
Isoprene is:
(A) 3-methyl-1,2-butadiene
(B) 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene
(C) 3-chloro-1, -butadiene
(D) 2-chloro-1,3-butadiene
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Isoprene is mainly used in manufacturing of rubber. It is an unsaturated hydrocarbon with a methyl group.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of isoprene is –
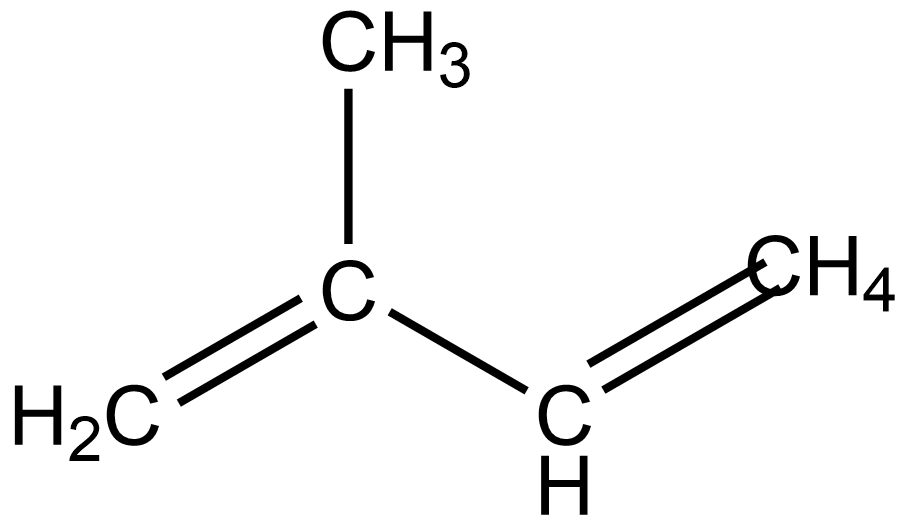
So, the name of this structure will be 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene.So, option B is correct.
Additional information:
It is an unsaturated hydrocarbon produced by many plants and animals. It is a colourless, volatile liquid in its pure form. Polymer of isoprene is a main component in production of natural rubber.
Natural Rubber and Synthetic Rubber are two types of rubber —
Natural rubbers are made up of solid particles suspended in a milky white liquid. They are found dripping from the bark of tropical and subtropical trees. We also call it Latex. It is made by the polymerization of isoprene i.e. 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene. They are made by loosely joining the monomers of isoprene in the form of a long chain.
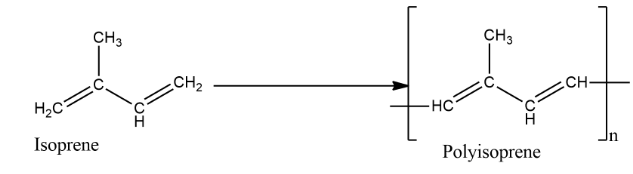
The polymeric chains in rubber contain between 320 and 35,000 isoprene units bound together with double bonds. This makes the chains stretchy. Large quantities of isoprene are used industrially today, nearly all of it to make synthetic rubber, and it is produced by the petroleum industry through cracking oil. Due to its outstanding mechanical properties and low cost, isoprene rubber is the preferred material for many engineering applications.
Note: Polymers of isoprene are mainly used in making of tires, anti-vibration mounts, drive couplings, bearings, and adhesives.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of isoprene is –

So, the name of this structure will be 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene.So, option B is correct.
Additional information:
It is an unsaturated hydrocarbon produced by many plants and animals. It is a colourless, volatile liquid in its pure form. Polymer of isoprene is a main component in production of natural rubber.
Natural Rubber and Synthetic Rubber are two types of rubber —
Natural rubbers are made up of solid particles suspended in a milky white liquid. They are found dripping from the bark of tropical and subtropical trees. We also call it Latex. It is made by the polymerization of isoprene i.e. 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene. They are made by loosely joining the monomers of isoprene in the form of a long chain.

The polymeric chains in rubber contain between 320 and 35,000 isoprene units bound together with double bonds. This makes the chains stretchy. Large quantities of isoprene are used industrially today, nearly all of it to make synthetic rubber, and it is produced by the petroleum industry through cracking oil. Due to its outstanding mechanical properties and low cost, isoprene rubber is the preferred material for many engineering applications.
Note: Polymers of isoprene are mainly used in making of tires, anti-vibration mounts, drive couplings, bearings, and adhesives.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




