in any combined forms. Such tests always require an end point indication to confirm the presence; it can be odour, colour, effervescence, etc. So, now think which of the options can do so with carbohydrates.
Complete step by step solution:
-Molisch test has been named after Austrian botanist Hans Molisch.
-This test is used to check if carbohydrates are present or not. Monosaccharides, glycoproteins, disaccharides and polysaccharides all react to this test. Although monosaccharides react rapidly, while polysaccharides and disaccharides react a bit slower.
-The reagent used in this test is known as Molisch’s reagent. It consists of: α-naphthol (${C_{10}}{H_8}OH$) dissolved in ethanol (${C_2}{H_5}OH$).
-Principle: Carbohydrates are dehydrated with concentrated${H_2}S{O_4}$ to form its corresponding furfural derivatives which are then condensed by the α-naphthol to give a coloured condensation product.
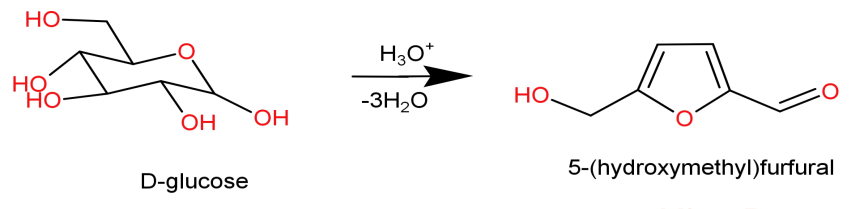
-here concentrated sulphuric acid (concentrated${H_2}S{O_4}$) acts like a strong dehydrating agent which dehydrates the carbohydrate or sugar into its corresponding furfural (from pentoses) or hydroxymethyl furfural (from hexoses).
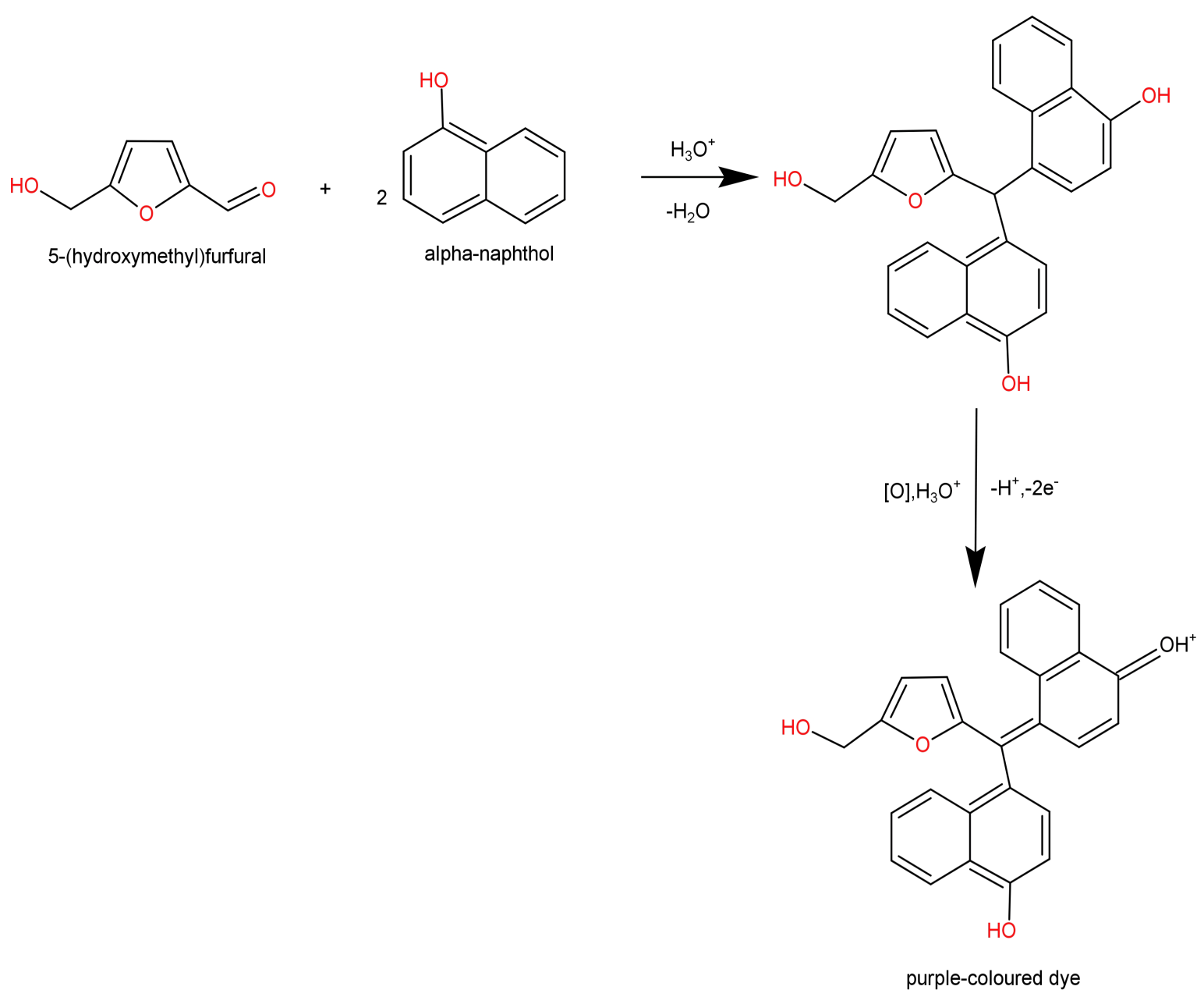
-Furfurals are then condensed using α-naphthol, which gives a violet or purple coloured product (ring is formed at the interface). This product is a furfuryl-diphenyl-methane-dye.
- When the carbohydrate is a poly- or disaccharide, first its monosaccharide components are hydrolysed to form the furfural derivatives.
-End point of this test: appearance of purple or violet ring at the interface. If seen then carbohydrate is present otherwise not.
So, the correct option is: B) α-naphthol in alcohol
Note: always remember that although α-naphthol and β-naphthol are isomers, it does not mean they are the same. The difference in the position of alcohol groups in both causes them to differ in their reactivity and that is why this test is not given by β-naphthol.
Complete step by step solution:
-Molisch test has been named after Austrian botanist Hans Molisch.
-This test is used to check if carbohydrates are present or not. Monosaccharides, glycoproteins, disaccharides and polysaccharides all react to this test. Although monosaccharides react rapidly, while polysaccharides and disaccharides react a bit slower.
-The reagent used in this test is known as Molisch’s reagent. It consists of: α-naphthol (${C_{10}}{H_8}OH$) dissolved in ethanol (${C_2}{H_5}OH$).
-Principle: Carbohydrates are dehydrated with concentrated${H_2}S{O_4}$ to form its corresponding furfural derivatives which are then condensed by the α-naphthol to give a coloured condensation product.
-here concentrated sulphuric acid (concentrated${H_2}S{O_4}$) acts like a strong dehydrating agent which dehydrates the carbohydrate or sugar into its corresponding furfural (from pentoses) or hydroxymethyl furfural (from hexoses).
-Furfurals are then condensed using α-naphthol, which gives a violet or purple coloured product (ring is formed at the interface). This product is a furfuryl-diphenyl-methane-dye.


- When the carbohydrate is a poly- or disaccharide, first its monosaccharide components are hydrolysed to form the furfural derivatives.
-End point of this test: appearance of purple or violet ring at the interface. If seen then carbohydrate is present otherwise not.
So, the correct option is: B) α-naphthol in alcohol
Note: always remember that although α-naphthol and β-naphthol are isomers, it does not mean they are the same. The difference in the position of alcohol groups in both causes them to differ in their reactivity and that is why this test is not given by β-naphthol.
Recently Updated Pages
Derivatives of Ammonia - Important Concepts and Tips for JEE

Equation of Trajectory: Step-by-Step Derivation

Degree of Dissociation in Chemistry: Concept, Formula & Examples

Cyclotron: Principles, Working & Uses Explained

Current Loop as a Magnetic Dipole: Concepts & Examples

Current and Potential Difference Explained Simply

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




